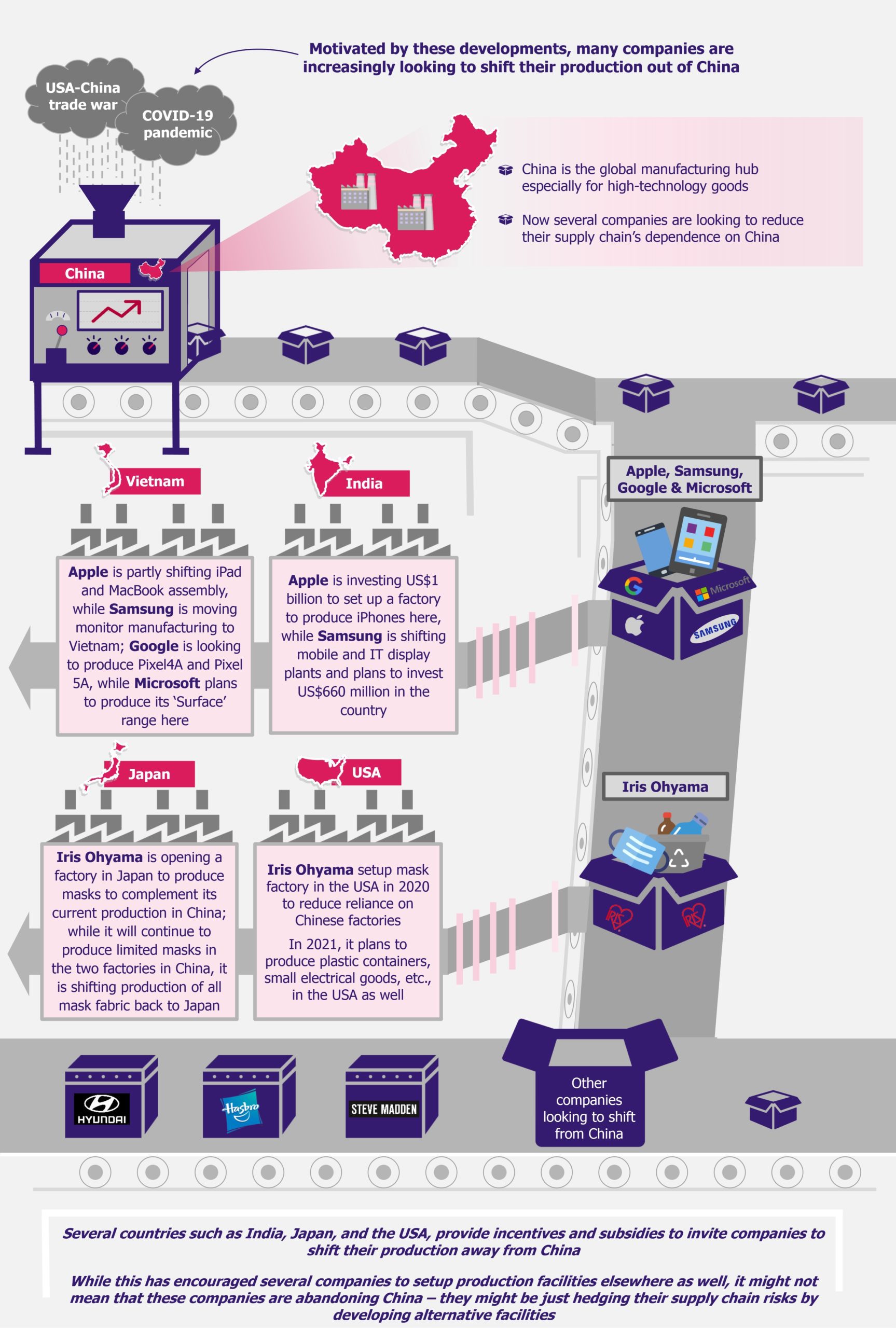
Dubbed as the factory to the world, China is an integral part of the supply chain of a host of products and brands. From manufacturers of simple products such as toys to complex goods such as automobiles, all are dependent on China for either end products or components. However, China’s ongoing trade war with the USA and the COVID-19 pandemic have made several brands question their supply chain dependence on this country, especially in some industries such as pharmaceuticals. Moreover, aggressive investment incentives offered by countries such as India and Japan have further cajoled companies to reassess their global supply chains and reconsider their dependence on China. However, with years of investment in the supply chain ecosystem, a shift such as this seems easier said than done.
China emerged as the manufacturing hub of the world in the 1990s and hasn’t looked back since. Owing to the vast availability of land and labor, technological advancements, and overall low cost of production, China became synonymous with manufacturing. Over the past decade, increasing labor and utility costs, and growing competition from neighboring low-cost countries such as India, Vietnam, Thailand, etc., have resulted in some companies shifting out from China. However, so far, this has been limited to a few low-skilled labor-intensive industries such as apparel.
The year 2020 has changed this drastically. The COVID-19 pandemic, along with the ongoing trade war between the USA and China, made companies realize and question their dependency on China. At the beginning of last year, COVID-19 brought China to a halt, which in turn impacted the supply chain for all companies producing in China. Moreover, several pharmaceutical companies also realized that they are highly dependent on China for a few basic medicines and medical supplies and equipment, which were in considerable shortage throughout 2020. This pushed several companies across sectors, such as pharmaceuticals, automobiles, and electronic goods, to reconsider their global supply chains to ensure reduced dependence on any one region, especially China.
Currently, several companies such as Apple, Google, and Microsoft are looking to shift their production from China to other South Asian countries, such as Vietnam and Thailand.
Some of the companies looking to reduce dependence on China:Apple In November 2020, Apple, along with its supplier Foxconn, expressed plans to shift the assembly of some iPads and MacBooks to Vietnam from China. The facility is expected to come online in the first half of 2021. Moreover, Apple is also considering shifting production of some of its Air Pods to Vietnam as well. In addition, it has invested US$1 billion in setting up a plant in Tamil Nadu, India, to assemble iPhones that are to be sold in India. Apple and Foxconn are consciously trying to reduce their reliance on China due to the ongoing USA-China trade war. Samsung In July 2020, Samsung announced plans to shift most of its computer monitor manufacturing plants from China to Vietnam. The move is its response to hedge the supply chain disruptions it faced due to factories being shut in China during the early phase of the pandemic. In addition, in December 2020, the company shared its plans to shift its mobile and IT display plants from China to India. Samsung plans to invest about US$660 million (INR 48 billion) to set up the new facility in Uttar Pradesh (India). Hasbro Hasbro has been moving its production out of China into Mexico, India, and Vietnam over the past year. It aimed to have only 50% of its products coming out of China by the end of 2020 and only 33% of its production to remain in China by the end of 2023. In 2019, about 66% of its toys were produced in China, while in 2012, 90% of its toys were manufactured in the country. The key reason behind the consistent switch is the souring trade relations between the USA and China. Hyundai During the past year, Hyundai Motors has been looking at developing India into its global sourcing hub instead of China in order to reduce its over-reliance on the latter. It has been encouraging its vendors, such as Continental, Aptiv, and Bosch, to ramp up production in India so as to move their supply chain away from China. It plans to source its auto parts from India (instead of China) for its existing factories in India, South America, and Eastern Europe, as well as a planned facility in Indonesia. Google is looking to manufacture its new low-cost smartphone, Pixel4A, and its flagship smartphone, Pixel5A, in Vietnam instead of China. In addition, in 2020, it also planned to shift production of its smart home products to Thailand. This move has been a part of an ongoing effort to reduce reliance on China, which, in fact, gained momentum after supply chain disruptions faced due to the coronavirus outbreak. Microsoft In early 2020, Microsoft expressed plans to shift the production base of its Surface range of notebooks and desktops to Vietnam. While the initial volume being produced in Vietnam is expected to be low, the company intends to ramp it up steadily to shift volumes away from China. Steve Madden In 2019, Steve Madden expressed plans to shift parts of its production out of China in 2020, given growing trade-based tensions between the USA and China. However, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, it could not make planned changes to its supply chain. In October 2020, it again expressed plans to start shifting part of its production away from China by spring 2021. It plans to procure raw materials from Mexico, Cambodia, Brazil, and Vietnam to reduce reliance on China. Iris Ohyama The Japanese consumer goods player expressed plans to open a factory in northeastern Japan to diversify its manufacturing base, which is based primarily in China. The company made this move on the back of increasing labor costs in China, rising import tariffs to the USA, and the supply disruptions it faced for procuring masks for the Japanese market. In 2020, it also set up a mask factory in the USA. In addition, the company plans to open additional plants in the USA and France for plastic containers and small electrical goods to cater to the local demand in these markets. |
Nations using this opportunity to promote domestic production
In August 2020, about 24 electronic goods companies, including Samsung and Apple, have shown interest in moving out of China and into India. These companies together have pledged to invest about US$1.5 billion to setup mobile phone factories in the country in order to diversify their supply chains. This move is a result of the Indian government offering incentives to companies looking to shift their production facilities to India.
In April 2020, the Indian government announced a production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme to attract companies looking to move out of China and set up large-scale manufacturing units in the electronics space. Under the scheme, the government is offering an incentive of 4-6% on incremental sales (over base year FY 2019-20) of goods manufactured in India. The scheme, which is applicable for five years, plans to give an incentive worth US$6 billion (INR 409.51 billion) over the time frame of the scheme.
In November 2020, the Indian government subsequently expanded the scheme to other sectors such as pharma, auto, textiles, and food processing. In addition, it is expected to provide a production-linked incentive of US$950 million (INR 70 billion) to domestic drug manufacturers in order to push domestic manufacturing and reduce dependence on Chinese imports. Apart from incentives, India is developing a land pool of about 461,589 hectares to offer to companies looking to move out of China. The identified land, which is spread across Gujarat, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, and Andhra Pradesh, makes it easy for companies looking to set up shop in India, as acquiring land has been one of the biggest challenges when it came to setting up production units in India.
On similar lines, the Japanese government is providing incentives to companies to shift their production lines out of China and to Japan. In May 2020, Japan announced an initiative to set up a US$2.2 billion stimulus package to encourage Japanese companies to shift production out of China. About JNY 220 billion (~US$2 billion) of the stimulus will be directed toward companies shifting production back to Japan, while JNY 23.5 billion (~US$200 million) will be given to companies seeking to move production to Vietnam, Myanmar, Thailand, and other Southeast Asian countries.
In the first round of subsidies, the Japanese government announced a list of 57 companies in July 2020, which will receive a total of US$535 million to open factories in Japan, while another 30 companies will be given subsidies to expand production in other countries such as Vietnam and Thailand. The move is a combination of Japan looking to shift manufacturing of high-value-added products back to the country, and the initial disruptions caused to the supply chain of Japanese automobiles and durable goods manufacturers.
Similarly, the USA, which has been at odds with China regarding trade for a couple of years now, is also encouraging its companies to limit their exposure in China and shift their production back home. In May 2020, the government proposed a US$25 billion ‘reshoring fund’ to enable manufacturers to move their production bases and complete the supply chain from China, preferably back to the USA, and in turn, reduce their reliance on China-made goods. The bill included primarily tax incentives and reshoring subsidies. However, the bill has not been passed in Congress yet, and now, with the leadership change in the USA, it is expected that president Biden may follow a more diplomatic strategic route with regard to China in comparison to his predecessor.
In addition to individual country efforts, in September 2020, Japan, India, and Australia together launched an initiative to achieve supply chain resilience in the Indo-Pacific region and reduce their trade dependence on China. The partnership aims at achieving regional cooperation to build a stable supply chain from the raw material to finished goods stage in 10 key sectors, namely petroleum and petrochemicals, automobiles, steel, pharmaceuticals, textiles and garments, marine products, financial services, IT services, tourism and travel services, and skill development.
Similarly, the USA is pushing to create an alliance called the ‘Economic Prosperity Network’, wherein it aims to work with Australia, India, Japan, New Zealand, Vietnam, and South Korea to restructure global supply chains to reduce dependence on China.
Is it feasible?
While these efforts are sure to help companies move part(s) of their supply chain out of China, the extent to which it is feasible is yet to be assessed. Although the coronavirus outbreak has highlighted and exposed several supply chain vulnerabilities for companies across sectors and countries, despite government support and incentives, it will be very difficult for them to wean off their dependence on China.
Companies have spent decades building their manufacturing ecosystems, which, in many cases, are highly reliant on China. These companies not only have their end products assembled or manufactured in the country but also engage Chinese suppliers for their raw materials, who in turn use further Chinese suppliers for their inputs. Therefore, moving out of China is not a simple process and will take a tremendous amount of time as well as financial resources.
While companies such as Google or Microsoft are looking to shift their assembling plants out of China, they are still dependent on China for parts. This is all the more relevant in the case of high-technology products, such as automobiles and telecommunication infrastructure, where companies have made significant investments in China for their supply chain and are dependent on the nation’s manufacturing capabilities for small, intricate but technologically advanced parts and components.
Moreover, despite significant efforts and reforms from countries such as India, Vietnam, and Thailand, they still cannot match China in terms of the availability of skilled labor, infrastructure, and scale, which is required by many companies, especially with regard to technologically advanced products. That being said, more companies are looking at a strategy where they are maintaining their presence in China, while also developing relatively smaller operations outside the country to have a fallback and to reduce total dependency on China. This is also dubbed as the China + 1 strategy.
Another reason going in China’s favor has been its capability to bounce back from the pandemic and resume production in a short span of time. While production had been halted from January to March 2020, it ramped up from April onwards and was back to normal standards within no time. This reinforced the faith of many companies in Chinese capabilities. Therefore, as some companies are already cash-strapped due to the pandemic, they are not interested in investing in modifying their supply chains when, in most cases, normalcy resumed in a relatively short span of time.
EOS Perspective
Companies have been looking to diversify their supply chains and reduce dependence on China for a couple of years now, however, the trend has gained momentum post the coronavirus pandemic and growing US-China trade tensions. The onset of the COVID-19 outbreak exposed several vulnerabilities in the supply chain of global manufacturers, who realized the extent of their dependence on China. Moreover, several countries realized that they relied on China for key medicines and medical supplies, which cost them heavily during the pandemic.
Given this situation, several nations such as Japan, India, and the USA – together and individually, have started giving incentives to companies to shift production from China into their own borders. While this has resulted in several companies, such as Apple, Microsoft, Sanofi, Samsung, etc., expanding their manufacturing operations out of China, it does not necessarily mean that they are moving out of China. This is primarily due to heavy investments (in terms of both time and money) that they have already made into developing their intricate supply chains, as well as the inherent benefits that China provides – technologically skilled labor, sophisticated production facilities, and quick revamping of production after a calamity.
That being said, it has come into the conscience of companies to reduce their over-reliance on China, and while it may not impact the scale and extent of operations in the country in the short run, it is quite likely that companies will phase out their presence (at least part of it) in China over the coming decade.
A lot depends on the level of incentives and facilities provided by other nations. While countries such as India, Vietnam, and Thailand can offer low-cost production with regard to labor and utilities, they currently do not have the technological sophistication possessed and developed by China. Alternatively, while Japan and the USA are technologically advanced, without recurring incentives and tax breaks, the cost of production would be much higher than that in China. Thus, until there is a worthy alternative, most companies will follow the China +1 strategy. However, with growing trade tensions between China and other nations and ongoing efforts by other nations to encourage and support domestic production, China may risk losing its positioning as the ‘factory of the world’ in the long run.