As the human wearables market begins to mature, a lot of interest and developments are also happening in the pet wearables space. An increasing number of pet owners becoming more technologically savvy has fueled product innovations in this segment, which traditionally was limited to GPS tracking. While location tracking continues to be the largest piece of the pie, other solutions, such as health monitoring devices, have been gaining prominence. However, this segment is still in its infancy and is toying with several technologies, such as biometrics, radar, and acoustic technology, to develop functional, accurate, and price-effective devices.
The last decade has witnessed exponential growth and advancements in human wearables. However, recent years have also seen the trend of wearables permeating the pet market. With upcoming technological advancements, the industry is expected to witness double-digit growth over the next six years and expand into new territories.
Read our related Perspective Poop to Pills: Is FMT the Future of Veterinary Medicine?
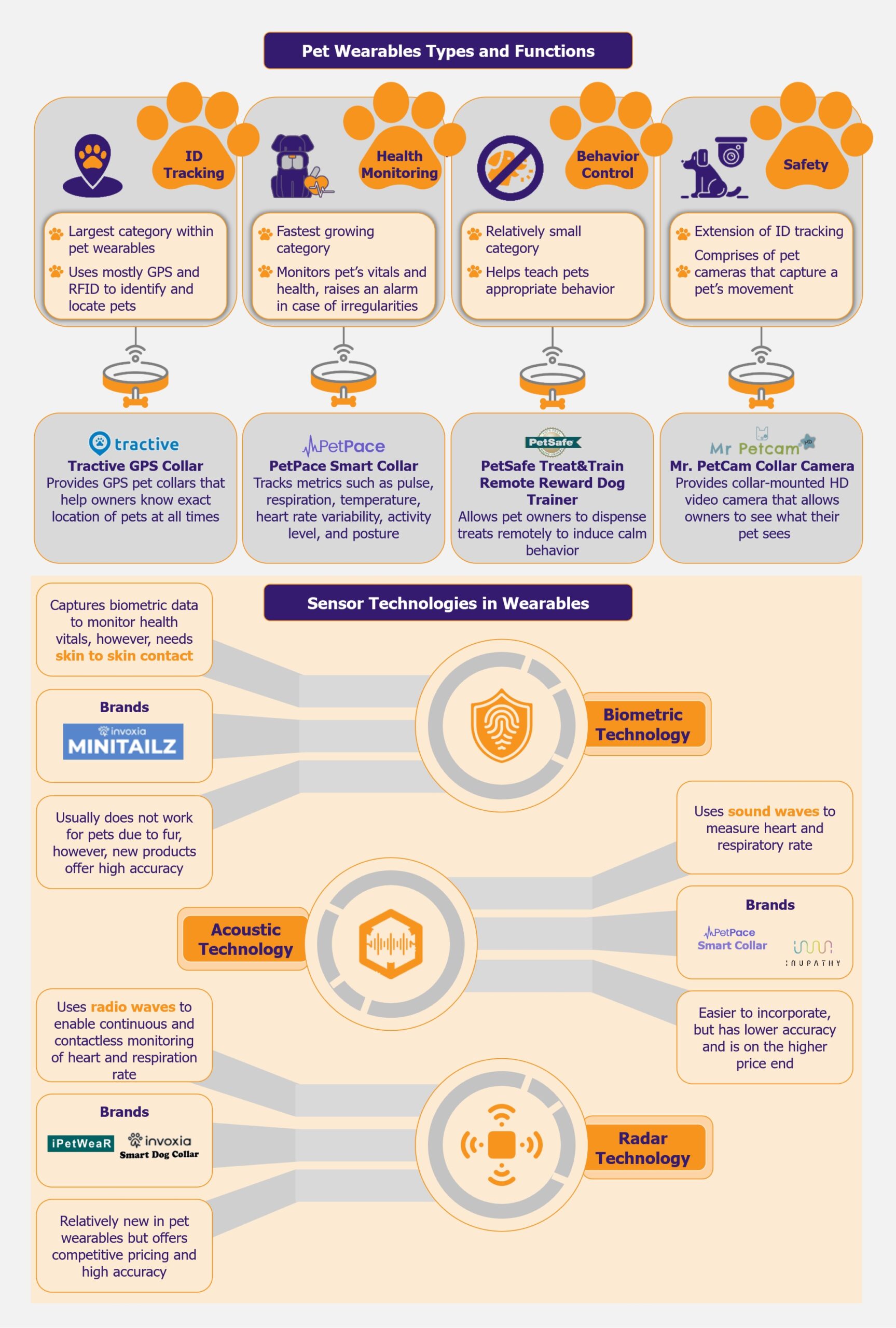
ID tracking is the largest category, health monitoring is growing the fastest
The pet wearables market is primarily bifurcated into four applications: ID tracking, behavior control, safety, and health monitoring. At the moment, the largest category within the market is ID tracking solutions, which comprise GPS—and RFID-based trackers that help identify and locate pets. One of the leading players in this space is US-based Tractive, which provides a GPS collar that allows pet owners to know the exact location of their pets at all times.
The fastest-growing category is health monitoring. This segment encompasses devices that monitor a pet’s vitals and general health and raise an alarm in case of any irregularities. Growing pet obesity cases have resulted in pet owners choosing health monitoring devices for their pets. A popular product in this space is the PetPace Smart Collar by US-based pet wearable company, PetPace, which tracks physiological metrics such as pulse, respiration, temperature, heart rate variability (HRV), activity level, and posture. Along with GPS tracking and emergency alerts, it helps in early symptom detection and disease management.
The behavior control segment, which is still relatively small, covers products that help teach pets appropriate behavior, such as bark collars, which deter dogs from barking continuously. An innovative and popular product in this category includes the PetSafe Treat & Train Remote Reward Dog Trainer by US-based pet-tech company PetSafe. The product allows pet owners to dispense treats remotely through an electronic trainer to induce calm behavior in case of distracting situations, as well as allows owners to reward their pets in case of good behavior.
The smallest category is safety, which is largely an extension of ID tracking and comprises pet cameras that capture a pet’s movement. Mr. Petcam is a US-based company that provides collar-mounted HD video cameras for dogs or cats, allowing pet owners to see what their pets see in the yard, at home, or during walks.
The industry is undergoing both organic and inorganic growth
Pet adoption increased significantly during the COVID-19 pandemic as people were confined to their homes and lacked social and emotional connection. As per the American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals, one in five Americans purchased or adopted a pet during COVID-19.
Many of these pet owners are adept in technology and spend vast sums of money on their pets. As pets are increasingly considered family members and with growing concerns for their health and well-being, pet wearables are experiencing a surge in popularity. The success of wearable technology for humans further fuels this trend. Moreover, increasing costs of veterinary services and treatments have propelled pet owners to invest in health and prevention-based wearables. Therefore, the industry is expected to grow significantly, especially in Europe and North America, in the coming years.
However, that being said, the industry is in its nascence and is highly fragmented at the moment. There is a large number of players fueled by several start-ups and new entrants. The industry is seeing a surge in acquisitions as players in the pet care and tech space are looking to expand their offerings to include pet wearables. Moreover, growing interest from venture capital firms is also resulting in large investments in companies showing promise in this space.
One of the leading players in the pet market, Mars Petcare, launched Companion Fund in 2018 and Companion Fund II in October 2023. The US$100 million and US$300 million venture capital funds, respectively, have been created to invest in start-ups in the pet care space, including pet wearables. Earlier, in 2016, Mars Petcare acquired the Whistle pet monitor and GPS tracker, similar to a Fitbit for dogs, for about US$117 million. This provided Mars Petcare an entry into the pet wearables space.
Several other players in the technology space have also acquired companies to expand their business to cover pet wearables. In 2019, Florida-based IoT company Smart Tracking Technologies acquired Link AKC for an undisclosed amount. This wearable pet technology company developed GPS-enabled dog collars and won the Best Innovation award at CES 2017 in the wearable technology category.
In April 2023, Ultrack, a leading global GPS tracking solutions provider, signed a contractual agreement to acquire and market Supreme Product’s wearable GPS-based Pet Tracker. The device is expected to have multiple features, such as health monitoring, behavior modification, predictive analytics, social media integration, and virtual fences.
Similarly, in May 2023, Datamars, a global data solutions company, acquired Kippy, an Italy-based GPS tracking and activity monitoring solution provider. Kippy collar’s main features include GPS tracking, customized activity monitoring and analysis, reminders and access to vet records, temperature alerts, tone and vibration training controls, a built-in flashlight, and the ability to create safe places for the pet.
While several companies are adopting the inorganic growth strategy, there is also a lot of venture capital interest, especially in ID tracking, which is the largest product category and acts as an entry point device for many customers in the pet wearables space. In 2021, Austria-based leading pet tracking company Tractive raised US$35 million Series A round (led by Guidepost Growth Equity) to expand its offerings in the USA. Similarly, in 2021, Fi, a US-based pet wearable start-up, received US$30 million in Series B funding (following a Series A funding of US$ 7 million in 2019) for its smart pet collars to expand its footprint across the USA.
Pet wearables companies seek the right tech for pet health monitoring
While most technologies used in pet wearables are fairly similar to those used in human wearables (such as GPS), one of the key differentiators is the effectiveness of biometric sensors for health monitoring. Biometric sensors are widely used in human wearables, although given the fur presence in animals, they are somewhat ineffective in the case of pets. Thus, pet wearables depend on other contactless sensors such as radar and acoustic. However, these have their own functional and developmental challenges.
Among these, acoustic sensors are some of the oldest and are used by one of the market leaders, PetPace. Acoustic technology uses sound waves to monitor a pet’s heart rate, heart rate variability (HRV), and respiratory rate. Players such as PetPace and Inupathy use this technology in their smart collars. Moreover, in 2020, the Bioengineering Department at Imperial College also developed wearable technology for sniffer dogs based on acoustic sensors.
While this technology is fairly widely used for clinically monitoring health for both humans and pets, there are certain challenges when it is translated into wearables for pets. Given external factors, such as background noise and motion artifacts, the PetPace collar is said to have only 53% heart rate detection sensitivity (i.e., in 53% of the cases, the standard deviation from measurements by PetPace and ECG was within 10%) based on a study conducted in 2020. However, based on another 2017 study, the device’s pulse monitoring accuracy levels can be much higher at 94.3%.
That being said, Tokyo-based Inupathy also uses acoustic sensors to capture a dog’s heart rate and HRV and displays colors and patterns on its pet collar to depict emotional state and heartbeat ranges. For instance, the calmest state is depicted with deep blue, whereas the most excited state is bright red. While the company claims to have 90% accuracy when compared with ECG monitors, the collar is marketed as a device to broadly understand the mental and physical state of the pet instead of accurately monitoring and projecting heart rate readings.
Thus, while acoustic technology can be used in pet wearables, it has limitations, especially regarding accuracy. With the PetPace collar being priced at about US$150 (with a monthly subscription of US$15) and Inupathy at US$200, the customer must be able to find value in the readings. One of the initial companies using acoustic sensors, Voyce, went out of business in 2016 due to slower-than-expected acceptability.
Acoustic sensors-based solutions by themselves may not be a sound product offering, however, when clubbed with other technologies and solutions, they can offer a wholesome solution to the pet owner. This can be seen in the case of PetPace Smart Collar, which, along with acoustic-based health monitoring, has additional offerings such as thermometers for temperature detection, 6-D accelerometers for activity, calories, and posture calculation, and GPS for location tracking.
A more promising and upcoming technology for health monitoring in pets is radar technology. The technology uses radio waves to enable continuous and contactless heart and respiration rate monitoring. While it is relatively new, it is expected to have better accuracy when compared with acoustic sensors. Two companies, France-based Invoxia, and Taiwan-based ITRI, launched smart collars with radar technology in 2022. Invoxia’s smart collar is priced competitively at US$99 (with a monthly subscription of US$13). It uses embedded artificial intelligence and miniaturized radar sensors to track a dog’s health. In addition, it monitors a dog’s daily activity, such as walking, running, scratching, eating or drinking, barking, and resting. The device has an accuracy of 98% for heart rate detection.
Similarly, ITRI also launched its smart wearable device, iPetWear, in 2022. The device uses contactless micro-physiological radar sensing technology to monitor a pet’s health. The sensor can monitor a pet’s heart rate, respiratory rate, sleep cycle, and activity levels through the detection of pulse and chest motion through its lower-power Doppler radar technology. The device claims to have an error rate of under 10% for heart and respiration rate and under 5% for activity monitoring. The device is priced at US$80.
Given the improved accuracies and competitive pricing of these products, it is safe to say that radar technology-based sensors can disrupt pet health monitoring wearables. However, this technology is difficult to develop, and at the moment, only a limited number of companies have managed to commercialize it.
Companies are also exploring ways to make biometric sensors effective for pets, even though furry pets present a challenge for such sensors. This is seen in the case of Invoxia, which had previously launched the radar-based Smart Collar. At CES 2024, Invoxia launched another pet wearable device, the Invoxia Minitailz Smart Pet Tracker. The tracker uses advanced miniaturized biometric sensors along with AI to track respiratory and heart vitals and detect anomalies in the behavior of both dogs and cats. In addition, it tracks a pet’s location and daily activities and can differentiate between types of movement. It also claims to be the first pet collar in the market to detect atrial fibrillation (AFib). The device also seems to have high accuracy (similar to radar technology) as it claims to have 97-99% accuracy rates for monitoring respiratory and heart vitals. The product, priced at US$99 with a monthly subscription cost of US$8.30, is relatively new in the market, and its effectiveness is yet to be established.
If Invoxia Minitailz Smart Pet Tracker is successful and delivers on its promise (with regard to accuracy and functionality), several other players will likely also explore biometric sensors for pet health monitoring.
Other technologies, such as LiDAR and infrared, are also being explored as potential alternatives. However, there are not many commercially successful solutions based on them yet.
Potential risk of data breach is one of the biggest threats to pet wearables
Given the expanding scope of all these technologies, the pet wearable market is booming. However, it comes with its own set of challenges. While companies claim to have high accuracy rates, no FDA approvals are required for pet wearables at the moment. Thus, there is no way to verify the actual effectiveness of these devices. Moreover, since they deal with critical health conditions, a missed reading or a misdiagnosis can have dire consequences. Pet owners can also not consider these devices to be a replacement for their vet visits at large, and the devices can only act as information gatherers that can help vets make quicker diagnoses.
The industry is also facing a significant obstacle in the form of substandard battery technology. Given the number of features on each device (such as GPS tracking, health monitoring, two-way communication, etc.), its continuous and real-time work requirement, and the limited lifespan of lithium-ion batteries, companies have difficulty providing sufficient battery life for their devices. In several cases, pet owners find that the battery gets discharged sooner than they can recharge it. Therefore, the device loses its purpose since it is meant to provide continuous real-time data to be effective. To mitigate this, companies are looking into other battery options, such as lead acid (less efficient than lithium-ion) and silicon carbide (a more expensive option).
Another issue with these devices is the potential risk of data breaches. Wearables collect large amounts of data about pets and pet owners. In a 2019 study by Bristol University, pet wearable devices collected four times more data about the pet owner than about the pet itself. If this data is not properly secured, it could result in data leaks and cyberattacks and put the owner at risk.
EOS Perspective
With pet ownership increasing, the market for pet wearables will undoubtedly grow. Moreover, as human wearables continue to permeate our daily lives, it is natural that pet owners are looking for a similar advanced level of monitoring for their beloved companions.
The market, which started with single functionality tracking devices, is now moving towards more complex and technologically advanced solutions. While tracking and GPS-based devices continue to form a significant portion of the market at the moment, several leading players in the space (such as Tractive) are now integrating other functionalities with their location-tracking offerings.
Thus, the market is expected to move towards multi-functional solutions that offer basic features such as tracking along with advanced features such as activity and health monitoring. Also, within health monitoring, offerings will continue to differ based on complexity. For instance, some devices offer insights only into weight and temperature changes, while more advanced devices offer heart and pulse rate monitoring. As seen in the case of human wearables, the market is likely to move towards the latter as continuous advanced health monitoring becomes a standard way of managing well-being for both humans and pets.
Given the industry’s nascence, fragmented market, lack of big established brands, and low brand loyalty, the products’ key differentiating factors are likely to remain competitive pricing, advanced offerings, and effective technology.
For this, it becomes essential for companies to stay ahead of the curve and to explore possible technologies, beyond what is effective in human wearables. Therefore, companies that are investing in exploring suitable technologies, such as radar and biometrics, for advanced features, such as heart rate monitoring, are likely to emerge as market leaders in the long run.
Moreover, the pet wearables market is likely to also benefit from integration with pet insurance in the future. Both industries have synergies as the insurance sector can gain from health-based data derived from pet wearables. On the other hand, increasing demand for pet insurance is expected to provide a push to the pet wearables market, as pet owners who track and monitor their pet’s health can negotiate better and more competitive insurance rates.
Undoubtedly, the industry is poised for steady and strong growth. The market will likely consolidate, while players offering technologically advanced wearables focused on health monitoring and priced at around US$100-150 will emerge as leaders.