Iran possesses significant mineral reserves, but its mining industry grapples with issues, including machinery shortages and international sanctions. The recent lithium discovery in Iran holds the potential to boost its mining sector and economy, depending on the viability of lithium extraction and processing, as well as geopolitical factors. It can serve as a bargaining chip to lift sanctions imposed by the Western world. China is poised to benefit the most from Iran’s lithium discovery due to its strategic partnership and expertise in lithium refining and extraction technologies. However, despite Iran’s strong mining potential, high infrastructure costs, technological limitations, and sanctions hinder its mining industry development.
Lithium discovery to help drive mining industry and economic upliftment in Iran
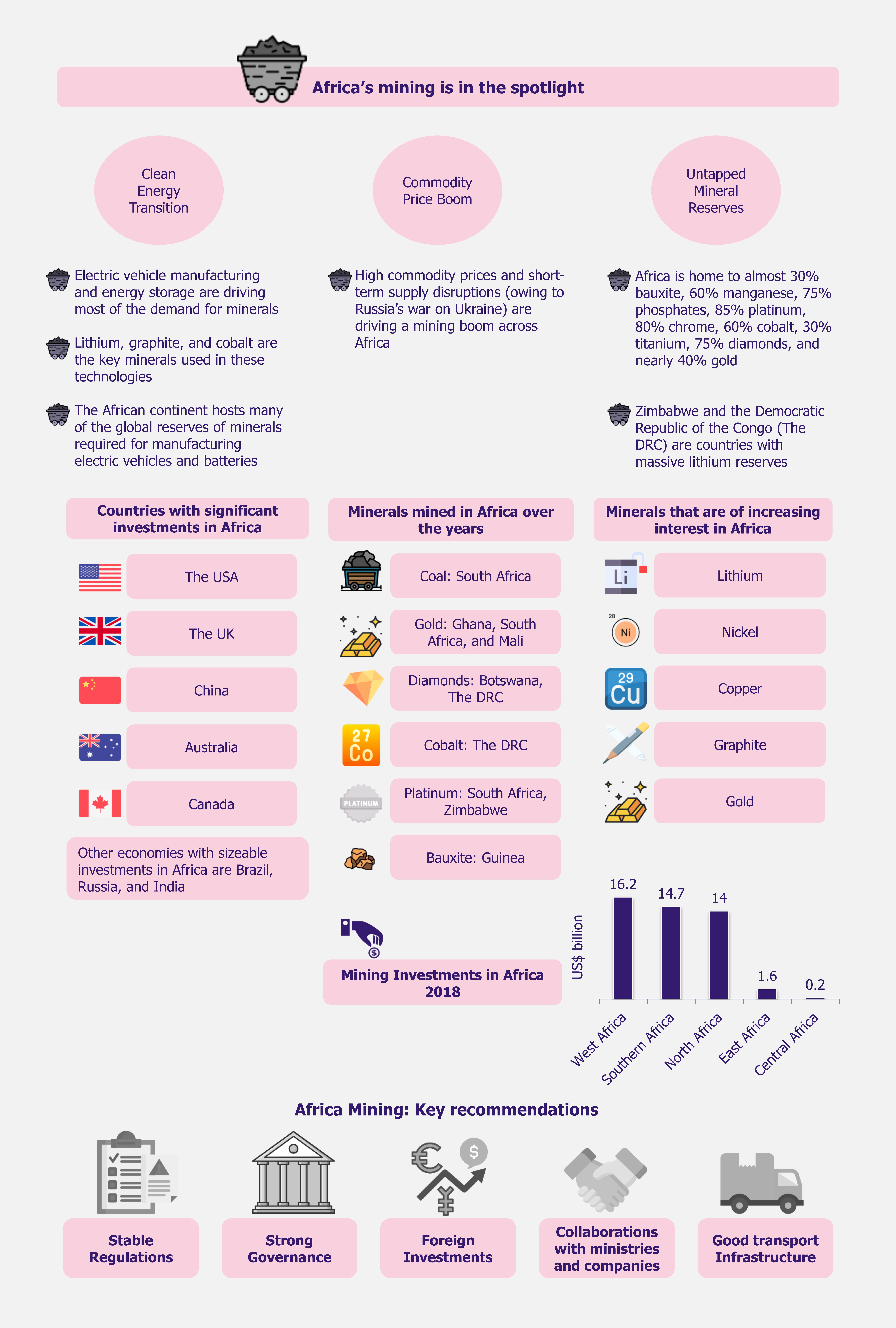
Iran is home to more than 7% of the world’s total mineral reserves and is rich in minerals, including zinc, copper, iron ore, coal, and gypsum. However, Iran’s mining industry is still nascent and barely contributes to economic growth due to a lack of necessary machinery and equipment as well as international sanctions.
In the past, Iran exported various minerals, such as iron ore, zinc, and copper, to Western countries. However, prolonged international sanctions, initially imposed in 2006 to restrain Iran’s nuclear development program, resulted in insufficient investment in the mining sector.
Announced in March 2023, the discovery of lithium deposits holding up to 8.5 million tons of lithium in Iran, if proven accurate, is expected to strengthen the country’s mining sector and overall economic growth. Iran is the first country in the Middle East to discover lithium deposits.
Lithium is a crucial component of lithium-ion batteries used in smartphones and electric vehicles. The increasing adoption of electric vehicles is fueling the demand for lithium at a significant rate globally. There is a great need to scale up lithium mining and processing to meet the demand, particularly for the manufacturing of electric vehicles.
International Energy Agency (IEA), in its global EV outlook for 2022, indicated that about 50 new average-sized mines need to be built to fulfill the rising lithium demand for electric vehicles and meet international carbon emission goals. There are already signs of lithium shortage as demand for lithium increases globally. The lithium reserve found in Iran holds the potential to reverse the lithium supply shortage into surplus in the coming years.
Read our related Perspective: Electric Vehicle Industry Jittery over Looming Lithium Supply Shortage
Hope for the lifting of sanctions and reestablishment of diplomatic relations
The lithium discovery in Iran is expected to redirect focus toward mining activities in the Middle East. Iran can leverage this discovery to persuade Western nations, such as the USA and the EU countries, to lift sanctions imposed for its nuclear program, support for terrorism, and human rights violations. These sanctions include restrictions on Iran’s access to the global financial system, travel bans on targeted individuals and entities involved in concerning activities, and limitations on trade in certain goods and technologies.
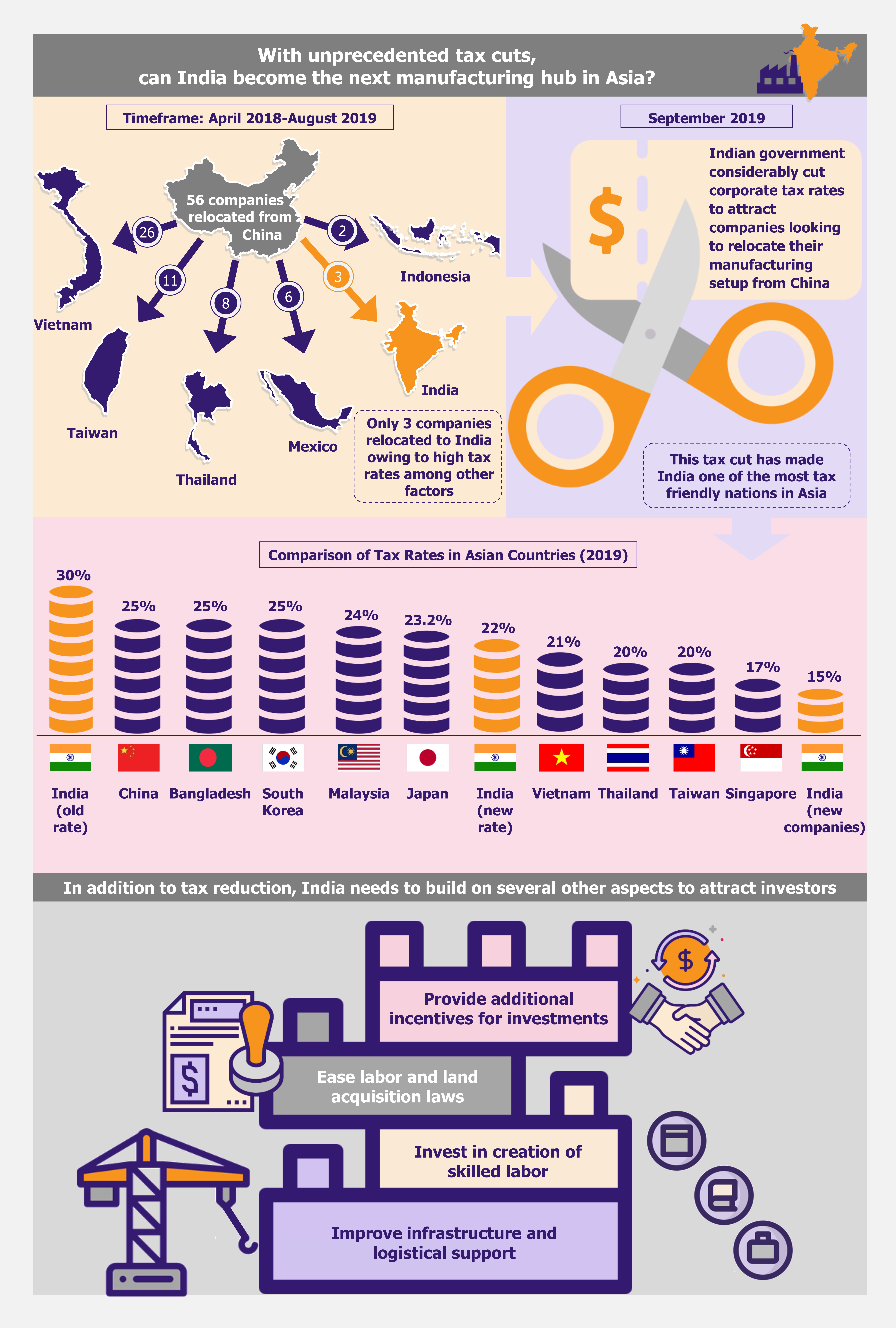
In August 2023, Iran and the USA reached an agreement wherein Iran intended to release detained Americans in exchange for the release of several imprisoned Iranians and access to frozen financial assets. Fulfillment of commitments demonstrates mutual trust among the countries, which could pave the way for improved relations, reduced tensions, and future diplomatic initiatives. The US government also permitted Iran to enrich uranium up to 60%. This can be interpreted as allowing Iran to meet their nuclear aspirations, which could encourage Iran to comply with the agreement signed with the USA. As cooperation and trust between the nations strengthen, this agreement could ease sanctions. Moreover, if relations continue to improve, Iran could potentially seek assistance from the USA for its lithium venture.
Also, in March 2023, Saudi Arabia and Iran, with the help of China, reached an agreement to resume their diplomatic relations, re-open embassies, and implement agreements covering economy, investment, trade, and security. With the reestablishment of cordial relations, Saudi Arabia is likely to engage in joint ventures within Iran’s mining sector, providing mutual benefits for both nations.
It can also be expected that India will seek to strengthen its ties with Iran by building strong collaborations to ensure a regular lithium supply, considering that India is one of the largest importers of lithium-ion batteries. Iran and India share strong and multifaceted relations across various areas, such as trade, energy, connectivity, culture, and strategic cooperation. As India strives to transition to renewable energy sources and reduce its carbon footprint, access to lithium reserves from Iran could facilitate the development and deployment of energy storage solutions, such as grid-scale batteries and off-grid systems.
Potential to disrupt the global lithium race and geopolitical relations
The announcement of lithium deposits in Iran is likely to impact the global competition for lithium resources significantly. It holds the power to disrupt the existing power dynamics in the global lithium race, as it is estimated to be the second-largest lithium reserve in the world after Chile.
Many countries compete to control lithium supply chains due to its strategic importance, particularly in the EV industry. A few countries dominate the global lithium production, including Australia, Chile, and China. The emergence of Iran as a significant lithium producer could diversify the global supply chain. China, the largest importer and processor of lithium and manufacturer of lithium batteries, holds a substantial share of the lithium market. China is particularly reliant on foreign lithium suppliers, including Australia, Brazil, Canada, and Zimbabwe, accounting for around 70% of its total lithium imports.
With China’s well-established economic and political relations with Iran, there is potential for collaborative ventures in the clean energy transition supply chain. In addition, China’s expertise in technological advancements in lithium-related technologies, particularly lithium-ion battery manufacturing, purification and refinement of lithium, battery management systems, and development of battery materials, will likely play a crucial role in gaining access to Iranian lithium. Increased access to lithium will reduce its dependence on the current lithium suppliers and gain dominance in the lithium supply, impacting the trade balance and economic growth of countries supplying lithium to China.
At the same time, Australia, which stands out as China’s current primary source of lithium, exporting around 90% of its lithium to China, might encounter political and economic challenges. Australia, being a close ally of the USA, is likely to face pressure to curb its lithium exports to China, aiming to limit China’s access to sources of lithium. Chile, also being the key supplier of lithium to China, may face similar pressure from the USA. The USA is likely to exert such pressures, as China’s strong position could undermine the USA’s technological competitiveness and leadership in the EV market, accelerating the existing tensions and disrupting power dynamics in the global lithium race.
Major influencing countries such as the USA, Canada, France, Japan, Australia, the UK, and Germany also formed the Sustainable Critical Minerals Alliance in 2022. The alliance aims to secure supply chains of critical minerals, including lithium, nickel, and cobalt, from countries with more robust environmental and labor standards to reduce dependency on China. Such initiatives are expected to impact China’s dominant global lithium supply chain position.
Inevitably, Iran’s lithium discovery and China’s potential involvement in securing access to the resource can influence international relations, particularly between China and the USA, and China and Australia.
China to deepen ties with Iran
China and Iran have established an extensive partnership focused on China’s energy needs and Iran’s abundant resources. China has remained Iran’s primary trading partner for more than a decade. Their relationship grew stronger, specifically after the USA pulled out of the nuclear agreement and reintroduced sanctions on Tehran in 2018. Both China and Iran are confronted with sanctions from the USA, which is expected to strengthen collaboration between the two to mitigate the impact of sanctions and to counterbalance US influence in the Middle East and Asia.
In March 2021, China and Iran signed a 25-year strategic collaborative agreement to reinforce the countries’ economic and political alliance, particularly focusing on investment in Iran’s energy and infrastructure industry and assuring regular oil and gas supply to China. This is expected to further strengthen the relations between Iran and China.
China, the most trusted strategic ally of Iran and a significant lithium producer will likely act as a critical partner in building up Iran’s lithium industry. As the global leader in electric vehicle adoption (in absolute terms), the demand for lithium in China has increased dramatically in recent years. Also, China stands out as the only trade partner capable of accessing and refining lithium on a large scale. This will strengthen the Iran-China relations further.
High infrastructure costs and lack of FDI to challenge the Iranian mining sector
Despite the presence of a vast mining potential in the country, certain factors such as inadequate access to essential machinery and equipment, lack of exploration facilities, lack of sufficient infrastructure and investment, absence of advanced technologies, and shortage of financial resources limit the growth of the mining sector in Iran.
Lack of access to new cutting-edge production technologies, exacerbated by international sanctions, results in inefficient utilization of resources, particularly water, fuel, and electricity in mining operations. In addition, high production costs, mandatory pricing, and lack of skilled labor further pose obstacles in mining operations. This, together with the fact that the lithium extraction process is generally expensive and time-consuming, has led to various small and medium-sized mines opting to cease their operations.
The absence of foreign investment due to international sanctions poses challenges in conducting mining operations in the country. The government seeks to attract foreign investment in the mining sector, a difficult task amid structural challenges, human rights abuse accusations, and international sanctions.
Exploitation of lithium reserves discovered in the country will be difficult due to the lack of advanced technologies required for extraction, processing, and refining. The assessment of lithium grade and its economic feasibility will play a crucial role in determining whether to exploit the reserve.
EOS Perspective
The scale of lithium reserves discovered in Iran is significant, but the exploitation of the mineral is not likely to happen in the near future. Its viability, economic feasibility, actual quantity, and grade are yet to be ascertained. Also, the country does not have access to the necessary technologies required to process and refine lithium, so it has to rely on foreign investors.
Foreign investment in Iran is hindered by the sanctions imposed by the USA and the EU against Iran’s nuclear development program. Back in 2015, Iran agreed to scale down its nuclear program and allow broader access to international inspections to its facilities in return for billions of dollars in sanctions relief. But that ended in 2018 when the USA withdrew from the deal. With the recent agreement signed in 2023, there is hope that it could pave the way for the relaxation of sanctions on Iran.
Additionally, considering lithium’s pivotal role in multiple industries and concerns about China’s dominant power in the lithium supply chain, the US government might consider easing sanctions. EU is not likely to ease or lift sanctions and invest in Iran immediately due to uncertainties about the viability of the reserve, its impact on the environment during extraction, and lack of energy investments in the country. However, the EU may consider easing sanctions in the future if the USA moves in that direction.
Russia and China, having economic and diplomatic ties with Iran, are more likely to show interest in Iran’s lithium discovery. Russia is focusing on expanding its presence in the lithium market to meet the increasing demand for lithium in vehicles and energy storage systems. As a step in this direction, in December 2023, Rosatom, a Russian state corporation, signed a deal to invest US$450 million in Bolivia to construct a pilot lithium plant. Russia is also likely to explore investment opportunities in Iran’s lithium sector.
China is expected to benefit the most from the lithium discovery in Iran, considering its longstanding relations with Iran. At the same time, Iran is also more likely to be eager to collaborate with China, considering China’s strength in the lithium industry and international sanctions.
However, Iran should not solely rely on China, considering China’s track record of engaging in debt-trap diplomacy to exert influence and dependence, particularly over low-income countries. For instance, in 2013, China launched its infamous Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), under which it started funding and executing several infrastructure projects in developing and underdeveloped countries across the globe. However, over the years, the BRI initiative has been criticized for resulting in an increased dependence and trapping of the partner countries in heavy debt through expansive projects, non-payment of which may lead to a significant economic and political burden on them. A collaborative agreement spanning 25 years was also signed by China with Iran, primarily focusing on investing in Iran’s energy and infrastructure sectors, facilitating Iran’s involvement in the BRI. Iran could also fall into a similar debt trap, having no viable alternative partner, a fact that China can take advantage of.
Read our related Perspective: China’s BRI Hits a Road Bump as Global Economies Partner to Challenge It
Many countries are likely to be interested in investing and building strong collaboration with Iran if the reserves’ viability is confirmed and the grade and quality of lithium are suitable for use. This could change the entire dynamics of the lithium supply chain and also lead to a decrease in lithium prices, which have been skyrocketing due to a significant surge in global lithium demand.