Scientists have been researching the possibility of using electrical impulses to treat many health conditions. The starting point was the introduction of the first TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) device in the 1970s in the USA. Its goal was to test the tolerance of chronic pain patients to electrical stimulation. In recent years, non-invasive neuromodulation has emerged as a promising field for treating various neurological disorders. This field will likely experience significant growth in the coming decade, thanks to technological advancements, such as AI-powered sophisticated wearables.
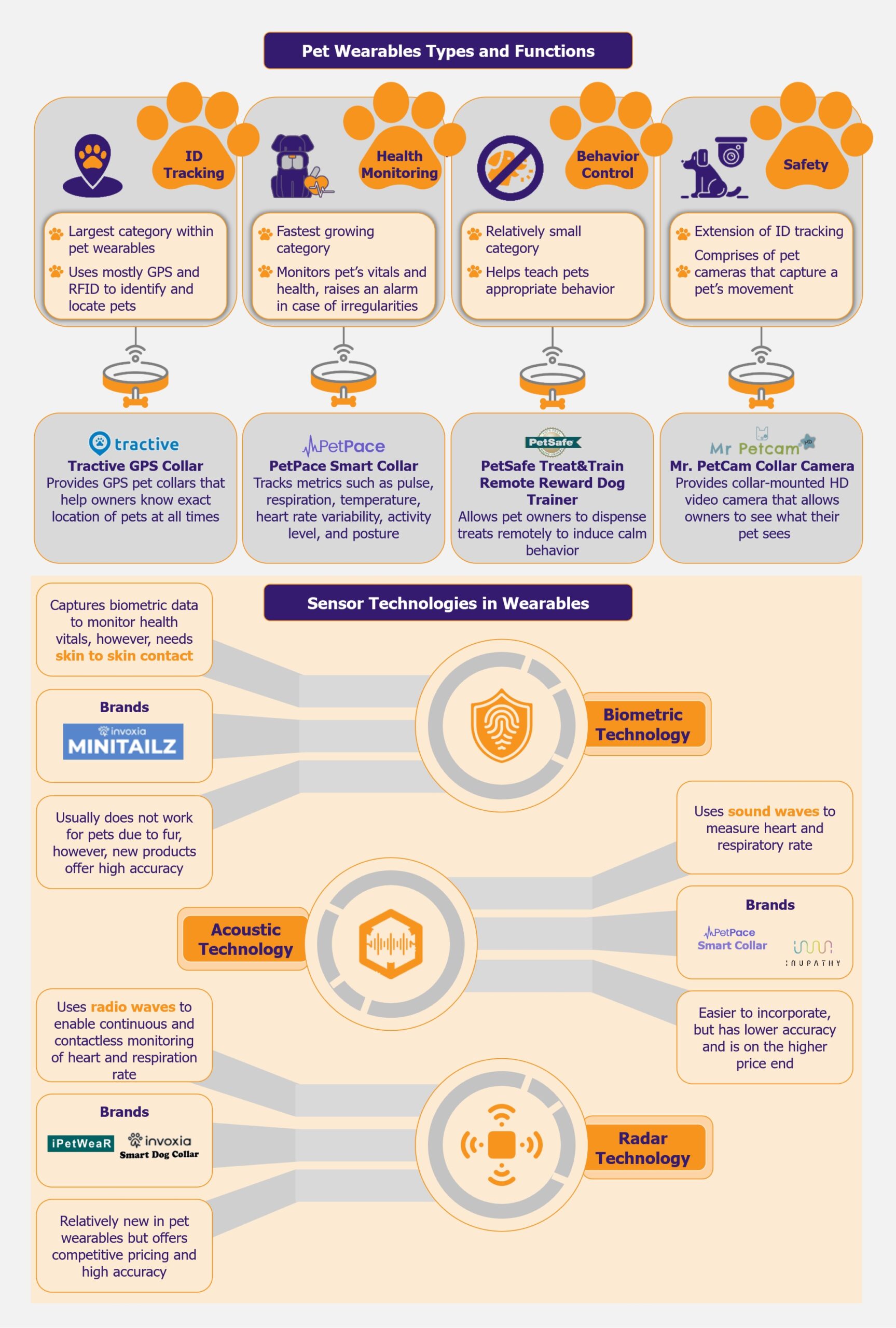
Non-invasive neuromodulation is emerging as a novel treatment for several diseases
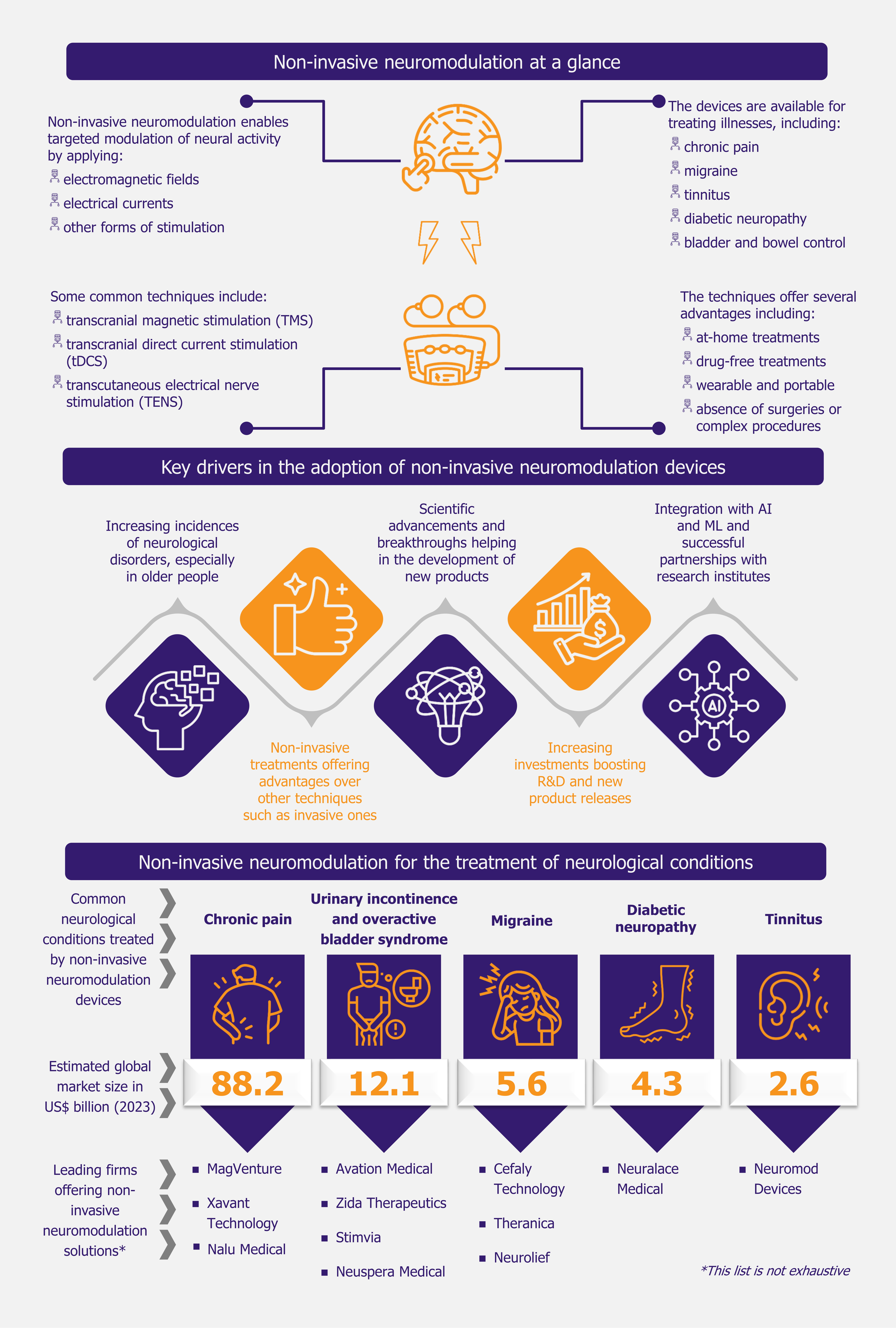
Non-invasive neuromodulation is a technique that uses external devices to apply electromagnetic fields, electrical currents, or other forms of stimulation to the brain to enable targeted modulation of neural activity.
The technique is effective in treating a range of conditions. Currently, several devices are available in the market for treating illnesses, including chronic pain, tinnitus, diabetic neuropathy, and functional disorders such as bladder and bowel control.
The non-invasive neuromodulation market encompasses a diverse array of devices that can modify neural activity without the need for invasive procedures. This includes transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), and TENS.
TMS therapy sessions typically require the presence of a physician. An example is MagVenture Pain Therapy, a TMS device developed by a Denmark-based company, MagVenture, for treating chronic pain.
TENS and tDCS devices are portable and, hence, suitable for at-home treatments. The FDA has not yet approved tDCS in the USA for medical use. However, its use falls under the Investigational Device Exception (IDA) regulations. Though it is marketed for non-medical uses in the USA, it is used for medical treatment in regions such as the EU, Singapore, and Israel.
TENS devices are small, battery-powered devices that consist of leads that connect to electrodes, sticky pads placed on the skin in the area that needs stimulation. An example is Cefaly, an FDA-approved TENS device developed by the US-based Cefaly Technology for pain management. This device works by stimulating and desensitizing the primary source of migraine pain, the trigeminal nerve, using a precise electrical impulse.
The non-invasive neuromodulation market is showing rapid growth
The global non-invasive neuromodulation devices market for neurological and psychiatric disorders was approximately US$1.2 billion in 2022. According to a 2023 report by Report Prime, an India-based market research firm, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.2% from 2023 to 2030, reaching US$2.1 billion by 2030.
Several reasons fuel this rapid growth in recent years, including the increasing prevalence of chronic pain and other neurological conditions (especially in older patients), the numerous advantages this technique has over invasive neuromodulation, breakthroughs in non-invasive technology, and a surge in investments.
Increasing incidence of neurological disorders is a major driver
The increasing incidence of debilitating disorders such as chronic pain, Parkinson’s disease, diabetic neuropathy, etc., is creating a pressing need for new and efficient treatments to address these conditions. A 2023 study by the CDC indicated that 20.9% of American adults suffered from chronic pain, and 6.9% experienced chronic pain that significantly limited their daily activities.
Similarly, Parkinson’s disease affects nearly 1 million people in the USA as of 2023, with this number expected to rise to 1.2 million by 2030. These statistics indicate a rising trend of neurological disease burden in the USA.
One major issue that many patients and physicians face is that the current treatments for many of these conditions fall short, leaving a significant gap in the care of patients. Typically, doctors treat people suffering from chronic pain, including that of diabetic neuropathy, using painkillers. Most patients develop medicine tolerance, experience drug-wearing-off effects, or suffer from severe side effects, diminishing the overall treatment effectiveness.
Some patients may even consider drastic and irreversible surgical procedures, such as nerve amputation, due to inadequate treatment results. However, even these may not always provide the desired relief. This indicates the need for a reliable and effective solution for managing the pain, discomfort, and other neurological symptoms associated with the primary disease.
As non-invasive neuromodulation stimulates the brain areas responsible for pain processing, it alters the patient’s perception of pain. With the growing incidence of neurological disorders, this desired neuromodulation effect will continue to be in high demand, contributing to the growth of the non-invasive neuromodulation devices market.
Non-invasive treatments offer advantages over other techniques
Typically, conditions such as chronic pain are treated using a combination of prescription medicines. However, these medications, including NSAIDs, opioids, etc., come with a variety of side effects, such as digestive issues, ulcers, drowsiness, etc. Long-term use of opioids can lead to a range of negative consequences, including the development of tolerance, physical dependence, and opioid use disorder, increasing the risk of overdose and death. Conventional treatment methods also need frequent hospital visits.
Invasive neuromodulation is an effective treatment option for various neurological conditions. However, it also carries significant risks, such as site infections, perioperative and postoperative complications, blood clots, and device malfunctions. Additionally, these techniques often require multiple hospital visits.
In contrast, non-invasive neuromodulation offers several advantages over invasive methods. These wearable devices provide drug-free treatments that do not require surgery or complex installation. As a result, they are easy for patients and physicians to use.
A comprehensive study about the efficacy of various non-invasive devices is not yet available. However, controlled individual studies by companies and developers have shown promising efficiency in treating various diseases.
Moreover, a 2019 report published in BMJ, a peer-reviewed medical journal, indicated that non-invasive neuromodulation offers a potential solution for patients who are sensitive to traditional treatments. This includes patient groups such as pregnant women, adolescents, and those who experience poor tolerability or lack of efficacy from pharmacological treatment therapies.
The need to treat health conditions of these patient groups may drive the use of non-invasive devices to treat health conditions.
Scientific advancements help improve efficacy and expand applications
The non-invasive neuromodulation field has seen several breakthroughs in recent years, showing promise for accelerated R&D and new and improved devices potentially entering the market in the future.
One example is the proprietary magnetic peripheral nerve stimulation (mPNS), marketed as Axon Therapy, developed in 2023 by US-based Neuralace Medical for managing painful diabetic neuropathy.
Another example is vibrotactile stimulation (VTS), currently under development by an interdisciplinary research team from the University of Minnesota as a treatment for spasmodic torticollis or cervical dystonia. This is a painful neurological condition that affects the neck. Though the product is not yet marketable, the clinical trials are showing significant promise.
VTS devices are also being developed for conditions other than pain. An example is the VTS glove, a wearable device developed by researchers at Stanford University and the Georgia Institute of Technology in 2024. The device applies high-frequency vibrations to the hands and fingers to relieve uncontrollable arm and hand spasms. In clinical trials, patients who used the device experienced significant improvements in symptoms, with some even reporting a reduction in their use of oral medications. The team is now working to develop the device further and make it available to patients as a publicly available therapy.
Furthermore, a new treatment for tinnitus, known as bimodal neuromodulation, which involves stimulating two sensory pathways in the brain, has been developed. Ireland-based company Neuromod offers the Lenire device, which combines headphones and a mouthpiece to deliver auditory and tactile stimuli to alleviate symptoms. Patients wear the device for an hour daily, for at least six weeks, to stimulate the tongue with electrical impulses while listening to tones.
These new developments are likely to give momentum to the ongoing R&D in the sector.
Increased investment signals growing market potential
The sector has also seen an uptick in investments. For example, Nalu Medical, a US-based company, secured US$65 million in funding in 2024 to advance its neurostimulation technology for treating chronic pain.
Similarly, Avation Medical, a US-based company focusing on treating bladder issues, raised over US$22 million in 2024 to launch the Vivally System. This wearable device treats patients with urge urinary incontinence (UUI) and overactive bladder (OAB) syndrome.
Massachusetts–based Cognito Therapeutics, a company focused on developing a new therapy for Alzheimer’s disease, raised around US$73 million in 2023.
This increasing trend in R&D investments shows investors’ rising interest in the field of non-invasive neuromodulation, indicating promising market prospects.
Integration with AI is expected to pave the way for future developments
Non-invasive neuromodulation is seeing considerable success in developing closed-loop systems that leverage artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to give customized therapeutic output. This trend is likely to see more growth, especially with the rapid advancements in the field of AI.
An example is Avation Medical’s Vivally System, a wearable neuromodulation device that uses closed-loop, autonomously adjusted electrical stimulation to treat patients with UUI and OAB syndrome. The device uses a smartphone app to calibrate itself for each patient and then delivers a constant current of electrical stimulation through a wearable garment. It also uses an advanced AI-powered closed-loop algorithm and electromyography (a medical test that measures the electrical signals sent by nerves to muscles and received back from them) to enable continuous real-time monitoring and therapy adjustment, ensuring uniformity and safety.
Non-invasive neuromodulation device companies are forming partnerships with research institutes to develop safe ways to treat various disorders using generative AI neuromodulation.
One such collaboration started in June 2024 between US-Swiss generative neuromodulation firm, Dandelion Science and Geneva-based research institute Wyss Center for Bio and Neuroengineering. The goal is to develop a generative AI neuromodulation platform for treating neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disorders.
Similar collaborations are likely to commence in the future, as it is clear that the combination of neuromodulation and AI is set to impact various treatment fields significantly.
Expansion of insurance coverage could boost treatment accessibility
Conventionally, chronic pain treatment involves a combination of drugs and physical therapy. The US patient usually pays 20% of their Medicare-approved amount. People with severe pain spend about US$7,700 on annual healthcare expenditures, and with insurance, they have to spend around US$1,600 annually. For the management of pain conditions such as migraine, the out-of-pocket expense can increase to 30% of their Medicare-approved amount.
Non-invasive neuromodulation treatment has proved to be more cost-effective than conventional treatments. Although many non-invasive pain management devices are not covered by insurance, some are eligible for reimbursement.
For instance, Nerivio, a wearable device for treating migraine, is covered by Medicaid and Highmark Insurance. Moreover, Theranica, Nerivio’s Israel-based parent company, introduced the Nerivio Savings Program in October 2020 to help US patients access the device. It is a reimbursement plan that allows patients to receive their first device for a copay of up to US$49 (for 18 treatments), depending on their insurance coverage. The refill costs US$89 for those without insurance.
Additionally, patients may be able to use Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) or Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) to pay for specific approved devices. An example is Cefaly, for which, though not covered by insurance in the USA, consumers can use HSA and FSA funds or finance their purchase with Affirm (a US-based financial technology company that offers flexible payment options) for US$36 per month upon qualifying. Without insurance or other financial aid, the upfront cost varies from US$330 to US$430, and an additional US$25 for three reusable electrodes, each usable up to 20 times each.
Non-invasive neuromodulation devices’ high upfront cost remains the key barrier to broader adoption
Overall, non-invasive neuromodulation devices offer a more cost-effective option than other treatments. The most significant barrier for patients opting for non-invasive neuromodulation is the high upfront cost, especially with no insurance coverage.
For example, Israel-based Zida Therapeutics’ Zida Control Sock, a device to treat urinary incontinence, comes with an upfront cost of US$750. Without insurance, many people may find it challenging to cover this cost. This is particularly true for older adults whom conditions such as chronic pain and urinary incontinence affect the most. According to 2023 data released by the US Census Bureau, 14.1% of Americans aged 65 and older live in poverty, making these devices less accessible to them without insurance coverage.
However, this situation may improve as several companies are now in talks to receive insurance coverage for their devices. With an increase in R&D, companies can also offer robust evidence to demonstrate the effectiveness and long-term safety of the devices, prompting insurance companies to provide coverage.
With reimbursement available for companies such as Theranica and Zida, and with several other companies such as Neurovalens planning to enter discussions with insurance providers to achieve reimbursement status, the accessibility has a chance to improve in the near future. This will likely drive adoption in the coming years.
EOS Perspective
Adopting non-invasive devices will likely increase as a standalone treatment and adjunct therapy. While non-invasive treatments currently focus on conditions such as chronic pain, tinnitus, urinary incontinence, etc., experts believe that this will soon expand into other neurological conditions, including ALS, and Parkinson’s disease.
Currently, there are only seven FDA-approved drugs for ALS treatment, all of them with limited effectiveness. The significant unmet need in this field presents a compelling opportunity for non-invasive neuromodulation companies. PathMaker Neurosystems is among the few companies conducting feasibility studies and developing non-invasive neuromodulation treatment options for ALS patients.
Research is also underway to develop a non-invasive treatment for Parkinson’s disease, which was previously treated using invasive techniques. Czech Republic-based STIMVIA has reported promising results from its initial pilot study of a new treatment for patients with Parkinson’s disease as an add-on therapy.
Several new non-invasive devices are also in the development pipeline, and their clinical trials are promising. An example that has shown positive results in a pivotal trial is a treatment for improving upper limb function by Netherlands-based ONWARD Medicals.
Non-invasive neuromodulation has the potential to revolutionize the treatment of chronic pain and other neurological disorders. As the field continues to evolve, with advancements in AI-powered wearables and increased investment in R&D, we can expect to see even more innovative solutions emerge in the coming years.