The rising prevalence of diabetes in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) underscores the need for advanced diabetes management solutions. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems are highly valuable but face limited adoption in LMICs due to high costs, infrastructure inadequacies, issues with accessibility, affordability, and limited insurance coverage. On the other hand, these countries offer opportunities to develop scalable CGM solutions tailored to the needs of LMICs and to penetrate these markets.
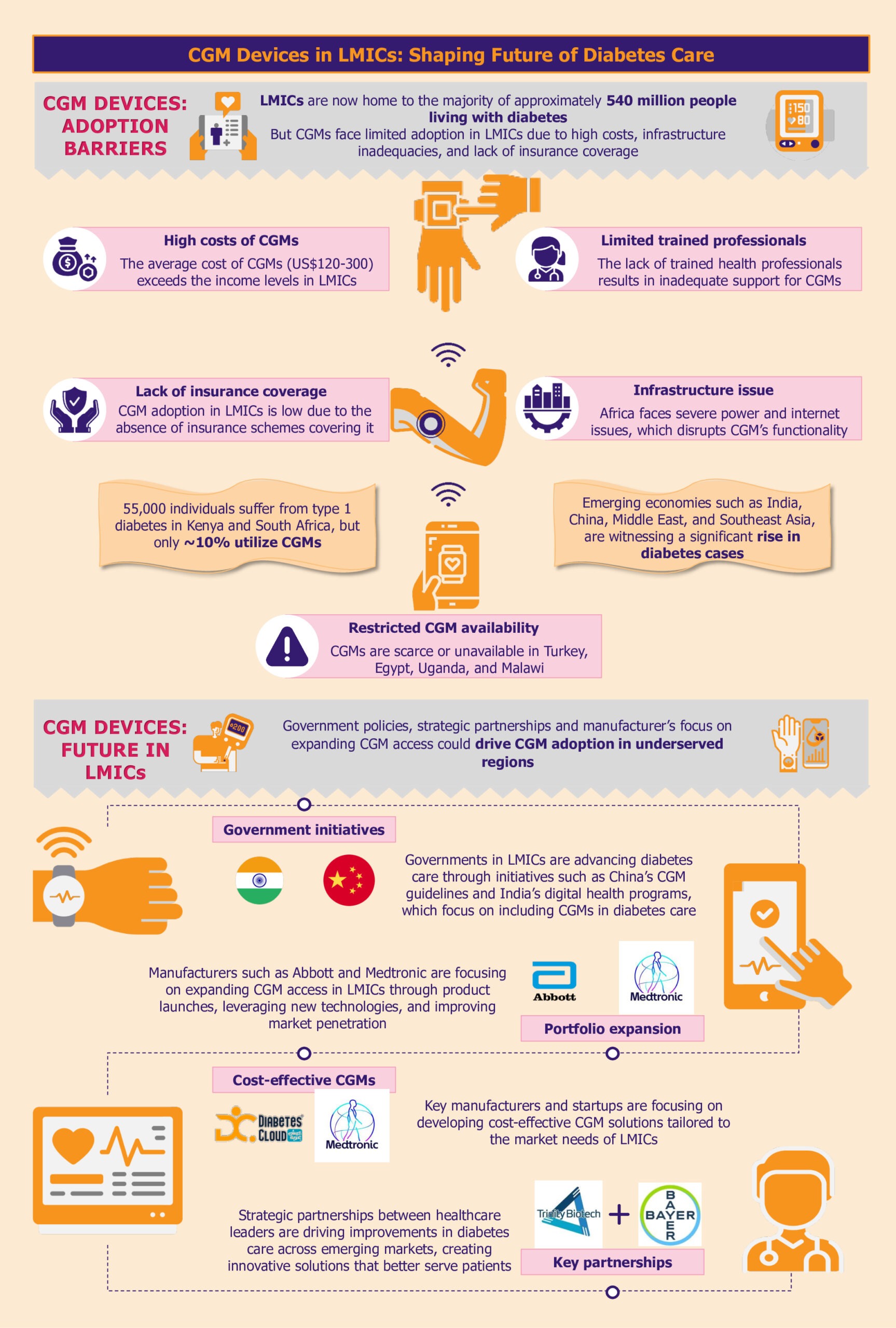
Over the past decade, the global prevalence of diabetes has surged, with a notable concentration in LMICs, particularly across India, China, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia. The LMICs now host the majority of nearly 540 million people living with diabetes.
Read our related Perspective:
The Future of Diabetes Care: Key Innovations in Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Effectively managing diabetes in LMICs is crucial and requires advanced solutions for precise and consistent monitoring of blood glucose levels. However, the CGM adoption rate remains low in developing and underdeveloped countries. As LMICs seek to incorporate these advanced solutions into their healthcare systems, they face numerous challenges.
Why is CGM adoption and acceptance lagging in emerging economies?
CGM systems are a revolutionary diabetes management tool. Despite the critical role it plays in advancing diabetes care, the high cost, uneven distribution, and inadequate infrastructure severely restrict their access, particularly in LMICs.
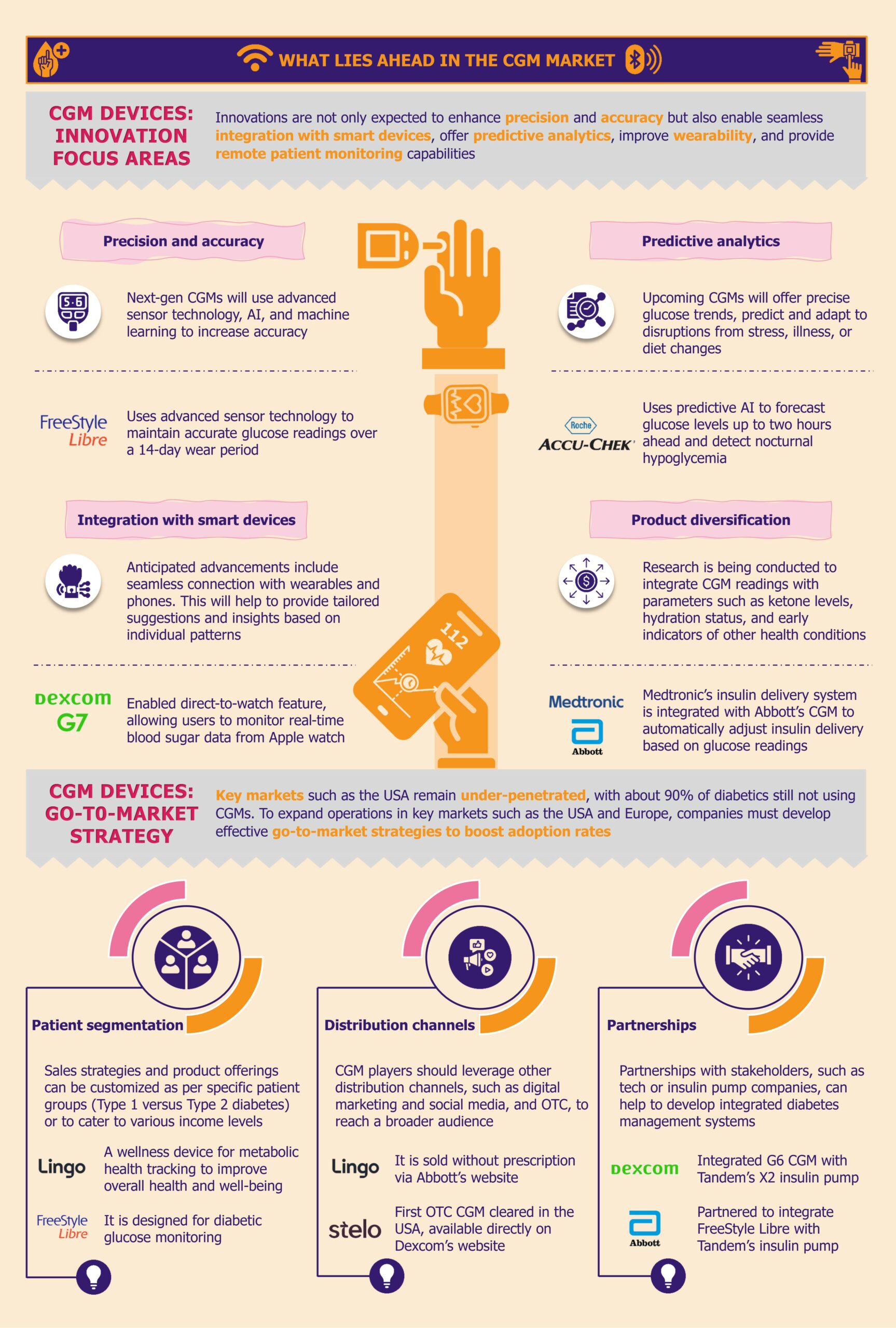
High costs hinder CGM adoption
A substantial barrier to adopting CGM systems in LMICs is their prohibitive cost. The average cost of CGM systems can be between US$120 and US$300 per month, placing them predominantly within the realm of those who can pay out of pocket.
For instance, the Dexcom G6 system, which includes sensors and transmitters, costs approximately US$300-US$350 per month. This price makes it out of reach for most individuals in LMICs, where average incomes are significantly lower.
As highlighted by a 2023 report by FIND, while an estimated 55,000 individuals live with type 1 diabetes in Kenya and South Africa, only about 10% are currently utilizing CGM systems. Many LMICs do not have subsidized healthcare or insurance coverage systems, which makes the situation worse. Consequently, the high cost of these devices creates a significant affordability gap, further entrenching healthcare inequalities.
In countries such as Iran, Lebanon, and Pakistan, the absence of governmental support and the unavailability of CGM technology highlight a broader issue. In many of these countries, private sector’s efforts are underway to bring diabetes-related innovations to the market, but the high costs associated with these technologies are a major obstacle.
Limited availability of CGM systems impedes diabetes management
In addition to high costs, the availability of CGM systems is another pressing issue. In many LMICs, including countries such as Turkey, Uganda, and Malawi, CGM solutions are either scarce or completely unavailable. This lack of availability limits access to advanced diabetes management technologies, crucial to improving health outcomes.
Similarly, In Egypt, where diabetes prevalence is notably high at 18.4% of the total adult population, the situation is equally challenging. The country lacks access to the latest innovations, while healthcare professionals need training in using CGM.
In LMICs, inadequate infrastructure poses a significant barrier to the widespread adoption of CGM devices. These tools rely on consistent power and internet connectivity to function optimally. However, frequent power outages, a common issue in many LMICs, can disrupt the continuous monitoring process, leading to data gaps and potential risks for patients who depend on CGM alerts for their health management.
Moreover, limited internet access, especially in rural areas, can severely impact the real-time data-sharing capabilities of CGM systems. This is particularly evident in African nations such as Niger, Nigeria, Chad, and South Africa, where infrastructure challenges are more pronounced.
For instance, South Sudan, with one of the lowest Infrastructure Index ratings in the region, faces critical limitations in accessing reliable power and internet services. These infrastructural deficits highlight the urgent need for targeted investments and solutions to bridge the infrastructure gap and enhance diabetes care in these regions.
Insurance coverage gaps stifle CGM access
The accessibility of diabetes management technologies, particularly CGM systems, is significantly hindered by inadequate insurance coverage and reimbursement policies.
This gap is especially noticeable in Asian LMICs such as the Philippines, where the healthcare system often does not include comprehensive coverage for these critical tools, placing a substantial financial burden on patients. In Vietnam, the National Health Insurance (NHI) scheme covers essential treatments such as oral antidiabetic medicines and insulin. However, it does not extend to glucose monitoring products. This lack of coverage forces patients to pay out-of-pocket for CGM, making it challenging for many to access.
What lies ahead for CGM in LMICs?
As diabetes increasingly poses a global health challenge, LMICs are ramping up efforts to enhance diabetes care. Progressive government policies, innovative programs, and manufacturers expanding reach across LMICs support this shift.
Government policies facilitating CGM integration with diabetes management
In many LMICs, government agencies and organizations are slowly working towards integrating advanced diabetes management solutions into healthcare infrastructure. This is visible through various initiatives undertaken that highlight the growing importance of CGM technologies.
For instance, the Chinese government demonstrated its commitment to standardizing CGM practices by issuing the Chinese Clinical Guidelines for CGM in 2009, with subsequent updates in 2012 and 2017. These guidelines establish clear protocols for device operation, data interpretation, and patient management. The guidelines also support training of healthcare professionals, improving quality assurance, and facilitating CGM integration into the national healthcare system. In several Chinese hospitals, the implantation, operation, and daily management of CGM systems are already handled by trained nurses and head nurses within the endocrinology departments.
India has also made significant strides, particularly in 2021, with the establishment of guidelines for optimizing diabetes management through CGM. The Indian government has introduced several initiatives to foster digital health advancements, including the National Digital Health Mission.
Advancing diabetes care, the ‘Access to CGMs for Equity in Diabetes Management’ initiative, a collaboration between the International Diabetes Federation and FIND, aims to integrate CGM solutions into African healthcare systems. This initiative seeks to double the number of CGM users in Kenya and South Africa by 2025, potentially impacting 21.5 million individuals with type 2 diabetes and 213,000 individuals with type 1 diabetes in Southern and Eastern Africa.
Government support for such initiatives is pivotal, as it can significantly enhance market access and ensure that CGM technologies reach underserved populations. These collaborative efforts and governmental actions are likely to drive extensive market reach and foster a more effective response to the global diabetes epidemic.
Manufacturers driving adoption by introducing affordable CGM solutions
Customizing CGM to meet the needs of LMICs offers manufacturers an opportunity to expand device access and adoption within these markets.
Medtronic is taking the lead by customizing its CGM solutions to reduce production and distribution costs specifically for LMIC markets. By optimizing its technology to be more cost-effective, Medtronic aims to increase the accessibility of its CGM systems in regions where diabetes management tools are often limited.
Similarly, emerging startups such as Diabetes Cloud (Aidex) and Meiqi are making strides in expanding CGM availability in South Africa. These companies are introducing more affordable CGM devices designed to meet the needs of local populations, thereby broadening access to critical diabetes management tools.
Manufacturers’ strategic initiatives accelerating CGM access
Manufacturers recognize the urgent need for effective diabetes care solutions in LMICs and the significant growth potential in the underpenetrated CGM market. To capitalize on this opportunity, they are focusing on expanding their product portfolios in these regions.
Additionally, Dexcom is planning to introduce the Dexcom ONE+ across the Middle East and Africa in the near future. This advanced CGM system can be worn in three locations on the body, enhancing comfort and usability. By accommodating individual preferences and needs, Dexcom aims to improve user experience. This strategic launch underscores Dexcom’s commitment to broadening its market presence and advancing its footprint in emerging regions.
Manufacturers are also supporting research initiatives across Africa. For instance, Abbott has donated its FreeStyle Libre Pro CGM devices for research in Uganda. The research’s favorable reviews and positive outcomes reflect a notable interest in and demand for sophisticated diabetes management technologies in these regions.
Moreover, strategic partnerships amongst manufacturers highlight a broader commitment to enhance the accessibility of CGM systems by leveraging combined expertise and innovative technologies. In January 2024, Trinity Biotech and Bayer partnered to introduce a CGM biosensor device in China and India. The collaboration is poised to leverage Bayer’s expertise and Trinity Biotech’s technological advancements to enhance diabetes care in these rapidly growing markets.
These strategic initiatives will likely impact the CGM market positively in emerging economies. Increased availability of CGM systems in LMICs will to drive higher adoption of glucose monitoring technologies and stimulate further investment in diabetes care.
EOS Perspective
Despite the challenges, the CGM market in LMICs presents a compelling growth opportunity for manufacturers. With diabetes cases on the rise, there is an increasing demand for CGM systems that offer real-time glucose data to improve patient outcomes. This demand, combined with progressive government initiatives and heightened awareness of diabetes care, creates a fertile ground for market development.
Manufacturers have a significant opportunity to capitalize on this emerging market by addressing the distinct regional needs. One of the primary challenges is the high cost of CGM systems, which limits their adoption. Hence, there’s a need to develop more affordable, scalable solutions tailored to the economic realities of LMICs. By focusing on local manufacturing and distribution strategies, healthcare companies can provide cost-effective solutions that meet the needs of underserved populations.
The shortage of trained healthcare professionals further complicates the widespread use of CGM. Manufacturers can address this by implementing comprehensive training programs for healthcare providers, equipping them with the skills needed to support patients in using CGM systems effectively.
This investment could foster greater acceptance of the technology. Non-profit organizations such as Medtronic LABS have made significant contributions, impacting over 1 million individuals with diabetes and training more than 3,000 healthcare workers across Kenya, Tanzania, Rwanda, Ghana, Sierra Leone, and India since 2013. The organization educates on diabetes management, equipping healthcare workers with skills to utilize CGM systems effectively. By enhancing the knowledge and capabilities of these health workers, Medtronic LABS ensures that communities receive better support in managing diabetes, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and CGM adoption.
Strategic partnerships with local entities, governments, NGOs, and international organizations can further enhance market reach. Collaborations can help manufacturers navigate the complexities of the market, overcome logistical challenges, and strengthen distribution networks. Partnering with organizations with established connections and regional expertise can facilitate more effective market entry and expansion.
For instance, organizations such as FIND, the International Diabetes Federation, and the Helmsley Charitable Trust are working to create business opportunities for CGM manufacturers. They specifically target manufacturers whose CGM products are unavailable in markets such as Kenya and South Africa to improve access in these regions.
Further, programs such as the Access to CGMs for Equity in Diabetes Management and national health guidelines in countries such as China and India are laying the groundwork for improved diabetes care. By integrating CGM solutions into national healthcare plans and providing necessary training to healthcare professionals, these initiatives aim to establish a sustainable model for diabetes management. Other developing regions should replicate this approach.
In the future, sustained emphasis on innovation, affordability, and strategic collaborations are poised to transform the CGM landscape in LMICs, ensuring that these advancements are more accessible to all. As this gains traction, access to advanced diabetes management technologies is expected to improve, offering a promising outlook for millions of individuals living with diabetes.