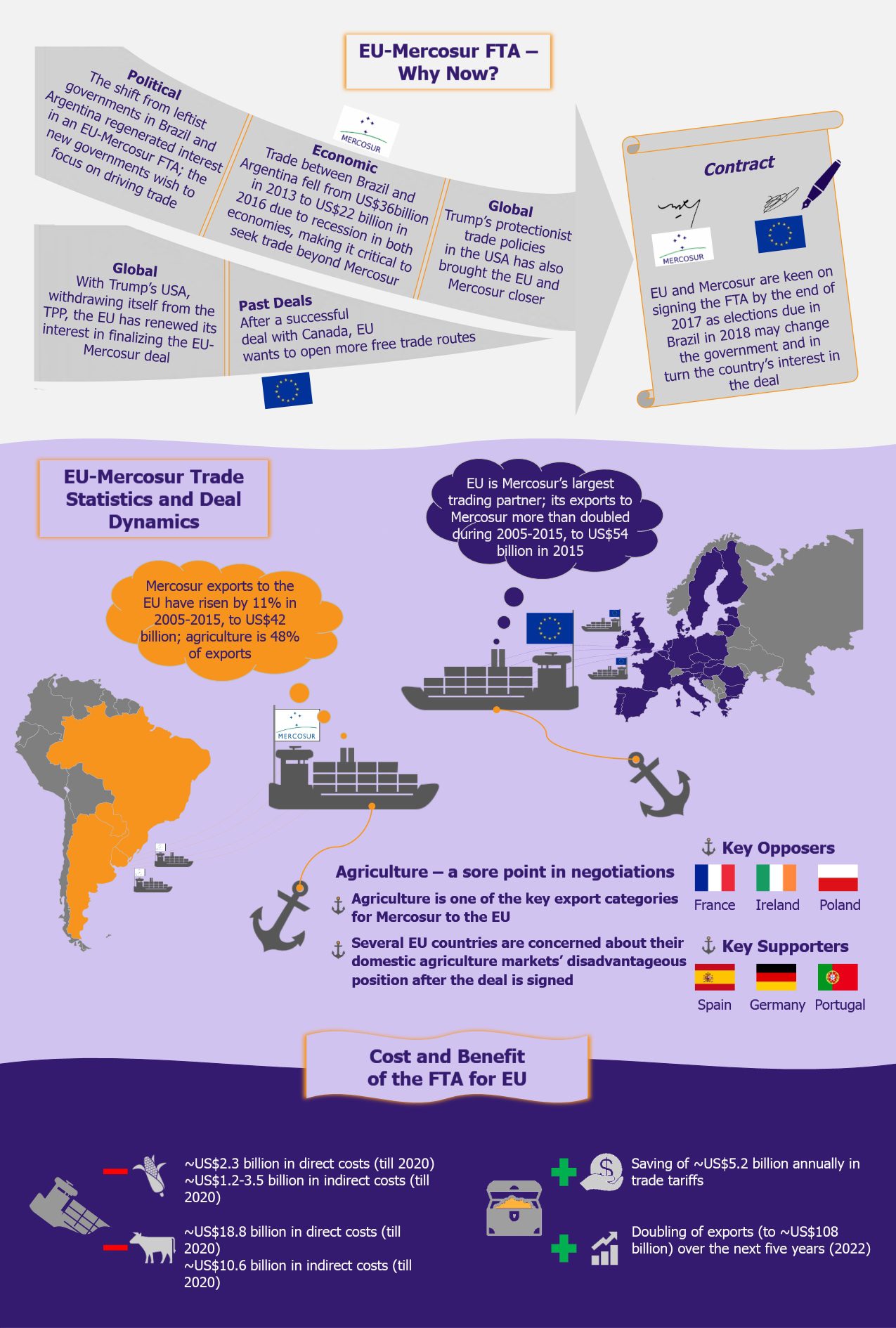
The EU and Mercosur (a trade bloc comprising Brazil, Argentina, Uruguay, and Paraguay*) free trade agreement (FTA) negotiations date back almost two decades, to 1999. After failing to seal the deal in 1999 and again in 2004, the countries initiated new negotiations in 2010 and though started out slowly, they accelerated the process in 2016 (with hopes to finalize the deal by the end of 2017). A trade deal at this moment will be of significant importance to both sides owing to substantial amount of trade between the two blocs. The EU is Mercosur’s largest trading partner accounting for 21% of the bloc’s trade in 2015, while Brazil alone is the EU’s eleventh largest trading partner. However, despite a positive framework for the agreement to happen, there is still a great deal of resistance from few EU countries regarding the opening up of their agriculture sectors. Now it remains to see whether the two blocs can reach the much needed compromises and end up with an agreement by the end of the year or talks will remain hanging once more.
*Venezuela has been suspended from the trade bloc in 2016 and therefore is out of the negotiations
While this may not be the first time the EU and Mercosur sit to negotiate the terms of an FTA, it definitely seems to be the most promising one. The main reason the earlier efforts have gone in vain was the Argentinian leftist government’s adverse stance on trading outside their own backyard. This changed with the election of president Mauricio Macri in December 2015, who unlike his predecessor (Cristina Fernandez de Kirchner), looks at international trade as a growth opportunity for Argentina. Similarly, the impeachment of the Brazilian president Dilma Rousseff in May 2016 resulted in a new political wave in Brazil. While Brazil’s former president did take small steps towards trade liberalization, her successor, Michel Temer, has accelerated this process and has made the EU-Mercosur deal one of his top priorities.
Another reason this deal has gained immense importance for the Latin American bloc has been a declining bilateral trade among Mercosur’s two largest members, Argentina and Brazil, owing to recession. Trade between the countries declined from US$36 billion to US$22 billion during 2013-2016. This has forced the two nations to soften their stance on global trade.
Considering these developments, as well as the changing political and trade dynamics between several Latin American countries and the USA, following the arrival of Trumps administration at the White House, Mercosur’s openness and renewed interest in strengthening international trade ties is fully understandable. We wrote about it in February 2017 in our article Trump in Action: Triumph or Tremor for Latin America? and again later in June 2017 in Japan Hopes to Get a Slice of Mercosur Opportunity Cake as LATAM Exports to USA Decline.
On the other side of the negotiations table, as the EU has maintained a positive outlook towards foreign trade in general, the lost prospect of a Trans-Atlantic Trade and Investment Partnership with the USA under Donald Trump has also reinvigorated EU’s interest in the Mercosur FTA. Moreover, the EU views the deal with Mercosur as a suitable counter-measure to the growing Chinese influence in Latin America.
Apart from these aspects, the main reason for renewed commitment to the deal by both sides is the significant and increasing level of trade and investment between the two blocs. In 2014, EU’s investments in Mercosur countries reached US$494 billion. The EU’s exports to Mercosur expanded from about US$24.6 billion (€21 billion) in 2005 to about US$54 billion (€46 billion) in 2015. Similarly for Mercosur, its exports to the EU increased from US$37.5 billion (€32 billion) to US$49 billion (€42 billion) during the same period. Agriculture products constituted 48% of Mercosur’s exports to the EU, while machinery (29% of exports) and vehicle and parts (17% of exports) were EU’s largest export categories to the Latin American bloc.
The EU stands to gain a great deal from the FTA. As per current calculations, EU exporters would save about US$5.2 billion (€4.4 billion) annually on trade tariffs and stand to double their exports within five years of reaching a deal.
Despite hefty trade benefits and a lot of political and economic factors being in favor of the deal, agriculture remains a sore point. Several EU countries, led by France, do not want to open up their agriculture sector to Mercosur’s exports as they feel their domestic produce (especially grains and meat) cannot compete with that of Brazil and Argentina in terms of price. In addition, they are concerned that Mercosur’s agricultural produce are not subject to the same health standards as their domestic produce.
A quick glance at the average production costs indicates that the EU farmers have a reason to worry. As per estimates, if the deal comes through, the amount of maize available in Brazil and Argentina for export by 2020 will be between 23 and 26 million tonnes. While the average production cost of cereal in Mercosur is close to US$94/ tonne (€80/tonne), it is about US$141/tonne (€120/tonne) in the EU. This is likely to result in substitution of EU-grown maize with that from Mercosur, which will most likely result in a loss of about US$2.3 billion (€2 billion) by 2020 for EU’s agriculture sector. In addition, it can be expected to result in an indirect loss of about US$1.2-3.5 billion (€1-3 billion) as Mercosur-produced maize is likely to also replace wheat for animal feed during high production and harvest months.
In case of meat products, beef produced in Mercosur is more competitive than EU’s beef in terms of pricing. Moreover, a study of the usual trend of beef quotas suggest that they are first filled with noble cuts exports (including filet, entrecote, and rump steak) followed by other hindquarter cuts (such as topside and silverside). In case the deal takes place, it is expected that Mercosur’s beef will largely substitute local beef produce with Mercosur’s export volume (keeping in mind higher quantities of noble cuts, such as Hilton beef) expecting to reach 1 million tonnes. These would be worth US$18.8 billion (€16 billion) and would directly impact the local production and sales value. To bring this into perspective, the value of Brazil’s beef exports (the largest beef exporter among the Mercosur countries) to the EU was US$485 million in 2016. Moreover, low-priced imports from Mercosur will put pressure on the pricing in the domestic EU market resulting in close to a 30% downward price revision, which in turn is highly likely to result in further losses of about US$10.6 billion (€9 billion). In case the EU agreed to 300,000 tonnes at zero duty, this would expectedly result in US$3.5 billion (€3 billion) in direct costs and US$7.1 billion in indirect costs (€6 billion).
In addition to this, there are several non-tariff related issues with Mercosur’s produce, such as lack of tagging and traceability of livestock to identify and guarantee origin. Also, several drugs, such as hormones and growth promoters, as well as few antibiotics and insecticides that are banned in the EU are legally used in Mercosur. These factors have resulted in countries such as France, Ireland, and Poland opposing the EU-Mercosur FTA.
Another source of disagreement for the EU lies in the trade of sugar and ethanol, which the European producers claim should be excluded from the list of freely-traded items. This stems primarily from the fact that the Brazilian government provides subsidies worth US$1.8 billion annually to its ethanol and sugar producers, a fact providing them with an undue advantage compared to the European counterparts.
On the other hand, Mercosur is discontent with EU’s limited concessions on agricultural imports and its stance to continue quotas on the Mercosur’s food imports. Mercosur also has some concerns regarding providing the EU with access to public tenders, which in Brazil alone are worth about US$176 billion (€150 billion), however, they are positive that they will be able to reach a consensus during negotiations.
While few points of contention remain, negotiators at both ends are keen on resolving these issues and signing the deal by the end of 2017, remaining aware of the significance of this deal for both the sides as well as of the tendency for these talks to remain unresolved if not pushed soon. Moreover, both sides want to exploit the current favorable political scenario in Brazil and Argentina. With Brazil heading for presidential elections in 2018, the chances of a leftist-government coming to power do exist, and this can again put the deal in danger if it is not completed by then. Both sides of the negotiating table want to reach an agreement sought-after for the past 20 years as early as possible, even if it means compromising on some expectations.
EOS Perspective
A goal of completing the deal by the end of 2017 seems like quite a gun to the heads of both the blocs, as past experience, both in the case of this deal as well as other FTAs, proves that the process is never quick nor simple. Moreover, the EU seems somewhat divided on the deal, with Spain, Portugal, and Germany advocating for it and France, Poland, and Ireland opposing it. That being said, this deal – which has been on and off again and again since 1999 – has never been as close to getting finalized as it is now. This is primarily due to the fact that both Argentina and Brazil (that were the two main factors holding the deal back all these years) are extremely keen on reaching this agreement with EU, to the extent that they may be willing to compromise quite a bit as long as the deal includes provisions that leave room for future improvements and it brings increase in trade and thus growth for local economies. However, it remains to be seen whether they will be willing to stretch their compromises far enough to agree to the EU’s terms on the agriculture produce trade. At the same time, it is not clear how much the EU is going to push for these provisions, so there is a chance that both parties will manage to reach a well-rounded deal for both the sides. The least probable scenario is that the deal will come to a stand-still once more, however till the ink dries on the deal, nothing can be considered as certain.