China is one of the most promising markets for cosmetics and skin care companies globally, only being second to the USA in size. Despite its size and potential, the Chinese beauty market has remained relatively closed to several international players that make cruelty-free and vegan products. This is because of Chinese regulations that required compulsory animal testing pre- and post-market entry for international brands. However, in 2021, the Chinese government squashed the mandated animal testing requirement and introduced other certification methods. While this opens the market for a plethora of players who have till now shied away from entering the Chinese market, steering through the Chinese turf may still not be very simple.
China’s new cosmetic regulations easing entry for imported products
China is currently the second-largest cosmetics market globally, and has an immense potential to grow further. As per China’s Ministry of Commerce, the value of imported cosmetics grew by 30% in 2020, underlining the strong potential for international brands in the Chinese market. At the same time, several international companies have kept their distance from this US$57 billion beauty and personal care market, owing to stringent regulations.
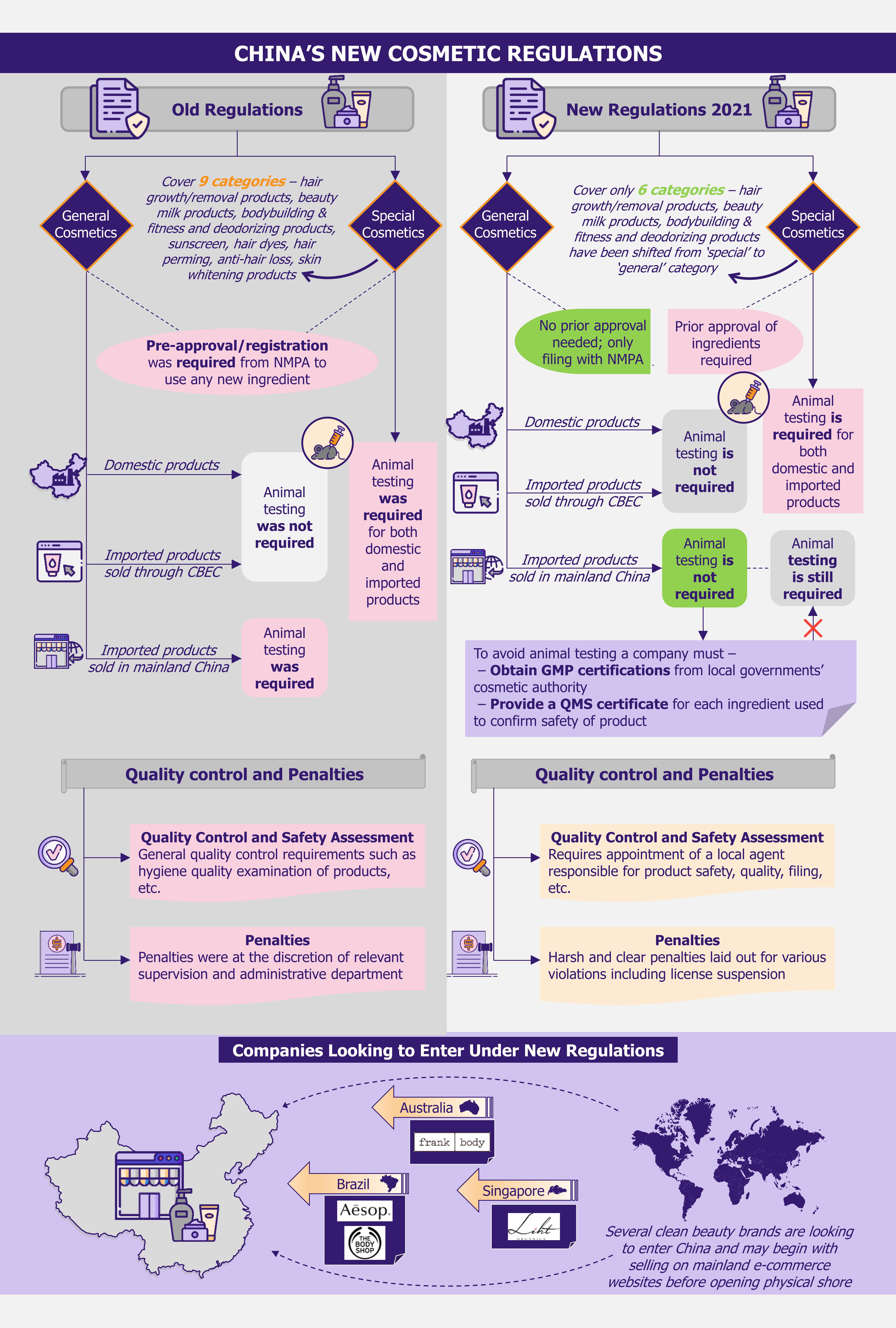
However, in 2021, the government introduced new rulings for cosmetics and beauty products, which have altered the regulatory landscape in China. As per Chinese regulations, cosmetics are divided into two categories, special and general cosmetics, and the two are subject to different pre-market registration requirements.
As per the new regulations, while the former will continue to be subject to pre-registration with National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) before being allowed to be manufactured or imported, general cosmetics now only require filing documentation of the product with the authority. Earlier, the general category also required prior approval before import.
In addition to streamlining the process for the general category, the government has reduced the number of special product categories from nine to six. As of 2021, the only product categories under the special category encompass hair dye products, hair perm products, spots removal and skin whitening products, sunscreen products, and hair loss prevention products. The streamlining of the registration process for general category is expected to have a direct impact on the cost of warehousing and logistics for global brands as it is likely to quicken the import cycle.
Another regulation that was a deterrent to entering the Chinese market was that international beauty companies were expected to perform animal testing for their products both pre-and post-market entry. This created an issue for the growing number of global clean beauty brands who position themselves as vegan or cruelty-free. These brands could either choose to dilute their brand positioning by undertaking animal testing for the Chinese region or had to keep away from this goldmine market.
However, these companies did have one channel to enter this market, and that was through cross-border e-commerce sites, such as Alibaba’s Tmall. Although this resulted in a limited presence as the cross-border market size has government restrictions and is about one-tenth the size of the domestic market. Moreover, physical retail still continues to dominate the Chinese market with regards to cosmetics sale, with growing popularity of multi-brand stores.
As per the new regulations, global companies do not require animal testing anymore before entering the Chinese market. This will level the playing field between international imports and domestic brands, as domestic brands have been exempt from animal testing since 2014.
However, there are a few conditions to be met by companies looking to bypass animal testing. The brand must provide relevant quality certifications from their country of origin, the product should not be aimed at children or babies, the product should not contain any raw material that is not included in China’s approved list of raw materials, and the applicant brand and its Chinese representative should not have been flagged as requiring further supervision by the authorities.
Companies responding to the new regulations
This opens the door for several international players who position themselves as cruelty-free. In May 2021, Australian clean beauty brand, Frank Body, welcomed a closed investment from Chinese private equity firm, EverYi Capital, which put the value of the brand at about US$74 million (AUD 100 million). The investment, which includes the creation of a Shanghai team for the brand, will help the company find a strong footing in the Chinese market in the light of the latest animal testing relaxation. The brand is expected to enter the market over the next 12 to 18 months, with prospects of opening a physical store.
In a similar move, Brazilian beauty conglomerate, Natura & Co., mentioned during its 2020 fiscal year results that it is looking to expand into China with its brands, Aesop and The Body Shop. The two brands were expected to complete their registration in China by first half of 2021, with Aesop expected to open its first store in Shanghai by the end of 2021, while The Body Shop is scheduled to open its first store in 2022 (however, there is no information regarding the completion of the registration process yet). While these brands have been available in China through cross-border e-commerce, they expect that physical retail presence will help establish a strong foothold in this growing market.
Nerissa Low, founder of Singapore-based organic and cruelty-free cosmetic company, Liht Organics, has also welcomed the decision and expressed interest in entering the offline Chinese market. Liht Organics, which entered China in 2020 through cross-border e-commerce, gained significant traction in the Chinese market. However, the brand refused to enter the offline market when approached by several Chinese distributors, as the company did not want to compromise on its cruelty-free ethos. Given the change in regulations, the founder has expressed interest in expanding beyond cross-border e-commerce considering the potential in the offline market and is looking for the right partner and opportunity.
Moreover, popular international brands such as Drunk Elephant, Fenty Beauty, and The Ordinary, which are currently limited to be selling through Alibaba Tmall, are expected to enter the Chinese market and establish a physical presence there. While a lot of these brands might wait to establish physical stores and may penetrate the market through mainland e-commerce websites such as Tmall (instead of Tmall Global) to reach a larger audience, presence in multi-brand retail stores or opening pop-up stores will be the natural next step.
Despite new regulations, challenges remain
However, entering the Chinese market (despite the abolishment of the animal testing rules) will be no easy feat. Owing to the recent changes in regulations, the companies need to keep up higher standards in terms of product quality, marketing, and operations. Moreover, some of these regulations have made it harder for foreign players to comply as they require a complete overhaul of their local marketing strategies and operational functions.
Firstly, as per the new regulations, the NMPA of China has made it mandatory for international companies to have a domestic agent who must be based in China. This agent will be responsible for the registration process, which includes massive paperwork and approval procedures. Moreover, these agents will be held completely accountable for the company’s products and operations in China and will be answerable and responsible for any safety concerns arising in the product. In addition, they will be responsible for ensuring that the product, its ingredients, and its marketing are compliant with the Chinese regulations. Thus it will be a challenge for foreign players to find a Chinese agent to fill this capacity as in reality, such a person/company may have no impact on how the ingredients or final product are made. This is also definitely expected to increase costs for the company.
The government has also imposed harsher penalties for non-compliance and various violations such as misleading advertising, non-compliance of new cosmetic naming guidelines, non-submission of approved hygiene license and certificates, etc. This makes it critical for companies that the Chinese agent is well aware of all regulations and is thorough with all registration requirements as violations can also result in cancellation of license.
Secondly, while the removal of animal testing for imported cosmetics is a welcome news for a great number of global cosmetic brands, the policies put in place of this pose to be equally challenging and complex to steer through. Under the new regulations, cosmetics falling under the general category require a Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) certificate to avoid animal testing. These GMP certificates need to be issued from the brand’s local government regulatory department. Considering that different countries will have different authorities and templates for issuing these certificates, there is a lot of ambiguity regarding what is acceptable and what is not.
Moreover, cosmetic companies need to provide a manufacturing quality management system (QMS) for each individual ingredient used in the cosmetic formulations. This requires companies to collect information on each and every ingredient manufacturer and supplier, including their quality specification documents and certificates. This is a tedious process since a company may use ingredients from several manufacturers for a single product. In addition, in case a company plans to change a supplier, it will have to undergo this process and update the information with the Chinese authorities for the new supplier, which is both money and time consuming.
On the one hand, it is true that the exemption from animal testing has given an opportunity of many cruelty-free brands to enter the Chinese market. However, on the other hand, the lengthy procedure and strict scrutiny over the process is undermining the overall market entry process for mid to small size companies. Non-compliance with these certifications will reverse the relaxation on animal testing for the companies that don’t meet the new procedural requirements and then their products will need to undergo animal testing for selling in China.
Furthermore, despite getting the green light to enter the Chinese market, the cruelty-free cosmetic companies would still need to deal with another challenge arising from the consumer side. While the clean beauty segment is definitely growing, it is currently not a major factor in purchasing decisions by consumers, unlike in the USA. Chinese consumers seek products that are functional and have healthier, milder, and more reliable formulas. Hence, to ensure a right placement of their cruelty-free products, companies would need to undergo distinctive marketing strategies to grab a good consumer base. Education and awareness regarding cruelty-free products and creating a substantial market for such products may require significant marketing funds.
In addition to the changes in regulations with regards to animal testing, the Chinese government added new regulations regarding product labelling. As per the new regulations, the labels must have corresponding Chinese explanation to everything mentioned and they must a have larger font size than the explanation in foreign language. Also, the label should contain the Chinese name and special cosmetics registration certificate numbers, product implementation number, name and address of the person responsible in China and of the manufacturer along with the production license number.
Adding to these is a ban on use of any kind of medical term, names/pictures/endorsement of celebrities in the medical field, and implication of medical effects to avoid any misleading of information. Although all these changes are implemented in order to curb the market of counterfeit products, they are expected to make the product approval process lengthier, as now companies would be required to undergo a comprehensive regulatory review of the guidelines to ensure hassle-free entry into the Chinese market.
EOS Perspective
While the new regulations provided a pathway for several foreign clean beauty players to enter the Chinese market, the process still requires a lot of navigation, especially since a lot of rulings regarding safety requirements, GMP authorities, and template remain ambiguous.
Moreover, since these certificates need to be derived from the country of origin, the country’s overall political and business equation with China might also play a subtle role in their acceptance by the Chinese authorities. For instance, China has not yet declared the jurisdictions that will be recognized for the QMS certificate. Given the current political friction with Australia and the USA, the Chinese authorities may not accept QMS certificates from these countries at the moment. Thus brands from these countries may have to look to find suppliers or shift part production to other countries to be able to enter the Chinese market.
While currently there is no clarity regarding what terms and jurisdictions will initially be accepted for the GMP and QMS certificates, it is expected that clarity on the matter will be provided by the government shortly. In the long run, these regulations are a move in the right direction. As the government has overall simplified the filing process and focused on quality and safety measures, the new regulations are a positive development for international cosmetic companies, especially clean beauty brands that have been unable to enter the second largest beauty market in the world.