Blockchain technology has captured the interest of several industries and aviation is no exception. Its decentralized, secure, and immutable nature makes blockchain technology ideal for many operational aspects and verticals within the aviation industry. In fact, most of the blockchain-based solutions in the aviation sector extend beyond basic financial transactions and range across security and identity management, ticketing, maintenance, baggage management, and loyalty programs. Various stakeholders in the aviation industry, including airlines, airports, aircraft manufacturers and maintenance providers, and airspace technology providers, etc., are partnering together to explore and develop blockchain-based capabilities across the industry’s value chain.
Blockchain technology is fast emerging as the revolutionary technology in the aviation industry with most airline and airport CIOs investing huge resources and effort in exploring this space. As per Air Transport IT Insights 2018 report by SITA, one of the world’s leading air transport communications and information technology company, about 60% airlines have invested in blockchain-based pilot projects or research programs for implementation by 2021. This shows an increase from 2017, when only 42% airlines invested in blockchain-based research programs. Moreover, airports are also exploring this technology, with 34% airports planning blockchain-based R&D projects by 2021.
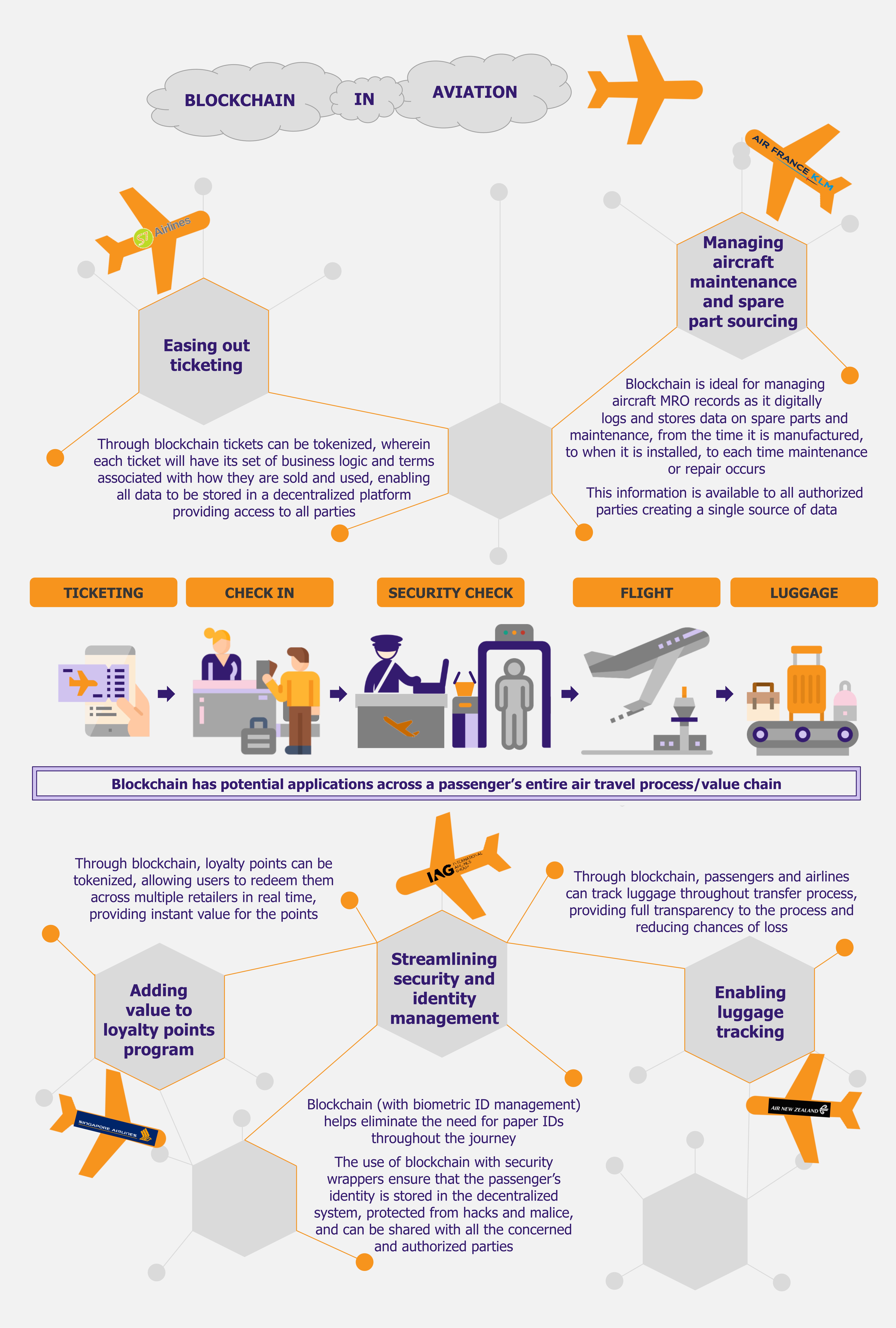
Owing to its decentralized, scalable, transparent, and secure nature, blockchain technology’s capabilities align well with the needs of the aviation sector, especially in the fields of ticketing, maintenance, luggage tracking, loyalty programs, and identity management.
Blockchain to streamline security and identity management
Passenger identity management is one of the most sought-after uses of blockchain in aviation. As per the SITA study, about 40% airlines and 36% airports claim passenger identity management to be one of the most prominent areas of application and benefit of blockchain technology.
Blockchain technology has the ability to streamline the identity management of passengers through the combined use of blockchain, biometrics, and mobile (or wearable devices). Currently, a passenger needs to pass several checkpoints where different parties (airport staff, airlines, control authorities, etc.) verify their physical IDs. This process is cumbersome, time consuming, and also vulnerable to human errors. Moreover, it results in a great amount of duplication of data as each stakeholder stores and verifies passenger information at their own level.
Blockchain, owing to its immutable, decentralized, and secure nature, helps solve these issues by validating identities using biometrics. Blockchain with security wrappers ensures that the information stored in the system is protected and helps share it with all the stakeholders through the use of authorized access protocols. Thus, blockchain and biometric-based ID management help eliminate the need for paper documentation (such as passport and visa) across the entire journey. This will facilitate a smoother and quicker travel experience for the passenger, as compared with the current verification and multiple checkpoints. Moreover, it will reduce security lapses as the need for paper documents (that can be forged) and human intervention is low.
Blockchain start-up Sho Card, which provides digital identification cards through blockchain, has partnered with SITA to develop a digital identity card as a proof of concept, wherein the traveler obtains a single travel token for his journey.
Under this concept, the traveler undergoes an initial check at the travel counter, where he is positively identified using biometrics and issued a travel token. A photo of the traveler is also taken for verification. This information (biometric ID information, travel token, photo) is stored on the travelers mobile or wearable device and replaces the requirement of any physical/paper identification. When the traveler approaches any gate or checkpoint, he presents the travel token via a QR code on the SITA traveler app. The agent at the checkpoint scans the QR code and validates the travel token and the individual matches to that in the photo. The traveler is allowed to pass if the information matches. This significantly reduces costs and time taken at several checkpoints for document validation. Moreover it reduces the human liability around documents check.
Other blockchain players, such as UK-based ObjectTech and VChain Technology, have also entered into agreements with Dubai’s Immigration and Visa Department and International Airlines Group (AIG), respectively, to provide blockchain-based solutions to streamline passenger data management for the aviation sector.
Blockchain and biometric-based ID management help eliminate the need for paper documentation (such as passport and visa) across the entire journey. This will facilitate a smoother and quicker travel experience for the passenger, as compared with the current verification and multiple checkpoints.
Smart contracts to ease out ticketing
Airlines currently sell paper-based or electronic tickets through their centralized ticketing system. For each booking, there are multiple touchpoints, which include airlines, travel agencies (online and offline), banks and card providers, and government agencies. Upon the sale of a ticket, each party stores passenger data at their individual level, which makes the process complex and vulnerable to errors. In addition, ticketing information being currently stored in a centralized database by airlines and airports makes it vulnerable to hacks and glitches, which in turn can result in reputation and revenue loss for the airlines or airport. This was seen in case of Southwest Airlines in July 2016, when the centralized ticketing database failed, resulting in the cancellation of about 2,000 flights and a revenue loss of US$82 million.
The use of blockchain-based smart contracts helps eliminate the need for paper tickets and e-tickets can be tokenized. Tokenized tickets can have their own set of embedded business logic and terms and conditions associated with how they are sold and used including pricing and timings for the flights. Moreover, further stipulations can be added to the ticket such as the class of the ticket, lounge access, etc. The decentralized nature of blockchain insulates it from hacking and system failures and also mitigates data sharing errors. Furthermore, it allows for the sale of tickets in real-time from different partners across the globe. It also improves customer experience and cost effectiveness of service by automating time consuming tasks, streamlining payment process, and reducing settlement times.
The use of blockchain-based smart contracts helps eliminate the need for paper tickets and e-tickets can be tokenized. Tokenized tickets can have their own set of business logic and terms and conditions associated with how they are sold and used including pricing and timings for the flights.
In July 2018, Russia’s second largest airline, S7 Airlines partnered with Russian commercial Bank, Alfa Bank, to build and sell its airline tickets over an ethereum-based private blockchain platform. The use of blockchain enabled the airlines to securely connect its online booking system with the bank’s payment processing systems, thereby speeding the payment processing time (from about two weeks to less than a minute) and reducing manual paperwork. In July 2019, the airline’s blockchain-based ticketing platform witnessed sales of US$1 million, indicating the success of the venture.
Blockchain to enable luggage tracking
One of the areas where airlines are constantly working on improving customer service and reducing costs is cargo and passenger baggage management. A passenger’s baggage passes through several automated and manual processes before being handed back to them and data about the cargo/luggage’s journey is usually stored in a non-standardized form on an individual level by multiple players that handle the cargo/luggage, including airlines personnel, transportation companies, airports, and local authorities.
This process results in passenger luggage being often lost or misdirected, a fact that impacts the airlines both in terms of reputation and cost. As per SITA’s Baggage Report 2018, this translated into additional costs of about US$2.3 billion for airlines in 2017.
Blockchain, which functions as an online record-keeping system maintained on a peer-to-peer network rather than a central agency or authority, can help airlines tackle the issues of lost luggage. Using blockchain, customers (and airlines) can track the luggage throughout its transfer process, which provides full transparency to the process. Thus if a bag is misplaced, the airlines can track back the entire journey of the lost luggage to identify the point where it went missing and why.
In November 2017, Air New Zealand partnered with Swiss-based start-up Winding Tree (which is a blockchain-based distribution platform for the travel industry), to explore applications based on blockchain technology that could help the carrier improve the efficiency and security of booking and baggage tracking services. The potential applications that Air New Zealand is looking to explore include cargo and baggage tracking, retail distribution, and loyalty program opportunities.
Another use of blockchain in baggage management is in determining lost baggage compensation. Through the use of smart contracts, airlines could automate insurance claims for lost baggage and instantaneously compensate customers. Rega, a blockchain insurance platform, has been deploying blockchain to create a “crowd-insurance” platform in which the risk of lost luggage is shared across the community. This works primarily as a peer-to-peer insurance that uses smart contracts and smart tokens to insure baggage for a group of passengers without the need for any insurance companies, agents, or intermediaries. Through this method, it has managed to reduce lost baggage premium to about US$12 annually for a coverage of up to US$5,000.
Blockchain to better manage maintenance history and spare parts sourcing
Flight maintenance is one of the largest cost-heads for an airline. As per IATA, in 2017, airlines globally spent US$76 billion on MRO (maintenance, repair, and overhaul), representing about 11% of total operational costs.
Currently, the MRO process is extremely complex, with the value chain encompassing multiple players such as manufacturers, component traders, airlines, service providers, and regulatory authorities. Moreover, each of these bodies store information in separate databases or physical ledgers. This makes obtaining information about components and maintenance extremely challenging and time consuming. Moreover, it can lead to data discrepancy (as it is stored at individual levels by the various parties), which in turn questions the reliability of this data and the safety of the component. In these cases, the worthiness of the component is established through an expensive and time consuming investigation, testing, and recertification process.
Blockchain’s decentralized, immutable, and transparent nature, makes it ideal for managing MRO records for airlines. Blockchain digitally logs and stores data regarding aircraft spare parts and maintenance, from the time the part is manufactured, to when it is installed, to every time maintenance or repair occurs. This decentralized, transparent, and real-time storage of data ensures that the information is available to all authorized parties (from airlines to MRO service providers) in a prompt and accurate manner, thereby saving on time and costs while achieving better safety and maintenance standards.
Blockchain’s decentralized, immutable, and transparent nature, makes it ideal for managing MRO records for airlines.
In addition, the use of blockchain enables airlines to engage in more predictive maintenance, by enabling technicians to review the complete configuration and history of the various components in the aircraft on a blockchain-based ledger. This helps them tackle issues in a preventive manner rather than taking action after a problem has occurred. Similarly, MRO providers can also use blockchain to offer predictive maintenance services to airlines, saving money for both themselves and the airlines.
Blockchain also helps in sourcing spare parts and removing middle men in the sourcing process. Currently, aircraft components are sourced from vendors or traders in a marketplace, who then further scout for the component with manufacturers or sometimes other traders/resellers. This process is expensive (due to multiple mark-ups) and time consuming and most of all, lacks transparency. To tackle this, various manufacturers, airlines, and MROs can create a blockchain-powered aerospace marketplace, where the buyers can share the serial number of the product needed, which in turn can be matched to the real-time ownership and location of the seller currently holding the product. This would eliminate the need for middle men in the industry and also save time and reduce costs especially in case of scarce parts.
In October 2017, Air France-KLM announced its plans to evaluate and develop a blockchain-based system to manage replacement parts on in-service airplanes and improve aircraft maintenance procedures and record keeping. Similarly, in August 2018, Russian airlines, S7, in association with Russian energy player, Gazprom Neft, announced the successful development and implementation of a blockchain-based system to refuel aircraft using smart contracts. The smart contracts will remove the need for pre-payment, bank guarantees, and will further insulate the parties from any unforeseen financial risks involved in the refueling process. This is expected to help reduce cost and also save time both for the airlines as well as their energy partner.
Blockchain to add value to airlines loyalty programs
Flyer loyalty programs, better known as frequent flyer miles, are an integral part of an airline’s customer engagement program. All airlines run a loyalty program, whether individually or as an alliance. However, in traditional loyalty programs travelers need to wait to accrue a certain amount of points to utilize them, with limitations on where and when they can use them. Loyalty programs for alliances have an even more complex structure when compared with stand-alone loyalty programs. This results in limited incentive for travelers to remain loyal to a certain airline(s), thereby defeating the purpose of frequent flyer programs.
Blockchain has the ability to streamline the frequent flyer programs, especially for alliances. By tokenizing loyalty points on the blockchain, travelers can obtain instant value for the points by redeeming them in real-time and across a great number of partnering merchants. Thus with points being accepted as a form of “currency” across a pool of merchants, travelers can use these points in a faster and more efficient manner, thereby remaining motivated to maintain loyalty with a particular airline(s).
In July 2018, Singapore Airlines was the first airline globally to launch a blockchain-based loyalty program for frequent flyers. Under this program, Singapore Airline members can convert their miles into units of payments which are stored in a digital wallet, called KrisPay. This digital wallet was developed by Singapore Airlines in partnership with KPMG and Microsoft. The airline has partnered with 18 merchants across Singapore (including eateries, gas stations, beauty parlors, etc.) where customers can use KrisPay units.
Blockchain initiatives
Considering the various applications of blockchain across the aviation sector, a great number of airlines and airspace technology providers are investing heavily to explore this space and develop blockchain-based solutions for various verticals.
In July 2018, Lufthansa airlines partnered with SAP to launch a global Aviation Blockchain Challenge in order to support blockchain R&D in the sector. Through this venture, the two companies are seeking ideas from entrepreneurs and blockchain start-ups with regards to enhancing passenger experience, improving airline operations, processes, and maintenance, and streamlining the aviation supply chain.
Similarly in July 2018, SITA, which is the air transport industry’s largest technology provider and is jointly owned by a large number of airlines, launched the Aviation Blockchain Sandbox project. Through the Sandbox project, the technology provider aims to achieve intra-industry collaboration to understand and explore the applications of blockchain in the aviation space and undertake cross-industry initiatives. This platform gives access to smart contracts known as FlightChain, which will help improve flight status data problem for airlines and airports by storing all flight information on the blockchain to provide consistent data across the network.
EOS Perspective
Blockchain technology has taken several industries by storm, and shows great potential in several others (read our previous publications: Blockchain Technology – Next Frontier in Healthcare?, Blockchain Paving Its Way into Retail Industry, and Blockchain: A Potential Disruptor in Car Rental and Leasing Industry to find out more). Aviation seems to be no exception. Although application of blockchain in the aviation industry still seems to be largely at the exploration stage (with most companies running proof of concepts and investing in testing phases), it definitely holds the potential to transform the way air travel is currently done.
Explore our other Perspectives on blockchain
That being said, blockchain cannot be seen as a universal remedy for all the issues faced by the aviation sector. To ensure that blockchain is used in the most efficient and cost effective manner, it is critical for players to have a solution-oriented approach when exploring blockchain-based applications, i.e. starting with a specific problem and working towards developing solutions, rather than making blockchain a solution and looking for problems to solve with it. With blockchain becoming the buzz word across the board, it is very common for companies to get carried away with the technology trying to fit in places, where its needs or costs are not justified. Considering that the technology is relatively new and has limited scalability at the moment, a lot of blockchain-solutions that may work well in theory may not be practical in today’s day and may need to wait for the blockchain technology to evolve further.
Moreover, for blockchain to be successfully applied across the industry, it is very important for the stakeholders to collaborate to develop blockchain solutions with regards to sharing data, technology, and costs related to R&D. This is also somewhat of a challenge as adoption of blockchain requires transparency and most companies are wary of sharing their data and information with external players.
Despite these challenges, the adoption of blockchain technology by the aviation sector seems more like a matter of “when”, rather than “if”. Most players in the aviation sector have been operating through traditional business practices for several decades now and may take time to embrace blockchain in mainstream operations. However, several players such as Lufthansa and Air France-KLM have started leading the way. With promises of cost savings and better services, it is to be seen if blockchain can enjoy a smooth landing in the aviation sector.