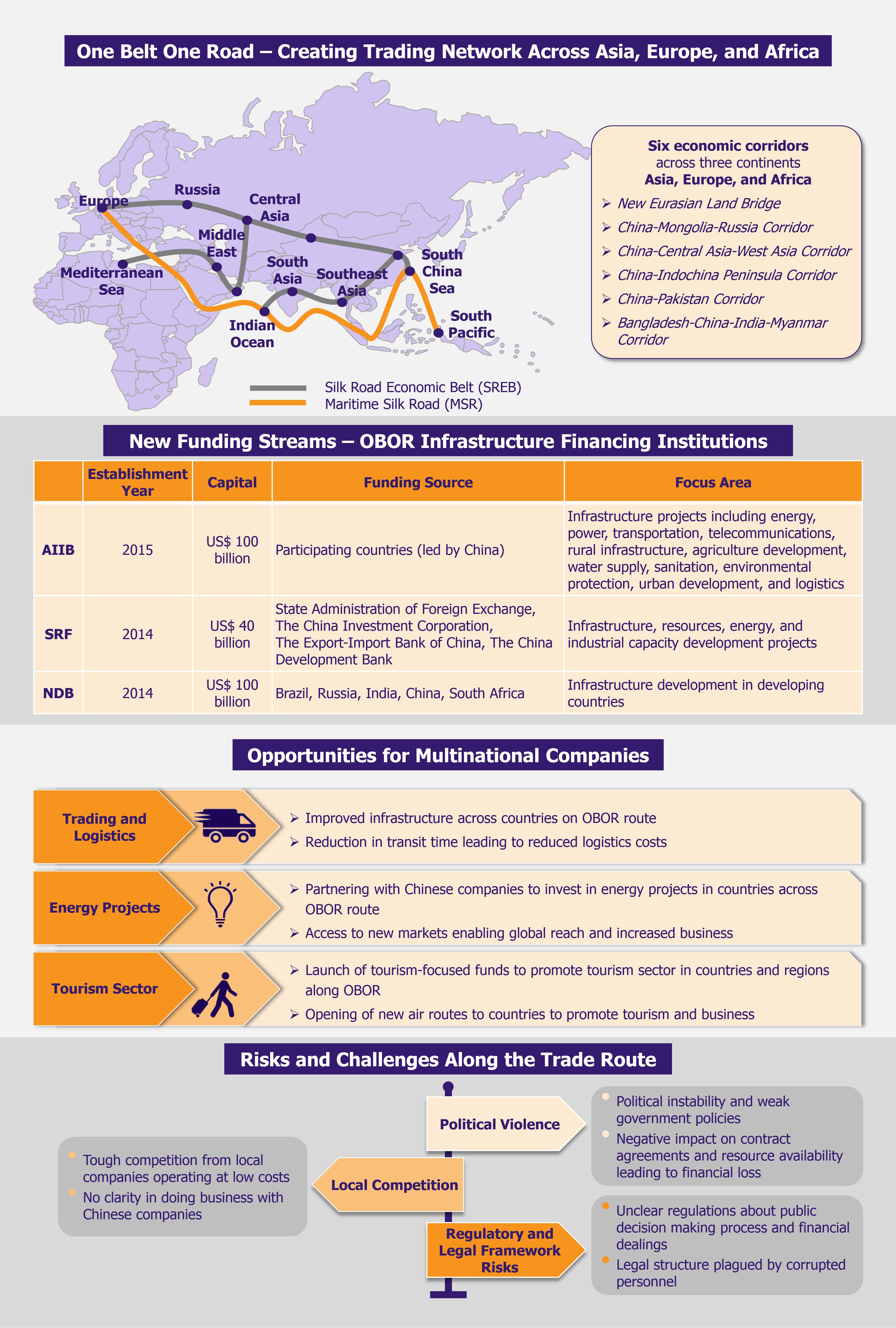
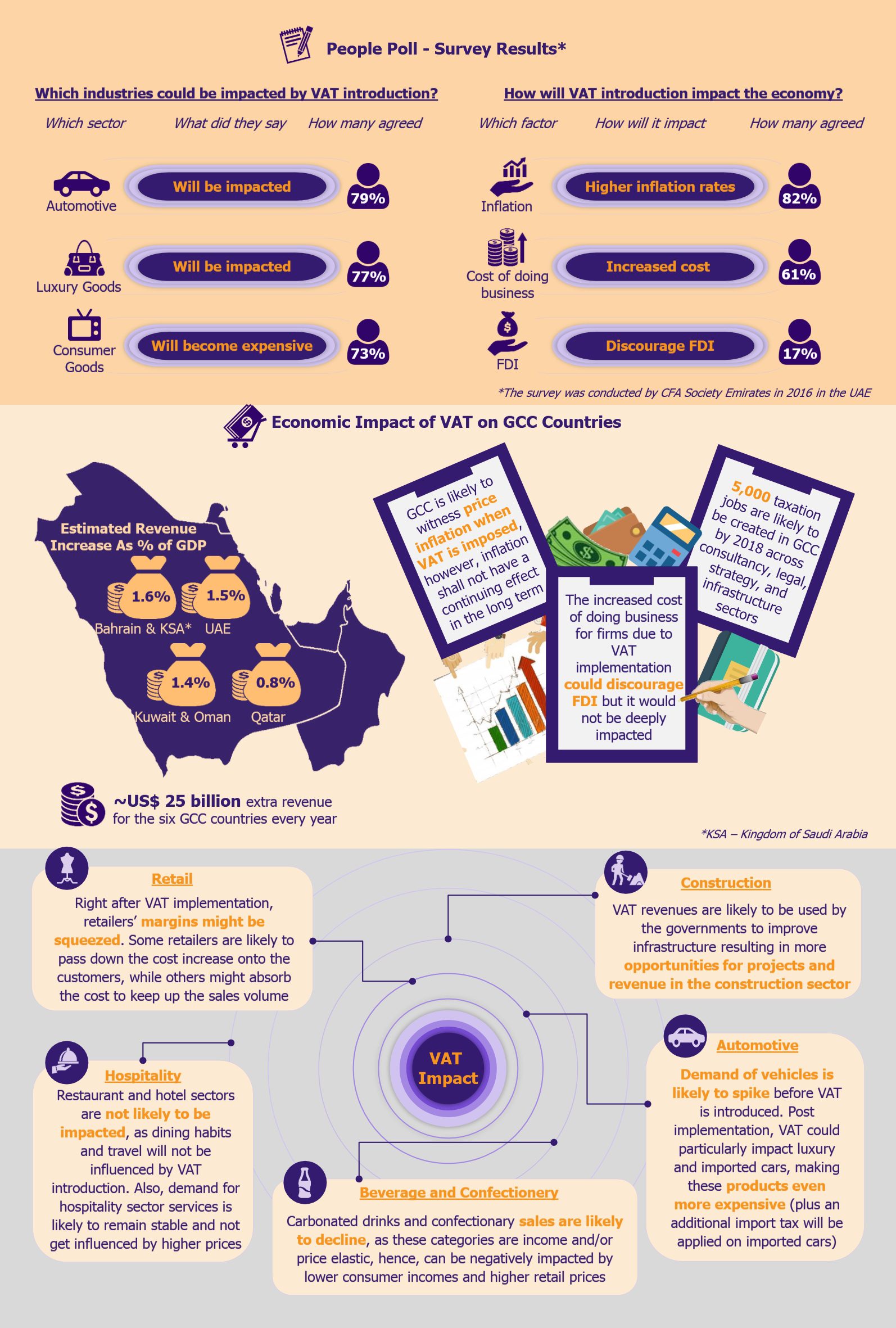
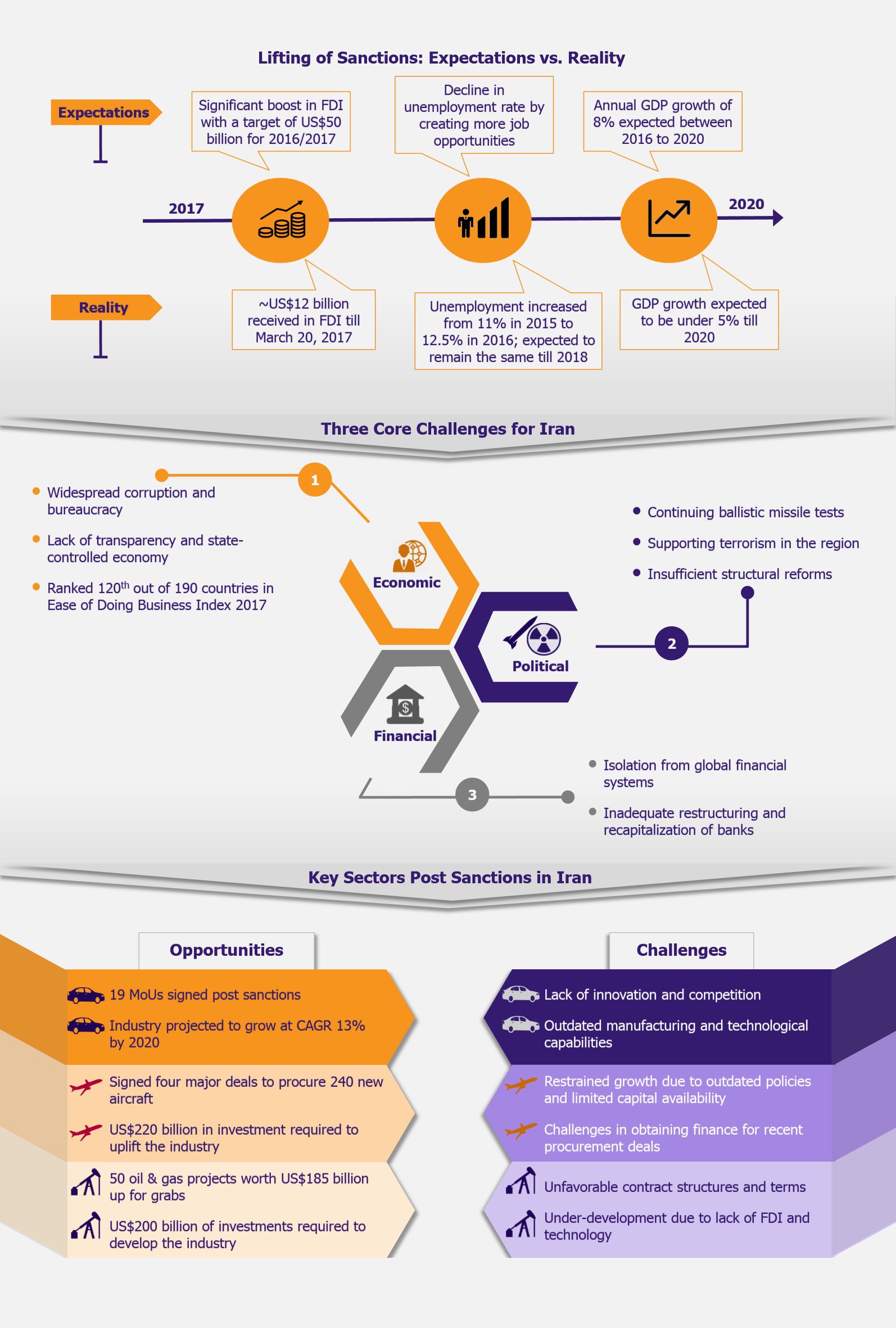
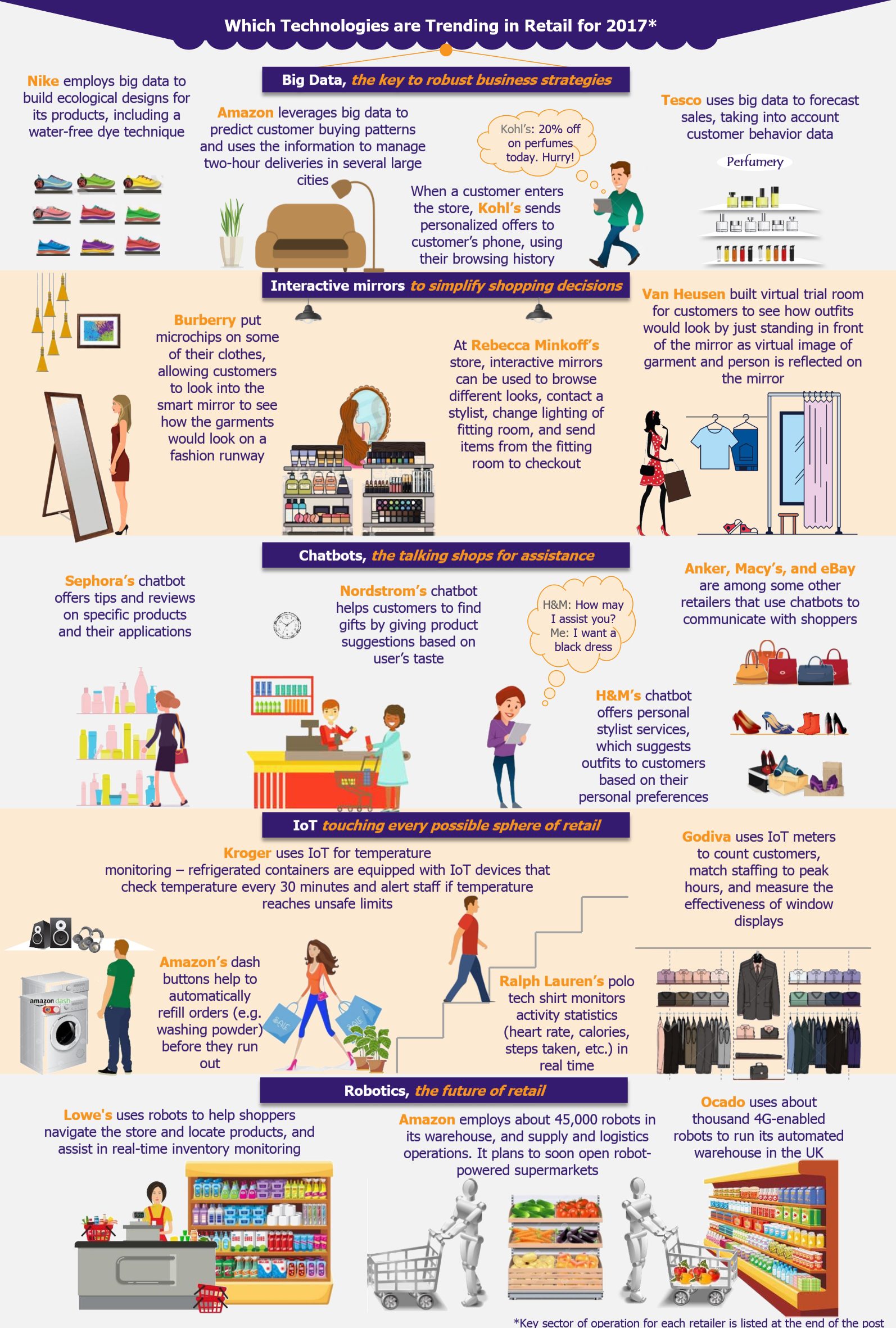
Digital transformation buzz has revolutionized the way companies operate and interact with their customers across virtually all industries. Automotive industry is no exception. Customer expectations today are more demanding than ever, primarily due to the service level benchmarks set up by the likes of Amazon, Uber, and Apple, as well as due to plethora of information customers can get through the internet and social media. The rise of digital channels is fundamentally transforming the entire auto retailing business. In order to stay ahead of the game, automakers will have to break their legacy systems and build new customer-centric marketing models.
The automotive industry has always been characterized by an extremely time consuming as well as complex sales processes that often result in an unpleasant customer experience. The industry notion “People love shopping for cars; they hate buying cars” precisely depicts the challenge auto retailers have to deal with and the need for industry players to rethink their sales and marketing models to enhance the overall customer experience. The Apple and Amazon retail ethos of seamless customer interaction, simple and streamlined sales processes, effortless and speedy customer services has become the benchmark for all retailers. Even in the automotive industry, changing customer preferences, digital transformation, increased connectivity are reshaping the entire retail supply chain, with major impact on the final parts of the chain involving direct customer interaction. The rise of cutting edge technologies, tech and information savvy consumers, and new market entrants are forcing traditional players to rethink and reinvent their entire business models.

The advent of technology has significantly lowered entry barriers for new entrants in the automotive retail segment, who have brought innovative business models and fresh ideas to help customers find, evaluate, and buy new vehicles. With slogans such as “Skip the dealership” and “Find deals. Not dealers!” new players such as Roadster or Rockar are transforming automotive retailing by offering a bargain-free and smooth car buying experience that can allow the customer to purchase a car and have it delivered to their doorstep within few hours. Traditional retailers have started to realize that, equipped with massive information at their fingertips, car buyers today are better informed than ever when it comes to car purchasing. One bad experience and customers will be very reluctant to ever come back to the same retailer. Despite this realization, many companies are still ‘moving metal’ the old-fashioned way using traditional media and other marketing approaches to attract consumers to their stores.
Statistics from many industry studies make it clear that with the mass proliferation of technologies, car buying journey is becoming increasingly digital, with most customers spending a significant part of their buying time online. Studies indicate that more than 65% of the information-gathering and decision-making process is already made prior to visiting a dealership. Therefore, it becomes vital for OEMs and dealers to rethink their entire marketing and customer engagement approach. They need to interact more effectively and engage consumers early and throughout their purchase journey.
OEMs and dealers need to understand that the whole process of buying cars is quite different from the process in some other retail segments. For example, to buy consumer electronics, many consumers visit the store to see/touch/feel the product and then buy it online because of the price benefits and other offers. In case of buying cars, most customers do their research and comparison online. They visit the local dealership to see/touch/feel the car and buy it there to benefit from special discounts and offers. Hence, it is very crucial to have an integrated and seamless transition across various channels in a frictionless manner.
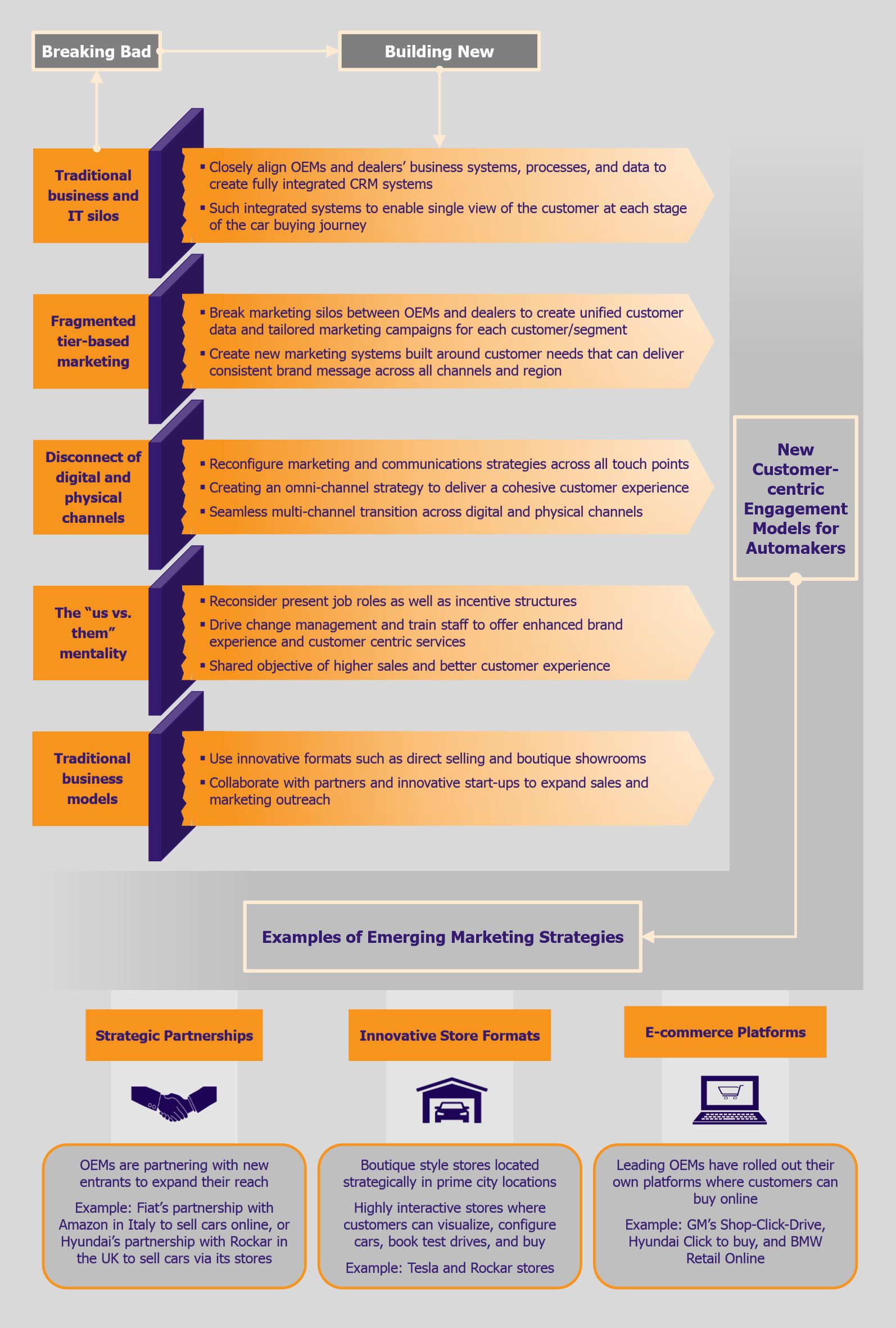
The introduction of new business models (direct-to-customer) and customer experience strategies (highly interactive and pressure-free brand stores) created by the likes of Tesla, or Rockar, have caught the eyes of many traditional players, who have gauged the significance of realigning their marketing and customer engagement strategies as per demands of the rapidly evolving industry. Many OEMs and dealers have started to take a hard look at their entire customer lifecycle processes to assess the current gaps and address them. Companies are reconfiguring their touch points across channels by eliminating redundant processes and services. Recently, automakers such as BMW, Audi, and Mercedes have rolled out brand stores similar to Apple’s, where customers can visualize their cars, configure them to their own specifications, get experts to answer their questions, and even buy cars in a non-pressurized sales environment. Having already seen some positive results, these OEMs are likely to ramp up their efforts to roll out such brand stores on a larger scale across cities, states, as well as countries in the near future. While not all automakers have plans to launch such stores at present, it is expected that it will not be long before OEMs with no such current plans observe and eventually follow the footsteps of OEM players that have already reaped these rewards and showed what advantages such stores can offer.
EOS Perspective
As digital transformation continues to revolutionize the auto retailing landscape, there is no doubt that advancing technologies will make the car buying process increasingly digital for the years to come. We can expect a rapid surge of various online platforms that provide customers with the ability to easily research, evaluate, and buy cars. Operating within such a highly competitive marketplace with changing customer preferences, auto retailers will have to transform their business models to become more customer-centric and deliver on customers’ expectations. They will have to reinvent customer engagement frameworks to create ones that are built around customer needs, and are simple, frictionless, more transparent, quicker, and convenient for today’s savvy car buyers. On the one hand, this will help OEMs and dealers win more business, while on the other hand customers will benefit from an accelerated and hassle-free sales process, resulting in an improved customer experience.
Although transforming current customer engagement model seems inevitable, this will not come easy and will involve massive changes in existing marketing models. At present, majority of industry players lack the resources, infrastructure, and systems required to execute this transformation. In addition, as signification investments will be required, amid current business environment with high cost and competitive pressure, many automakers as well as dealers will still continue to engage in sales the old fashioned way or adopt a ‘wait-and-watch’ stance. At a dealer level, implementation of new customer engagement model will be much slower primarily due to capabilities and resources constraints.
In the end, one thing is obvious – in order to retain today’s customers and to win new ones, OEMs and dealers will have to reinvent their marketing and customer engagement strategies. To achieve this transformation, these players will have to work together to deliver rich brand experience and match the simplified and streamlined buying experiences set by Amazon and others. OEMs and dealers should take John F. Kennedy’s words to heart “Change is the law of life. And those who look only to the past, or the present, are certain to miss the future.”