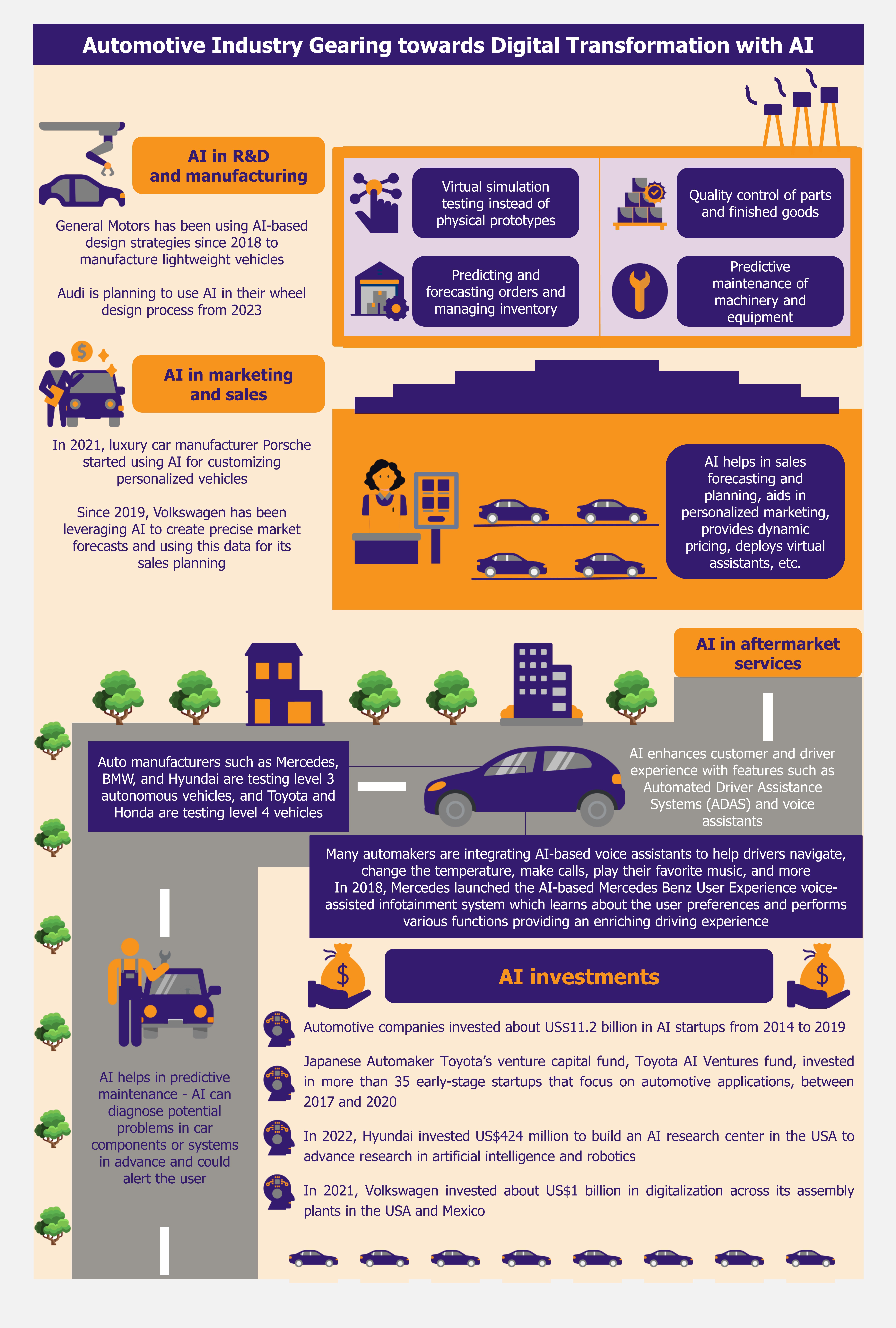
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become an integral part of almost every industry, and the automotive sector is no exception. From self-driving cars to predictive maintenance, AI is evolving as a major disruptor in the auto industry, slowly transforming how automobiles are designed, manufactured, and sold. This digital swing is driven mainly by increased competition, consumer preferences for smart mobility, and the benefits of AI. However, AI adoption in the automotive industry is not mainstream yet, with the technology deployed only at the pilot level and in selective business segments. As the world gears toward an era of digital transformation and automation, AI is expected to be part of various business processes in the automotive industry in the coming years.
Artificial intelligence in the auto industry is typically associated with autonomous and self-driving cars. However, the technology has increasingly found its way into other applications over the last few years. Leading auto OEMs are showing an interest in deploying AI-driven innovations across the value chain, investing in tech start-ups, partnering with software providers, and building new business entities.
For instance, a venture capital fund owned by Japanese automaker Toyota, Toyota AI Ventures (rebranded as Toyota Ventures now), with US$200 million in assets under management, invested in almost 35 early-age startups that focus on AI, autonomy, mobility, and robotics between 2017 and 2020. Similarly, in 2022, South Korean automotive manufacturer Hyundai invested US$424 million to build an AI research center in the USA to advance research in AI and robotics. In the same year, CARIAD, a software division of the Germany-based Volkswagen Group, acquired Paragon Semvox GmbH, a Germany-based company that develops AI-based voice control and smart assistance systems, for US$42 million.
Changing consumer preferences, competitive pressures, and various advantages of AI are driving this transformation. According to a 2019 Capgemini research study, nearly 25% of auto manufacturers in the USA implemented AI solutions at scale, followed by the UK (14%) and Germany (12%) by the end of 2019.
There are numerous applications of AI in the automotive industry. Some of the more common and innovative uses of AI include virtual simulation models, inventory management, quality control of parts and finished goods, automated driver assistance systems (ADAS), predictive maintenance, and personalized vehicles, to name a few.
AI-based virtual simulation models used for effective R&D processes
Due to changing customer preferences, increasing regulations concerning safety and fuel emissions, and technological disruption, OEMs are finding it more expensive to make cars nowadays. A 2020 report by PricewaterhouseCoopers says that conceptualization and product development account for 77% of the cost and 65% of the time spent in a typical automotive manufacturing process.
To make R&D cost-effective and more efficient, some auto manufacturers and tier-I suppliers are turning to AI. AI enables the simulation of digital prototypes, eliminating a lot of physical prototypes, thus reducing the costs and time for product development. One interesting concept that is emerging and catching attention in this area is the “digital twin”. The concept employs a virtual model mimicking an entire process or environment and its physical behavior. There are numerous uses of digital twins – in vehicle design and development, factory and supply chain simulations, autonomous driving simulations, etc. In vehicle design and development, digital twins make simulations easier, validate each step of the development in order to predict outcomes, improve performance, and identify possible failures before the product enters the production line.
For instance, in 2019, Continental, a Germany-based automotive parts manufacturing company, entered into a collaboration with a Germany-based start-up, Automotive Artificial Intelligence (AAI), to develop a modular virtual simulation program for its Automated Driver Assistance System (ADAS) application and also invested an undisclosed amount in the company. The virtual simulation program could generate phenomenal vehicle test data of 5,000 miles per hour compared to 6,500 miles of physical test driving per month, reducing both time and costs.
Many leading automotive companies are also looking to utilize this innovative concept in streamlining the entire manufacturing operations. For example, in early 2023, Mercedes-Benz announced that the company is partnering with Nvidia Technologies, a US-based technology company specializing in AI-based hardware and software, to build a digital twin of one of its automotive plants in Germany. Mercedes-Benz is hoping that the digital twin can help them monitor the entire plant and make quick changes in their production processes without interruptions.
General Motors, Volkswagen, and Hyundai use AI for smart manufacturing
Automation processes and industrial robots have been in automotive manufacturing for a long time. However, these systems can perform only programmed routine and repetitive tasks and cannot act on complex real-life scenarios.
The use of AI in automotive manufacturing makes these production processes smarter and more efficient. Some of the applications of AI in manufacturing include forecasting component failures, predicting demand for components and managing inventory, using collaborative robots for heavy material handling, etc.
For instance, General Motors, a US-based automotive manufacturing company, has been using AI-based design strategies since 2018 to manufacture lightweight vehicles. In 2019, the company also deployed an AI-based image classification tool in its robots to detect equipment failures on pilot-level experimentation.
Similarly, a Germany-based luxury car manufacturer, Audi, has been using AI to monitor the quality of spot welds since 2021 and is also planning to use AI in its wheel design process starting in 2023. In 2021, Audi’s parent company, Volkswagen, also invested about US$1 billion to bring technologies such as cloud-based industrial software, intelligent robotics, and AI into its factory operations. With this, the company aims to drive a 30% increase in manufacturing performance in its plants in the USA and Mexico by 2025.
In another instance, South Korean automotive manufacturer Hyundai uses AI to improve the well-being of its employees. In 2018, the company developed wearable robots for its workers, who spend most of their time in assembly lines. These robots can sense the type of work of employees, adjust their motions, and boost load support and mobility, preventing work-related musculoskeletal disorders. Thus, AI is transforming every facet of automobile manufacturing, from designing to improving the well-being of employees.
Companies provide more ADAS features amidst increasing competition
Automated Driver Assistance System (ADAS) is one of the powerful applications of AI in the automotive industry. ADAS are intelligent systems that aim to make driving safer and more efficient. ADAS primarily uses cameras and Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging) sensors to generate a high-resolution 360-degree view of the car and assists the driver or enables cars to take autonomous actions. Demand for ADAS is growing globally due to consumers’ rising preference for luxury, better safety, and comfort. It is estimated that by 2025, ADAS will become a default feature of nearly every new vehicle sold worldwide. ADAS is classified into 6 levels:
| Level 0 | No automation |
| Level 1 | Driver assistance: the vehicle has at least a single automation system |
| Level 2 | Partial driving automation: the vehicle has more than one automated system; the driver has to be on alert at all times |
| Level 3 | Conditional driving automation: the vehicle has multiple driver assistance functions that control most driving tasks; the driver has to be present to take over if anything goes wrong |
| Level 4 | High driving automation: the vehicle can make decisions itself in most circumstances; the driver has the option to manually control the car |
| Level 5 | Full driving automation: the vehicle can do everything on its own without the presence of a driver |
At present, cars from level 0 to level 2 are on the market. To meet the growing competitive edge, several auto manufacturers are adding more automation features to the level 2 type. Companies have also been making significant strides toward developing autonomous vehicles. For instance, auto manufacturers such as Mercedes, BMW, and Hyundai are testing level 3 autonomous vehicles, and Toyota and Honda are testing and trialing level 4 vehicles. This indicates that the future of mobility will be highly automated relying upon technologies such as AI.
Volkswagen and Porsche use AI in automotive marketing and sales
There are various applications of AI in marketing and sales operations – in sales forecasting and planning, personalized marketing, AI-assisted virtual assistants, etc. According to a May 2022 Boston Consulting Group (BCG) report, auto OEMs can gain faster returns with lower investments by deploying AI in their marketing and sales operations.
Some automotive companies have already started to deploy AI in sales and marketing. For instance, since 2019, Volkswagen has been leveraging AI to create precise market forecasts based on certain variables and uses the data for its sales planning. Similarly, in 2021, a Germany-based luxury car manufacturer, Porsche, launched an AI tool that suggests various vehicle options and their prices based on the customer’s preferences.
Automakers integrate AI-assisted voice assistants into cars
Cars nowadays are not only perceived as a means of transportation, but consumers also expect sophisticated features, convenience, comfort, and an enriching experience during their journey. AI enhances every aspect of the cockpit and deploys personalized infotainment systems that learn from user preferences and habits over time. Many automakers are integrating AI-based voice assistants to help drivers navigate through traffic, change the temperature, make calls, play their favorite music, and more.
For instance, in 2018, Mercedes-Benz introduced the Mercedes Benz User Experience (MBUX) voice-assisted infotainment system, which gets activated with the keyword “Hey Mercedes”. Amazon, Apple, and Google are also planning to get carmakers to integrate their technologies into in-car infotainment systems. It is expected that 90% of new vehicles sold globally will have voice assistants by 2028.
Integration and technological challenges hamper the adoption of AI
The adoption of AI in the automotive industry is still at a nascent stage. Several OEM manufacturers in the automotive industry are leveraging various AI solutions only at the pilot level, and scaling up is slow due to the various challenges associated with AI.
At the technology level, the creation of AI algorithms remains the main challenge, requiring extensive training of neural networks that rely on large data sets. Organizations lack the skills and expertise in AI-related tools to successfully build and test AI models, which is time-consuming and expensive. AI technology also uses a variety of high-priced advanced sensors and microprocessors, thus hindering the technology from being economically feasible.
Moreover, AI acts more or less like a black box, and it remains difficult to determine how AI models make decisions. This obscurity remains a big problem, especially for autonomous vehicles.
At the organizational level, integration challenges make it difficult to implement the technology with existing infrastructure, tools, and systems. Lack of knowledge of selecting and investing in the right AI application and lack of information on potential economic returns are other biggest organizational hurdles.
EOS Perspective
The applications of AI in the automotive industry are broad, and many are yet to be envisioned. There has been an upswing in the number of automotive AI patents since 2015, with an average of 3,700 patents granted every year. It is evident that many disrupting high-value automotive applications of AI are likely to be deployed in the coming decade. Automotive organizations are bolstering their AI skills and capabilities by investing in AI-led start-ups. These companies together already invested about US$11.2 billion in these startups from 2014 to 2019.
There is also an increase in the hiring pattern of AI-related roles in the industry. Many automotive industry leaders are optimistic that AI technology can bring significant economic and operational benefits to their businesses. AI can turn out to be a powerful steering wheel to drive growth in the industry. The future of many industries will be digital, and so will be for the automotive sector. Hence, for automotive businesses that are yet to make strides toward this digital transformation, it is better to get into this trend before it gets too late to keep up with the competition.