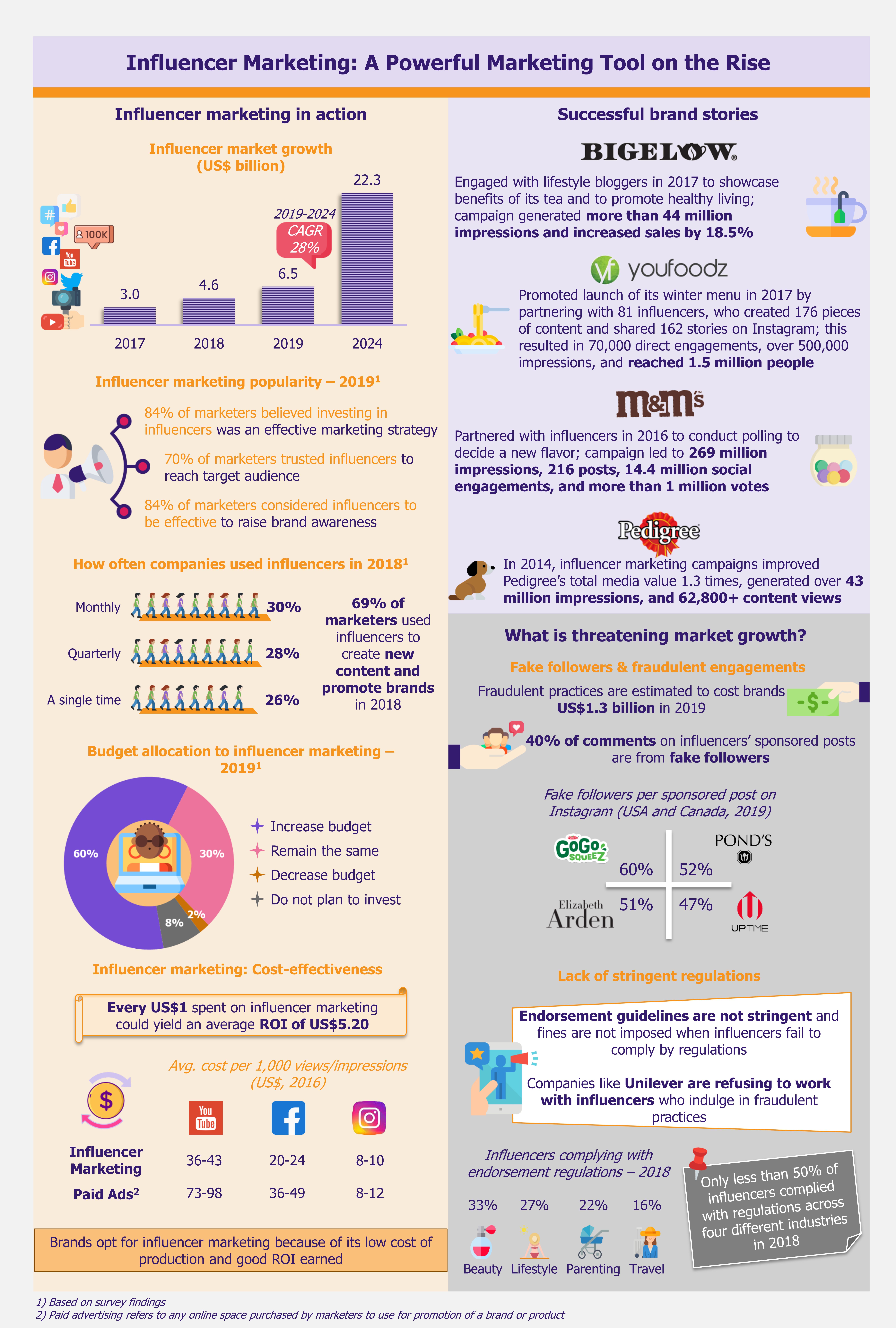
Influencer marketing, until fairly recently a new marketing tool, is now on the frontier of becoming a mainstream marketing channel. The real, relatable, and reaction-stimulating content created by influencers, distinguishes this form of marketing from traditional marketing channels. Influencer marketing offers effective means for brands to communicate and engage with customers on social media, a fact that is driving its popularity. Laden with potential to drive sales and grow brand awareness, the influencer marketing market is likely to reach US$22.3 billion by 2024. However, certain challenges do exist in the market, and if not addressed, they can potentially hinder market growth.
Influencer marketing started shaping up around 2005 with mere video blogs on YouTube, but quickly grew in prominence as marketers took notice of its potential. Growing at a CAGR of 28% between 2019 and 2024, the industry is becoming a marketing mainstay for brands across various markets. This is driven by the fact that influencers generate a sense of proximity with their audiences, which helps in molding their shopping behavior under discrete suggestions and recommendations.
What is driving adoption of influencer marketing?
Consumers, especially millennials, are embracing a different approach to making purchasing decisions. Consumers are relying on Instagram models, Twitter personalities, and YouTube influencers to seek recommendations or to understand which brand or product is trending in the market. This has resulted in brands endorsing products through various social media channels using influencers.
Moreover, it is a proven fact that word-of-mouth marketing leads to twice as high sales as paid advertising, and influencer marketing is nothing but a form of word-of-mouth marketing. Studies also suggest that shoppers purchasing product through word-of-mouth have a 37% higher retention rate, another reason why brands want to reach their consumers through influencer marketing.
Additionally, the way that we consume media has changed. Social media boom is slowly driving consumers away from traditional forms of advertising and marketing. More than ever, social channels are becoming means to start a conversation with consumers and build direct relationships with them. With traditional advertising being sidelined by consumers (about 65% of people skip ads posted during or before online videos), influencer marketing has become an integral channel to connect with them.
How have influencers assisted companies to increase sales and grow brand awareness?
Engaging with influencers is proving to be an effective way of getting a sale, hence, brands are investing considerable budgets in influencer marketing. Brands are partnering with influencers to launch various types of innovative campaigns, with primary focus on increasing brand awareness (84%), reaching new audience (71%), and generating sales (64%), according to a survey conducted by Mediakix in 2019.
For example, YouFoodz, an Australian food chain, used Instagram to promote the launch of its 2017 winter menu. It collaborated with 81 influencers, who posted 162 Instagram stories and 176 pieces of content, which reached 1.5 million Instagram users. The campaign was a huge success, generating 70,000 direct engagements and over 500,000 impressions (number of times particular content is displayed, regardless of if it was clicked or not).
Relying on influencer marketing, Bigelow Tea (an America tea manufacturer) was able to showcase healthy aspects of drinking tea and promote its product to a large audience. Influencers incorporated Bigelow tea into their content in various ways. Culinary influencers developed different recipes to use tea in innovative ways, while craft bloggers turned packaging into DIY arts, for example, creating flower pots from the tea packaging. The campaign led to more than 44 million impressions and increased sales by 18.5%.
Further, M&M (a product of US-based confectionary and food company, Mar Incorporated) launched an innovative campaign in 2016 to let audience decide its new peanut flavor (a choice between Honey Nut, Chili Nut, and Coffee Nut) by running a mini-election. It partnered with a television personality and a team of influencers to encourage people to try the flavors and cast their votes. Finally, coffee nut flavor was selected, and the campaign generated 269 million impressions, 216 influencer posts, 14.4 million social engagements, and more than 1 million votes.
Is influencer marketing cost effective?
Influencer marketing has proven to be quite budget friendly, allowing large brands and small start-ups to launch compelling marketing campaigns. Traditional forms of advertising campaigns, through television commercials, magazines and newspaper ads, etc., require substantial investment.
On the other hand, influencer marketing is cost effective and simpler to execute. Companies with limited budget can engage with micro (comprising 1,000-5,000 followers) or nano (comprising less than 1,000 followers) influencers and still achieve remarkable results without spending a fortune.
In fact, according to a study conducted by Takumi, micro and nano influencers can generate high engagement rates – influencer with up to 1,000 followers could generate about 9.7% engagement rate, while influencers with 1,000-4,000 followers could provide 4.5% engagement rate. Micro and nano influencers tend to build strong trust and authenticity, and are relatable to their audience, which enhances their ability to engage an audience. According to a study conducted by Experticity, 82% of consumers have higher probability of listening to suggestions provided by micro influencers than those provided by influencers with large number of followers.
Moreover, surveys have determined that influencer marketing could yield a decent average ROI of US$ 5.20 for every dollar spent, which makes it an appealing option for marketers.
What challenges are hindering growth?
Lack of stringent regulations leading to poor compliance with guidelines
Current regulations and guidelines pertaining to influencer endorsements are not stringent or comprehensive, leading to malpractices. In the USA, the FTC (Federal Trade Commission) requires influencers to provide disclosure in case of sponsored content, however, no fines are applied for violations. As a result, most influencers do not adhere to the endorsement regulations, either due to lack of knowledge or in fear of losing followers. In 2018, out of 800 Instagram accounts from UK, USA, and Canada, only 25% fully complied with local regulations pertaining to sponsored content, according to a study released by Inkifi.
Such misleading conduct on influencer’s part could raise questions on their authenticity and lead to mistrust among their followers, who demand transparency. Moreover, large corporations such as Unilever (a consumer goods company) have strictly refused to work with influencers who indulge in fraudulent activities. Influencers are at risk of losing trust of their followers as well as of companies if they continue to indulge in misleading activities.
Fraudulent engagement
Typically, brands use the number of followers on an influencer’s account to estimate campaign results in terms of ROI, engagement rate, brand awareness, earned media value, among others. To seem more appropriate or popular, some influencers purchase their followers using bots – software designed to automatically like, comment, and share posts, increase views on videos, and inflate number of followers on accounts. Influencers have also started to fake their engagements by joining a community of real users to trade likes and comments. Despite these followers being real people, they are not likely to be interested in influencer’s content. Consequently, brands fail to meet the desired campaign result or reach the target audience.
In 2019, fraudulent activities were estimated to cost brands US$1.3 billion, about 23% of allocated budget for influencer marketing. Fraudulent practices are inhibiting market growth, as brands are increasingly becoming cautious of investing in influencer marketing – as of January 2019, about 53% of brands stated that fraudulent impressions were obstacles to increasing digital advertisement budgets.
EOS Perspective
Influencers are no longer an extra asset to marketing campaigns instead they have become a critical element of storytelling and building direct relationship between brands and customers. Influencers have positioned themselves as authentic gurus rather than simple advertisers, with 92% of consumers making purchasing decision based on influencers’ posts in 2018. Their relentless savviness to promote brands is what keeps audiences engaged and brands coming back for more.
Nonetheless, challenges do persist but the industry is continuously evolving and coming up with solutions. Measures are being taken against inauthentic engagements. Platforms such as Instagram have started to strictly regulate fraudulent activity and began to threaten offenders with fraud penalties, account suspension, and brand reputation damage. Companies have also become mindful and vigilant while engaging with influencers and started to thoroughly vet them to check for fake followers or use of bot to increase followers. On the legal side, a New York Attorney General has stated that selling fake followers on social media will be considered as an illegal activity in the state.
Further, in November 2019, FTC launched guidelines for sponsored content under ‘Disclosures 101 for Social Media Influencers’ that encompasses when and how influencers should disclose their engagement with brands, regardless of whether or not it includes payment. FTC has not made any major changes in the guidelines but the new guide is more user-friendly with abridged language, and photos and videos illustrating the correct way to endorse products on social media.
Find out how influencer marketing is reshaping fashion and beauty industry here
According to the guidelines, when partnering with brands, disclosure is mandatory when there’s a financial, employment, personal, or family relationship with a brand. Disclosure language should be simple and clear, and the disclosure should be hard to miss (for example, disclosures on Instagram are required to be placed at the beginning of the post’s description and before the ‘more’ button). FTC’s aim is to foster transparency in sponsored content by placing more liability on brands and influencers to explicitly reveal their relationship while recommending products.
Influencer marketing has well-established itself in the advertising industry and is moving towards becoming a mainstream marketing channel, and such measures taken by regulatory authorities, social media platforms such as Instagram, as well as the brands will further strengthen its position as a marketing channel. In future, not only will influencer marketing continue to grow in popularity, but is also likely to become a more purposeful and effective way to communicate and engage with audiences. Allured by endless opportunities, brands will continue to collaborate with influencers and the industry is poised to grow.