The emergence of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) has become a central focus in the global financial space, as it offers the potential for revolutionary shifts in how the world conducts and manages monetary transactions. While much of the spotlight has been on retail CBDCs, wholesale CBDCs are gaining momentum globally. Asia is leading the pack in developing wholesale CBDCs that offer opportunities that may significantly impact the global financial landscape.
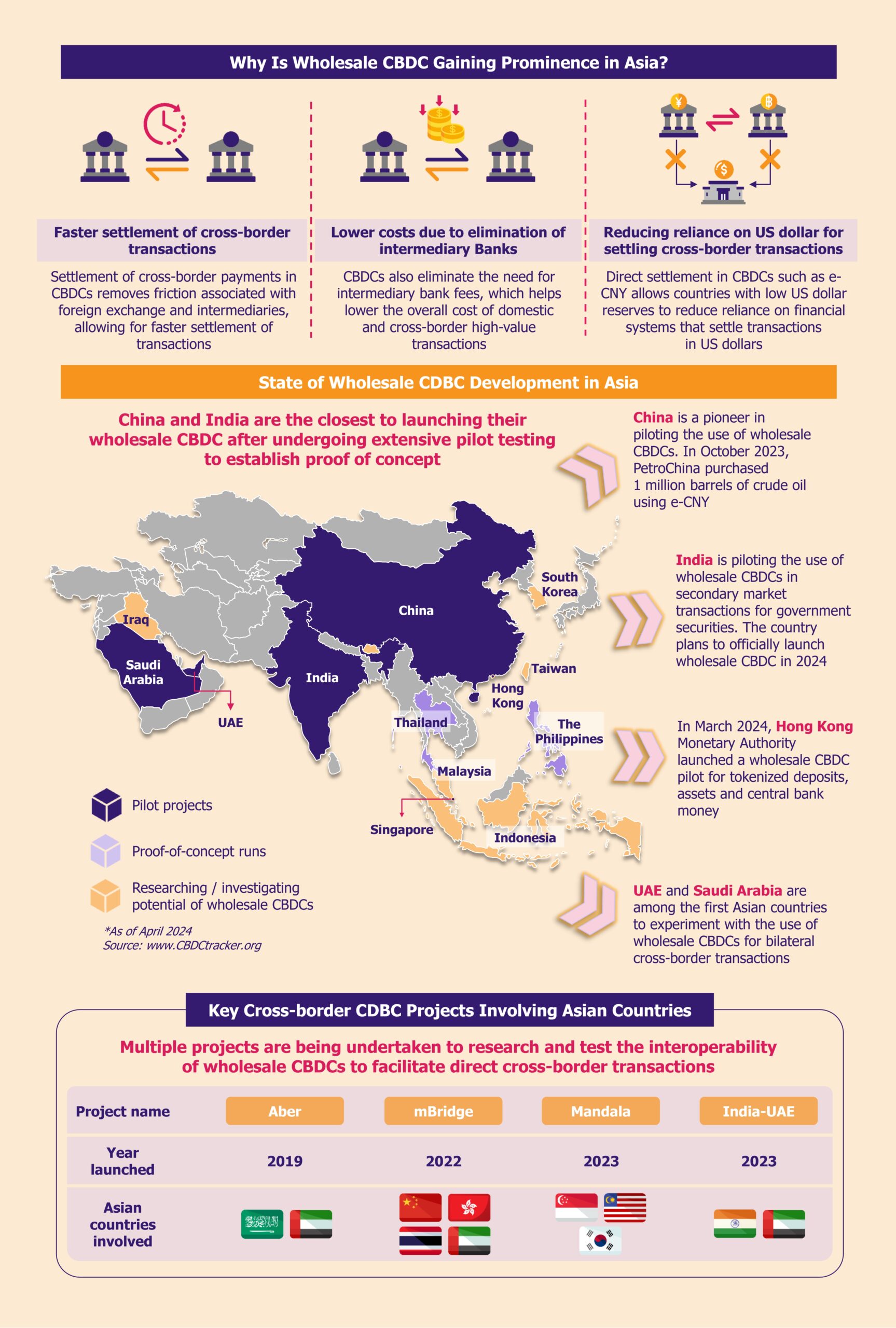
Asia is outpacing developed countries in the drive toward wholesale CBDCs
Wholesale CBDCs are digital forms of a country’s fiat currency. Unlike retail CBDCs, only a limited number of entities can access wholesale CBDCs, which are designed for undertaking interbank transactions and settlements. The concept of wholesale CBDCs is similar to currently available digital assets used for the settlement of interbank transactions, with the key differentiation being the use of technologies such as distributed ledger technology (DLT) and tokenization.
Wholesale CBDCs have garnered global interest with central banks. Facebook’s (albeit failed) attempt to launch its Libra cryptocurrency in 2019 was a breaking point for blockchain technology’s use in global finance, eventually spurring the development of wholesale CBDCs. Initially launched as a measure to counter private cryptocurrencies, wholesale CBDCs are fast emerging as a potential disruptor in the fintech space.
Currently, more than 30 countries are researching the use of wholesale CBDCs. Interestingly, about half of these countries are from Asia. The development of wholesale CBDCs in Asian countries has outpaced the efforts of financially strong economies such as the USA and the UK, as these CBDCs offer more tangible benefits to developing economies in Asia than their more developed counterparts.
Several Asian countries have engaged in pilot programs, and proof-of-concept runs to explore the use of wholesale CBDCs to improve the efficiency of domestic large-value transactions and cross-border transfers.
China has been at the forefront of the development and widespread testing of wholesale CBDCs. Several Southeast Asia and the Middle East countries, including India, the UAE, Thailand, and Singapore, have launched pilot programs to explore the viability of wholesale CBDCs and test interoperability for cross-border transactions.
Achieving faster and cheaper cross-border transactions is key to Asian central banks
Growth in global trade has resulted in exponential growth in cross-border transaction volumes. However, these cross-border transactions are faced with challenges. There may be involvement of potential intermediaries, varying time zones, and regulatory frictions that may cause slower settlement. Financial systems such as SWIFT have a stranglehold on the cross-border transaction ecosystem, with many of these transactions using SWIFT messaging to settle payments.
Potential intermediary fees and forex-related charges also lead to increased transaction costs. According to World Bank’s estimates, transaction costs for cross-border transactions may range up to 6% of the transfer value, a significant surcharge.
Removing friction associated with cross-border transactions is a key goal behind Asian countries’ push toward exploring wholesale CBDCs.
A growing interest in wholesale CBDCs is attracting investments in building large-value payment infrastructures in Asia, allowing for faster and more efficient cross-border transfers. Wholesale CBDCs enable central banks to transact directly with each other, removing the involvement of multiple intermediaries and resulting in quicker transaction settlement. This also results in the elimination of intermediary fees to help lower transaction costs.
Technology also adds elements of security and traceability to these digital transactions. It also offers the potential to program them by automating or restricting payments if certain conditions are met.
Challenging US dollar dominance in cross-border settlements offers additional motivation
Several Asian countries are also looking to reduce their reliance on financial settlement systems that involve US dollar reserves. Currently, most cross-border transactions involve the use of the US dollar. Countries with limited forex reserves also face the challenge of outgoing reserves, resulting in potential currency inflation and adding to the already high transaction costs.
Wholesale CBDCs offer several Asian countries, particularly those with limited US dollar reserves, an opportunity to directly transfer the amount in their local digital currencies and eliminate the need for US dollars in bilateral transactions.
Developing Asian economies, such as China and India, with significant cross-border transactions, are looking to promote their CBDCs as a potential reserve currency in the Asian region that would allow cross-border settlement directly in the digital currency. It is also in the interests of countries such as China to develop its CBDC (e-CNY) as a potential alternative to the US Dollar in cross-border trade to mitigate any potential currency-related challenges posed by economic sanctions from the USA and EU.
Tandem development and collaborations offer tailwinds to CBDC projects in Asia
Central banks of several Asian countries are undertaking information sharing and tandem development of CBDC infrastructures to mitigate some challenges associated with CBDC.
Recent pilot projects such as mBridge, launched by central banks of China, the UAE, Thailand, and Hong Kong, have been testing the use of a common ledger platform for real-time peer-to-peer transactions. The launch of several other projects, such as Project Mandala (involving Singapore, South Korea, and Malaysia) and Project Aber (involving Saudi Arabia and the UAE), is laying the groundwork for the widespread implementation of wholesale CBDCs.
Another potential avenue for collaboration includes forming partnerships with central banks to maintain reserves of digital cash to facilitate direct settlement. China, in particular, plans to develop e-CNY as a potential reserve currency alternative to the US dollar.
Interoperability and ownership are key challenges to CBDC implementation
While the use of wholesale CBDCs certainly comes forward as a boon, there are challenges in using these technology-driven digital currencies. CBDCs may have varying protocols, and interoperability between different CBDC frameworks remains a key challenge for implementing wholesale CBDCs for cross-border transactions.
Establishing common technical and operational standards is essential to ensure CBDC interoperability. Currently, most pilot programs involve CBDCs with common or similar technological frameworks and rules, which limit the application of wholesale CBDCs to a certain number of compatible entities.
Recent research projects are laying the groundwork for CBDCs’ compatibility with various ledgers and technical frameworks. However, significant testing will be required before compatibility can be established across the Asian region.
Ownership, governance, and regulatory oversight of wholesale CBDC technologies are other key concerns. Doubts exist over who will oversee the transactions and ledger entries, especially for any multi-party cross-border transaction.
Systems must also to adhere to anti-money laundering and counter-terrorism financing regulations. Varying financial laws may also hamper the seamless implementation of these anti-money laundering and counter-threat funding regulations across the region.
Lastly, like any digital asset, CBDCs are also susceptible to cyberattacks.
EOS Perspective
Wholesale CBDCs can potentially change the nature of cross-border transactions across Asia and globally.
We are likely to witness significant growth in test runs and pilot programs by several Asian countries to provide proof of concept for the applicability of wholesale CBDCs in countering the challenges associated with cross-border transactions. We can expect a spurt in CBDC alliances and treaties among countries with significant bilateral and intra-regional trade. Simultaneously, it may result in slightly reduced transaction volumes going through existing cross-border financial systems such as SWIFT.
The next stage of CBDC evolution is likely to coincide with the emergence of pilot programs involving multiple CBDCs with different technological frameworks, creating possibilities for easier and seamless cross-border transactions among banks or countries without any existing bilateral or regional partnerships.
These developments are likely to be aided by the development of enabling technologies such as RegTech (regulatory technologies) and SupTech (supervisory technologies), which could provide the sandbox environment for widespread testing of the CBDC systems, as well as lay the groundwork for potential regulatory systems to manage these infrastructures.
With the bulk of cross-border transactions still being conducted in the US dollar, wholesale CBDCs do not pose any imminent threat to its dominance. The US dollar’s future prospects in this role will depend on whether digital currencies such as e-CNY take off as a reserve currency, which is unlikely, at least in the short- to medium-term.
The overall success of wholesale CBDCs will depend on the level of cooperation that countries across Asia can develop over the next few years.