In the first part of our series on agritech in Africa, we took a look into how IT and other technology investments are helping small farmers in Africa. In the second part, we are exploring the impact that potential application of advanced technologies such as blockchain can have on the African agriculture sector.
Blockchain, or distributed ledger technology, is already finding utility across several business sectors including financial, banking, retail, automotive, and aviation industries (click here to read our previous Perspectives on blockchain technology). The technology is finding its way in agriculture too, and has the potential to revolutionize the way farming is done.
This article is the second part of a two-piece coverage focusing on technological advancements in agriculture across the African continent.
Read part one here: Agritech in Africa: Cultivating Opportunities for ICT in Agriculture
State of blockchain implementation in agriculture in Africa
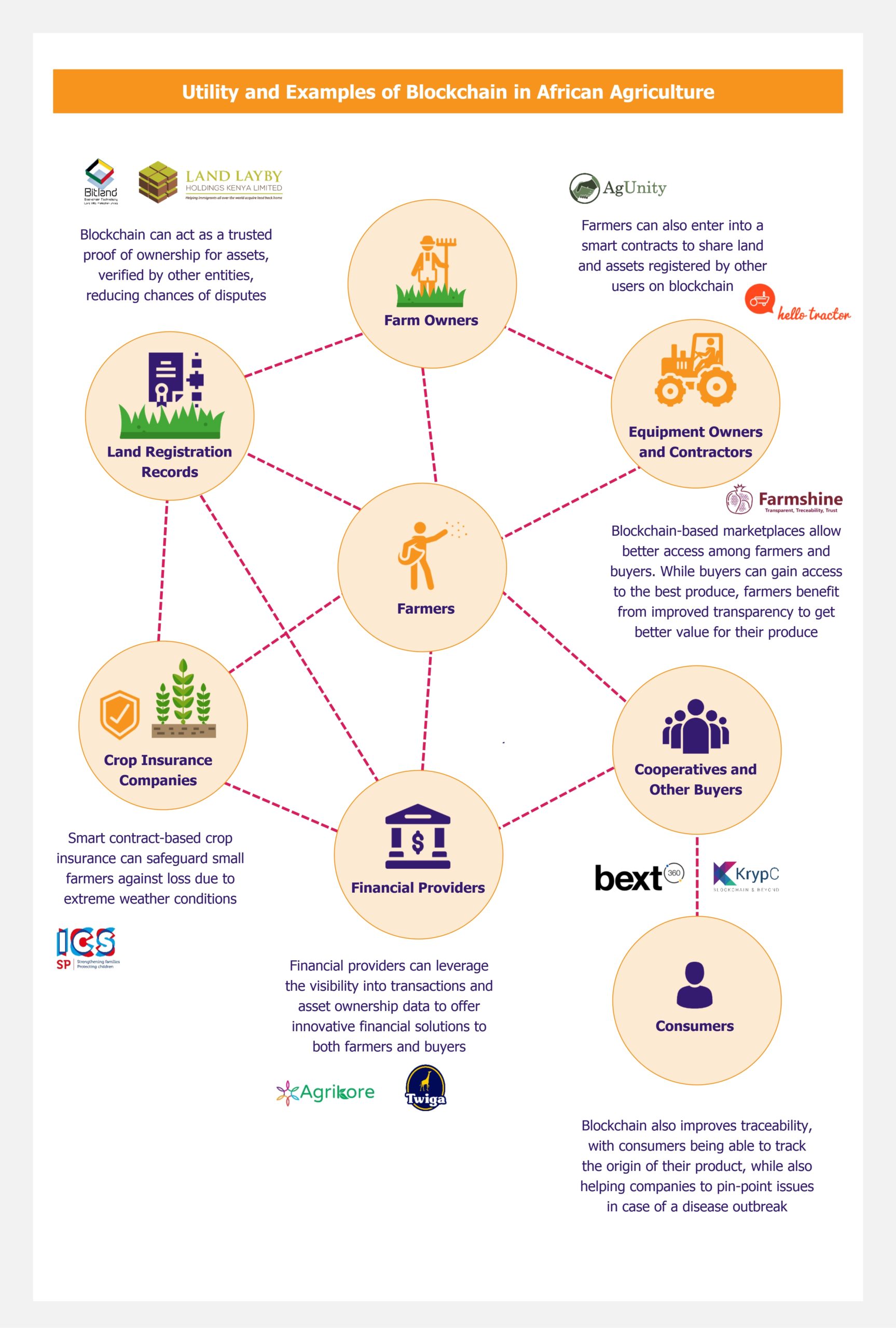
Agricultural sector in Africa has already witnessed the onset of blockchain based solutions being introduced in the market. Existing tech players and emerging start-ups have developed blockchain solutions, such as eMarketplaces, agricultural credit/financing platforms, and crop insurance services. Companies, globally as well as within Africa, are harnessing applications of blockchain to develop innovative solutions targeted at key stakeholders across the food value chain.
Blockchain to promote transparency across agriculture sector
The most common application of blockchain in any industry sector (and not only agriculture) is creating an immutable record of transactions or events, which is particularly helpful in creating a trusted record of land ownership for farmers, who are traditionally dependent on senior village officials to prove their ownership of land.
Since 2017, a Kenyan start-up, Land LayBy has been using an Ethereum-based shared ledger to keep records of land transactions. This offers farmers a trusted and transparent medium to establish land ownership, which can then further be used to obtain credit from banks or alternative financing companies. BanQu and BitLand are other examples of blockchain being used as a proof of land ownership.
This feature of blockchain also enables creation of a transparent environment where companies can trace the production and journey of agricultural products across their supply chain. Transparency across the supply chain helps create trust between farmers and buyers, and the improved visibility of prices further down the value chain also enables farmers to get better value for their produce.
In 2017, US-based Bext360 started a pilot project with US-based Coda Coffee and its Uganda-based coffee export partner, Great Lakes Coffee. The company developed a machine to grade and weigh coffee beans deposited to Great Lakes by individual farmers in East Uganda. The device uploads the data on a blockchain-based SaaS solution, which enables users to trace the coffee from its origin to end consumer. The blockchain solution is also used to make payments to the farmers based on the grade of their produce in form of tokens.
In 2017, Amsterdam-based Moyee Coffee also partnered with KrypC, a global blockchain, to create a fully blockchain-traceable coffee. The coffee beans are sourced from individual farmers in Ethiopia, and then roasted within the country, before being exported to the Netherlands.
This transparency can help food companies to isolate the cause of any disease outbreak impacting the food value chain. This also allows consumers can be aware of the source of the ingredients used in their food products.
Blockchain-based platforms to improve farmer and buyer collaboration
Blockchain can also act as a platform to connect farmers with vendors, food processing, and packaging companies, providing a secure and trusted environment to both buyers and suppliers to transact without the need of a middleman. This also results in elimination of margins that need to be paid to these intermediaries, and helps improve the margins for buyers.
Farmshine, a Kenyan start-up, created a blockchain-based platform to auger trade collaboration among farmers, buyers, and service providers in Kenya. In January 2020, the company also raised USD$250,000 from Gray Matters Capital, to finance its planned future expansion to Malawi.
These blockchain platforms can also be used to connect farmers to other farmers, for activities such as asset or land sharing, resulting in more efficiency in economical farming operations. Blockchain platform can also enable small farmers to lease idle farms from their peers, thereby providing them with access to additional revenue sources, which they would not be able to do traditionally.
AgUnity, an Australian-start-up established in 2016, developed a mobile application which enables farmers to record their produce and transactions over a distributed ledger, offering a trusted and transparent platform to work with co-operatives and third-party buyers. The platform also enables farmers to share farming equipment as per a set schedule to improve overall operational and cost efficiency. In Africa, AgUnity has launched pilot projects in Kenya and Ethiopia, targeted at helping farmers achieve better income for their produce.
A Nigerian start-up, Hello Tractor uses IBM’s blockchain technology to help small farmers in Nigeria, which cannot afford tractors on their own, to lease idle tractors from owners and contractors at affordable prices through a mobile application.
Smart contracts to transform agriculture finance and insurance
Less than 3% of small farmers in sub-Saharan Africa have adequate access to agricultural insurance coverage, which leaves them vulnerable to adverse climatic situations such as droughts.
Smart contracts based on blockchain can also be used to provide crop-insurance, which can be triggered given certain set conditions are met, enabling farmers to secure their farms and family livelihood in case of extreme climatic events such as floods or droughts.
SmartCrop, an Android-based mobile platform, provides affordable crop insurance to more than 20,000 small farms in Ghana, Kenya, and Uganda through blockchain-based smart contracts, which are triggered based on intelligent weather predictions.
Netherlands-based ICS, parent company of Agrics East Africa (which provides farm inputs on credit to small farmers in Kenya and Tanzania) is also exploring a blockchain-wallet based saving product, “drought coins”, which can be encashed by farmers depending on the weather conditions and forecasts.
Tracking of assets (such as land registries) and transactions on the blockchain can also be used to verify the farmers’ history, which can be used by alternative financing companies to offer loans or credits to farmers – e.g. in cases when farmers are not able to get such financing from traditional banks – transforming the banking and financial services available to farmers.
Several African start-ups such as Twiga Foods and Cellulant have tried to explore the use of blockchain technology to offer agriculture financing solutions to small farmers in Africa.
In late 2018, Africa’s leading mobile wallet company, Cellulant, launched Agrikore, a blockchain-based digital-payment, contracting, and marketplace system that connects small farmers with large commercial customers. The company started its operations in Nigeria and is exploring expansion of its business to Kenya.
In 2018, Kenya-based Twiga Foods (that connects farmers to urban retailers in an informal market) partnered with IBM to launch a blockchain-based lending platform which offered loans to small retailers in Kenya to purchase food products from suppliers listed on Twiga platform.
Read our previous Perspective Africa’s Fintech Market Striding into New Product Segments to find out more about innovative fintech products for agriculture and other sectors financing in Africa
And last, but not the least, blockchain or cryptocurrencies can simply be used as a mode of payment with a much lower transaction fee offered by traditional banking institutions.
Improving mobile internet access to boost blockchain implementation
While blockchain has shown potential to transform agriculture in Africa, its implementation is limited by the lack of mobile/internet access and technical know-how among small farmers. As of 2018, mobile internet had penetrated only 23% of the total population in Sub-Saharan Africa.
However, the GSM Association predicts mobile internet penetration to improve significantly over the next five years, to ~39% by 2025. Improved access to internet services is expected to boost the farmers’ ability to interact with the blockchain solutions, thereby increasing development and deployment of more blockchain-based solutions for farmers.
EOS Perspective
Agritech offers an immense opportunity in Africa, and blockchain is likely to be an integral part of this opportunity. Blockchain has already started witnessing implementation in systems providing proof of ownership, platforms for farmer cooperation, and agricultural financing tools.
Unlike Asian and Latin American countries, African markets have shown a relatively positive attitude towards adoption of blockchain, a fact that promises positive environment for development of such solutions.
At the moment, most development in blockchain agritech space is concentrated in Kenya, Nigeria, Uganda, and Ghana. However, there is potential to scale up operations in other countries across Africa as well, and some start-ups have already proved this (e.g. Farmshine was able to secure the necessary financing to expand its presence in Malawi). Other companies can follow suit, however, that would only be possible with the help of further private sector investments.
Still in the nascent stages of development, blockchain solutions face an uncertain future, at least in the short term, and are dependent on external influences to pick up growth they need to impact the agriculture sector significantly. However, once such solutions achieve certain scalability, and become increasingly integrated with other technologies, such as Internet of Things and artificial intelligence, blockchain has the capability of completely transform the way farming is done in Africa.