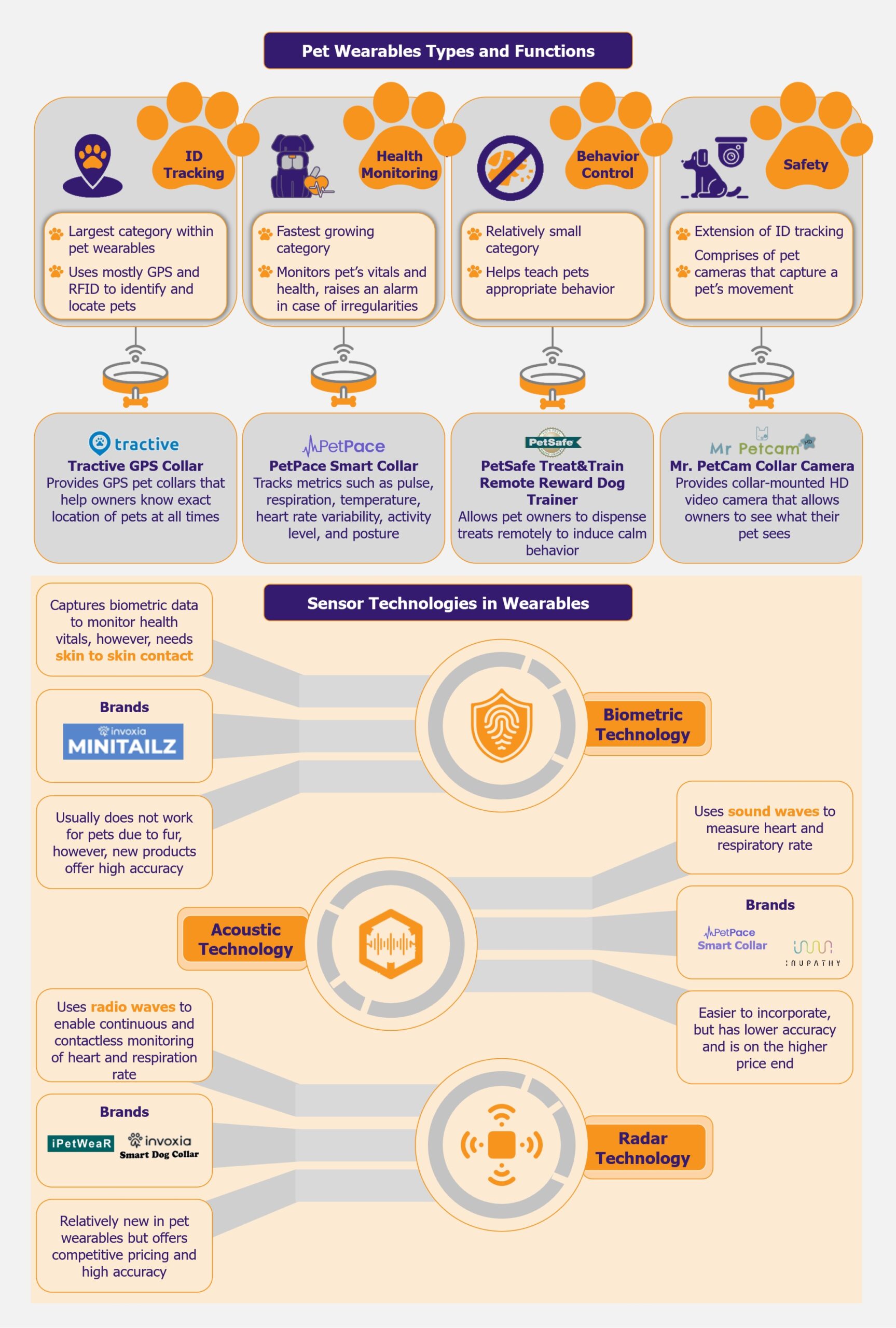
Vietnam possesses a vast potential capacity for wind and solar energy generation of approximately 1,000 GW. Its 3,000 km coastline also offers a chance to build a strong position in global offshore wind. It has taken several steps in its transition to clean energy, with renewable energy capacity growing approximately 8.5 times between 2018 and 2023. The country has committed to reaching net-zero carbon emissions by 2050. Meeting that goal requires both a rapid increase in renewable energy capacity and a strong policy framework. This transition could serve as a potential roadmap for other Southeast Asian countries, which are also embarking on their own journey toward renewable energy.
Vietnam’s FiT policy has fast-tracked renewable energy development
Vietnam’s leading position in the Southeast Asia renewable energy market is largely a result of its progressive and flexible policy framework. The government’s Power Development Plan 2021 to 2030 (PDP8) marked a clear shift from coal to renewable energy sources, especially solar and wind. The feed-in tariffs (FiTs) policy for solar energy proved to be the key driver for increased investment, with the country moving swiftly towards clean energy adoption.
Moreover, Vietnam’s quick decisiveness in introducing FiT enabled energy producers to sell the output for a fixed price over a fixed period. The FiT policy provided a jump start to Vietnam’s renewable projects. It led to a high foreign and domestic investment inflow, pumping US$11.3 billion into the clean energy sector between 2019 and 2021.
The policy has been instrumental to the country’s 25-fold growth in renewables installed capacity. However, after an initial success, the FiT model currently faces significant challenges with grid infrastructure, congestion, and inflated energy costs. As a result, this has led to a need for a dynamic and cost-effective pricing mechanism tailored to the requirements of various renewable projects.
The DPPA framework is crucial for advancing Vietnam’s clean energy transition
Regulatory reforms have further accelerated this shift by simplifying the licensing process. They also introduced mechanisms such as the Direct Power Purchase Agreement (DPPA) that opened up the energy market to local and foreign investors.
The 2024 DPPA policy framework marks an important milestone in Vietnam’s transition to clean energy and attracting FDI. The policy enables large energy consumers to purchase power from renewable energy producers directly, bypassing the state-owned energy operator, Vietnam Electricity (EVN). DPPA policy mobilizes the private sector to fill the gaps left by EVN, which has struggled to meet the energy demands across various consumer segments.
The framework will likely play a pivotal role by laying clear pathways for multinational manufacturers and service companies in Vietnam to speed up their complete transition to using clean energy and improve sustainability practices.
DPPA boosts tech investment and corporate sustainability in Vietnam
Vietnam’s Ministry of Industry and Trade’s 2023 survey revealed that 5,609 MW of capacity was ready for exchange through DPPA that year. Multinational companies with a long-established presence in Vietnam were looking to purchase electricity directly from the energy producers. Companies such as Nike, Samsung, and LEGO, operating in electronics, textiles, semiconductors, and consumer segments, were among the first to be interested in the direct purchase mechanism.
Further, in a separate but complementary development, Vietnam’s new telecommunication law, which came into effect in July 2024, allowed foreign companies 100% ownership of certain services, including data centers and cloud computing services. This presents an attractive investment and strategic prospect for tech giants such as Google, Apple, and Microsoft.
This supportive legislative framework will likely help these companies play a vital role in shaping the country’s digital infrastructure and meet their sustainability goals by leveraging renewable energy through the DPPA model. The new telecommunication law, in conjunction with DPPA, positions Vietnam as an attractive destination for both energy-intensive industries and technology-driven investments.
DPPA promotes a diverse, sustainable energy mix to reduce fossil fuel dependency
Vietnam relies heavily on coal and LNG (together accounting for 50% of the total energy mix) to meet its rising energy demand. This underscores the country’s dependence on these carbon-intensive and price-sensitive energy sources. The volatility, price fluctuation, and supply chain disruptions in the LNG and coal import market pose significant challenges for energy planners in stabilizing energy costs and energy security risks.
Implementing the DPPA policy is most likely to provide an effective solution to Vietnam’s price-sensitive sectors of the economy. The DPPA framework advocates for opening the energy market for private renewable energy players and developing a robust energy mix ecosystem to mitigate the energy challenges in the country effectively.
By enabling private sector participation, the DPPA framework will accelerate the coal phaseout by prioritizing renewable energy investments. Additionally, diversifying its energy mix will reduce the strain and stabilize the LNG market, making LNG a more strategic and cost-effective component of Vietnam’s energy mix.
Partnerships with foreign players fuel renewable energy expansion in Vietnam
Vietnam’s readiness to collaborate and build strategic partnerships with various international stakeholders supported the expansion of renewable energy. The country has collaborated with international institutions, including the World Bank, Asian Development Bank (ADB), and German Development Cooperation (GIZ), to obtain funding, technical support, and policy advice.
ADB funding drives private investment in Vietnam’s wind energy
In March 2021, the ADB approved a 15-year term loan of up to US$156 million to construct and operate three wind farms of 48 MW. The venture was one of the first internationally financed wind projects in Vietnam. It aligns with ADB’s energy policy to support wider access to energy through investments in renewable energy projects and encourage private sector participation.
The project contributed to the wind generation targets in Vietnam and aims to generate 6,000 MW by 2030. Additionally, in 2023, ADB approved US$1 million for technical assistance to identify potential financing opportunities and US$7 million for providing policy advice on developing financial technologies.
International collaboration is vital to laying a clear policy framework
German International Cooperation Agency (GIZ) has played a vital role in shaping Vietnam’s renewable energy sector by offering technical advice and policy recommendations. The agency set up an advisory platform used by political partners, facilitating the introduction of the FiT model in Vietnam. This cooperation enabled technology and knowledge transfer, laying one of the pillars of Vietnam’s journey to a clean energy transition.
The Just Energy Transition Partnership (JETP) is one of the largest collaborative initiatives between the International Partners Group (Canada, Denmark, France, Germany, Japan, Italy, Norway, and the USA) and Vietnam. The partnership focuses on reducing coal dependency and supporting Vietnam’s ambitious goal of net zero emissions by 2050 by mobilizing US$15 billion through public and private financing over the next few years. The partnership will likely bring regulatory reforms to support renewable energy expansion, increasing the share of renewable energy to 47% by 2030.
Vietnam’s transition to clean energy requires overcoming various challenges
Investment in power grid infrastructure is crucial for the clean energy transition
Grid infrastructure and integration are some of the challenges that Vietnam has been facing to date. The grid has not been able to handle the surge in capacity following the solar energy PV boom driven by the FiTs policy, which has allowed installations to reach 20 GW in 2019 and 2020.
The Vietnamese government has complete control of electricity transmission grids, with EVN operating all the substations and transmission lines in the country. Vietnam’s national transmission infrastructure is inadequate, with weak grid capacity, posing a key challenge for integrating new capacity from renewable energy projects.
The Ministry of Industry and Trade (MOIT) estimates that a capital investment of US$14 billion is needed to enhance and develop the country’s power grid infrastructure. The state budget alone may struggle to fulfill the financial requirements.
This marks the importance of private investment, challenging the monopoly of EVN. The government encourages private investment and revised the electricity law in 2022, allowing private players to develop and operate grid assets. However, only a few private investors, such as Trung Nam Group, invested in the transmission lines due to policy uncertainty and complex administration procedures for land acquisition, site identification, and compensation.
Gaps in the policy could weaken the progress enabled by the DPPA
The DPPA framework is seen as a progressive policy for Vietnam’s renewable energy projects. However, some existing gaps, including operational complexity, regulatory hurdles, and financial risk, may undermine the full potential of the DPPA.
The DPPA off-site model is a financial arrangement in which energy producers sell electricity to the grid (EVN). Energy consumers then purchase electricity from the grid under a contract that makes up the difference between the market price and the agreed contract price.
Solar and wind energy projects with a minimum capacity of 10 MW and energy consumers utilizing at least 200 MWh per month are eligible for off-site DPPA, excluding small renewable energy projects. Further, for off-site DPPA, the policy remains unclear on whether renewable energy producers bear the risk of transmission failures or if they must provide replacement power during shortfalls.
For onsite DPPA, which does not involve an intermediary, the regulation for foreign energy companies regarding the development, operation, and fees for private transmission lines remains unclear. Addressing these gaps in the DPPA model is essential to promote leading practices, new business models, and continued FDI in the country.
EOS Perspective
Early renewables gains bolster FDI attraction
Vietnam’s journey to clean energy transition so far has been a success, with a significant increase in solar and wind energy production in the last few years. Vietnam’s FiT has been attractive to many international energy developers and has been able to attract FDI. The introduction of DPPM further provides a progressive approach to solidify Vietnam’s position as one of the leading nations in the global clean energy sector.
Ongoing policy gaps undermine project viability
For Vietnam, to continue with its success, there is a surging need to address the gaps in its policies and regulations that are gradually impacting the current and potentially future energy projects. For instance, there is a lack of clarity around pricing, transmission fees, whether current FiT project owners can join the DPPA, and the cost implications for small energy producers and buyers. To fully realize the potential of these policies and implementation will require transparent pricing and robust policy support.
Offshore wind ambitions are stalled by regulations
Vietnam has great offshore wind energy production potential due to its geographical advantage of strong wind currents. Yet, it has been unable to make progress in this sector. Equinor, a Norwegian state-controlled energy company, halted its plans for offshore wind development in Vietnam and closed its Hanoi office in August 2024. Similarly, Ørsted, Denmark’s largest energy firm, paused its plans to invest in large offshore wind farms in Vietnam in 2023.
Regulatory delays for foreign players and a political push to prefer state-owned companies to run pilot projects in the contested South China Sea are some of the reasons that currently leave Vietnam with no offshore wind energy projects. To meet its ambitious target of generating 6 GW of offshore wind energy by 2030, Vietnam needs a robust regulatory framework that supports a collaborative ecosystem that attracts foreign investment.
Vietnam is a large power consumer and relies heavily on coal as the primary energy source due to its affordability and easy availability. Transitioning from coal will require significant investments in alternative energy sources and could disrupt existing economic structures.
Programs such as JETP offer momentum to accelerate the transition. However, they often face certain challenges in the form of substantial financial gaps and mismatched expectations and implementation standards between donor and recipient countries. Vietnam needs a staggering investment of US$135 billion to support its transition to clean energy. The funding is essential for stopping the permits for new coal plants, building renewable energy facilities, and upgrading electricity grids. Despite the US$15.5 billion in JETP, Vietnam faces a significant financing gap of 89%. To fully realize the JETP potential, Vietnam must seek other funding sources, including public financing, private investment, and commercial loans.