COVID-19 has disturbed practically every business vertical across the globe, and the travel and tourism sectors were one of the first ones to fall prey to the devastating effects of the pandemic. Complete lockdowns made taking a leisure trip or planning a vacation impossible for a long time to come. Not only were people unable to travel, but also multiple businesses serving in the tourism sector closed down temporarily, with some shutting their doors for good. Recently, leisure travel started to resume, but at a snail’s pace. In many countries, businesses, local authorities, and government agencies are developing a coordinated approach to aid the economic recovery of the sector. The actions and approaches taken in these uncertain times will lay the foundation for the future of the tourism sector.
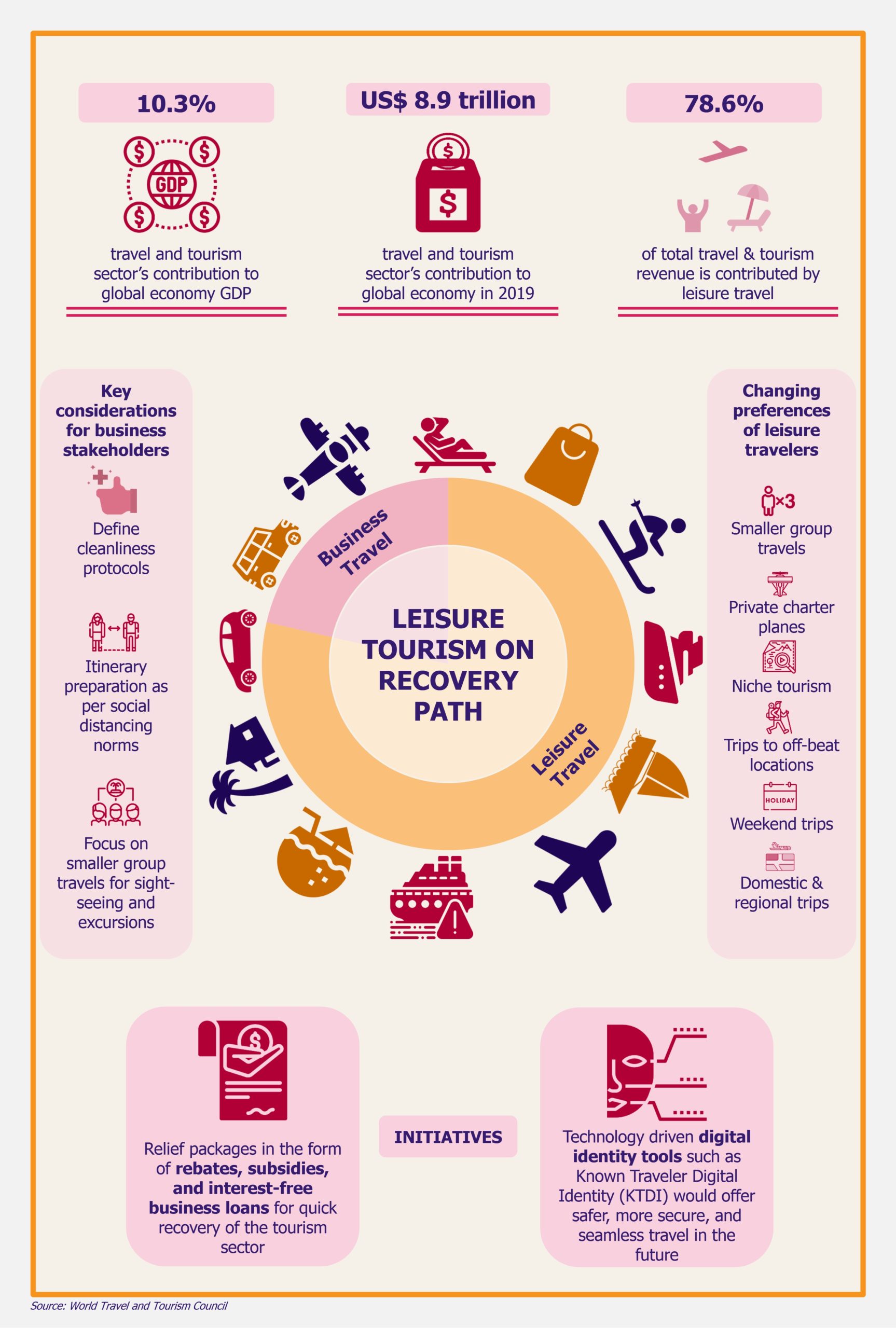
The travel & tourism industry contributed US$ 8.9 trillion to the global economy in 2019. Leisure travel made up the majority of total travel & tourism revenue, standing at 78.6%. The trend was expected to follow in 2020, but the coronavirus outbreak crippled the entire leisure tourism sector as travels were canceled globally for at least three months (mainly from April to June, though in many locations, those cancellations have continued at least till autumn, and again at the end of the year).
Read more on the pandemic impact on business travel in our previous Perspective: Business Travel: On the Mend but Long Recovery Ahead
Travelers evolving preferences
Demand for domestic leisure travel is expected to rise as people are likely to be less inclined to travel to international destinations due to safety, hygiene, and uncertainty concerns. Unwillingness to spend on international travel in the immediate future also suggests that people are less inclined to make trips to international destinations. Self-driving trips to nearby destinations and weekend getaways are likely to increase in popularity.
In terms of traveler type, the group travel segment (irrespective of the size of the group) has always generated higher revenue for the global leisure travel market, in comparison to the solo traveler segment (in 2018, the group travel segment contributed nearly 73% of revenue to the global leisure travel market). Travelers were always able to take advantage of group discounts offered by hotels, resorts, airlines, and vehicle rental companies.
It is anticipated that group travel will continue to be a common practice among travelers (both during the pandemic and post-pandemic). However, to avoid crowded places, it is highly likely in the future, travelers will need (and perhaps also desire) to travel in smaller groups. This trend is expected to continue in the distant future, mainly due to the growing acceptance of social distancing norms as the new normal for sanitation and hygiene purposes globally. However, whether or not this type of travel arrangement will be monetarily favorable to various market stakeholders (in terms of discounts and margins when compared to larger group travels) and what discounted rates would consumers receive is yet to be seen.
It is highly likely in the future, travelers would need (and perhaps also desire) to travel in smaller groups. This trend is expected to continue in the distant future mainly due to the growing acceptance of social distancing norms as the new normal for sanitation and hygiene purposes globally.
Demand for private charter flights is also rising among leisure travelers. Wary of flying with regular flights, people are turning to charter planes for taking vacation trips to safe destinations (for both short and long-distance locations). However, this trend is expected to be short-lived mainly because only upper-class travelers will be able to afford such travel, and most of the demand for charter flights comes from business travelers (which is also limited to a need-only basis, for now, at least).
Moreover, interest in trips to off-the-beaten-path locations and niche tourism (such as adventure tourism, wellness tourism, and heritage tourism) is also expected to grow as these locations are likely to be considered safer to travel to in comparison to famous tourist locations, at least for some time in the foreseeable future.
Governments to the rescue
Travel and tourism businesses have been hit hard as they had to temporarily close business operations (many small and medium-sized business players are permanently out of business) and suffered heavy revenue losses. To mitigate the impact of coronavirus (on both the travel and tourism sectors and economies), many governments have offered aid packages to help the sector.
Governments globally have taken a range of measures to revive the sector in order to shield the economy and protect employment. For instance, Italy, one of the most popular tourist destinations and also one of the worst-hit economies by the first wave of the pandemic, announced a relief package to revive businesses in the travel sector. The package includes a US$ 645.7 million fund for the aviation sector, a US$ 129.1 million fund to support regions that generated lower revenue owing to lower number of people paying tourism taxes, US$ 19.3 million for tourism promotion, and subsidies worth US$ 129.1 million for museums and other cultural sites to recover lost ticket revenue for 2020, among others.
Similarly, under the Hong Kong government’s Anti-Epidemic Fund, licensed travel agents will receive a subsidy ranging from US$ 2,580 to US$ 25,803, travel agents’ staff and freelance tourist guides and tour escorts will receive a monthly subsidy of US$ 645 for six months, licensed hotels will receive a subsidy of US$ 38,705 or US$ 51,607 (depending on the size), and tour coach drivers a one-time subsidy of US$ 1,290. An additional US$ 90.3 million has been allotted to the Hong Kong Tourism Board for tourism promotion.
New Zealand announced that for the losses borne by travel agents for canceled travel plans by their consumers, the government will pay 7.5% of value for cash refunds or 5% of credit value to be capped at US$ 31.4 million.
In another example, the Australian government allotted a package of US$ 177.2 million for regional tourism, which will include US$ 35.4 million to support businesses in regions heavily reliant on international tourism and the remaining US$ 141.8 million to boost local infrastructure in regional communities, of which US$ 70.8 million will be used for tourism-related infrastructure. For regional tourism rebound, the Western Australian government has allotted US$ 10.2 million in the form of two funds – US$ 7.3 million as one-off cash grants of US$ 4,608 to up to 1600 individual small businesses and US$ 2.8 million as grants of US$ 17,723 to US$ 70,894 for tourism operators.
To revitalize tourism, some countries are assigning special reserves for campaigns as well. The UK initiated a US$ 12.9 million ‘Kick Start Tourism Package’ for the recovery and renewal of the tourism sector, wherein businesses can access government grants of up to US$ 6,462 to restart operations. Similarly, Norway allocated US$ 19.9 million for rebounding the country’s internal tourism businesses while Denmark assigned US$ 7.8 million for international tourism campaigns.
Various employee training programs and digital technology management processes are also being implemented to support the sector. One such example is the Singaporean government’s move to fund up to 90% of the training course and trainers’ fee for employee upgrading and talent development through its Training Industry Professionals in Tourism fund.
With minimal to no action happening in the travel and tourism segment, all these efforts are likely to not only protect jobs but also give the necessary push to restart the businesses, albeit from ground zero, in some cases.
Tourism-dependent least developed economies in deep waters
Considering that out of the 47 least developed countries identified by the United Nations, 45 consider travel and tourism of significant relevance to their economies in terms of job creation, growth prospects, and overall development, COVID-19 has a real potential to adversely affect these vulnerable countries.
In January 2020, through the ‘Visit Nepal Year 2020’ campaign, Nepal expected to attract two million visitors and generate US$ 2 billion in revenues in 2020. It should be noted that in normal circumstances, travel and tourism contribute nearly 6.7% to Nepal’s GDP. However, with the onset of the pandemic, not only was the campaign suspended, but also the tourist arrivals declined drastically – 177,975 tourists visited Nepal up until August 2020, only 24% of what had arrived during the same period in 2019 (739,000 tourists arrived between January and August). Also, nearly 20,000 tour and mountaineering guides risked losing jobs due to the cancellation of all mountaineering expeditions.
In Cambodia, where travel and tourism contribute nearly 26% to the nation’s GDP, the effects of the virus have also been damaging. The country may lose up to US$ 3 billion in revenues as the inflow of international travelers was down by 52% to 1.16 million between January and April 2020 (2.41 million visitors in 2019 during the same period). Up until May 2020, more than 45,000 jobs had been affected due to the pandemic.
Likewise, for countries such as Kiribati, Gambia, Sao Tome and Principe, Madagascar, Tanzania, Solomon Islands, Rwanda, and Comoros, the travel and tourism sector forms a key contributor to their economies by contributing 18%, 17.7%, 16.2%, 11.8%, 10.7%, 10.5% 10.2%, and 10.1%, respectively, to the countries’ GDPs.
In a normal scenario, the majority of the travel and tourism revenue in these countries is generated by leisure travel (for most of these countries, the leisure segment generates >50% of the revenue) as against business travelling. The sudden onset of the pandemic prohibited the entry of travelers (for vacationing purposes) within these countries, stopping cash inflow and thus hampering revenue generation.
Governments in most of these countries, through relief funds and aid packages, attempt to cushion the negative impact of the virus on the sector and the livelihoods of people involved. However, they are far from being able to fully offset the devastating repercussions, considering that these economies had already been at a disadvantageous position with limited growth and development even prior to the pandemic.
EOS Perspective
COVID-19 has altered most travelers’ perspective on vacationing, a fact that is unlikely to change in the short term. It is now upon the various stakeholders operating the leisure tourism sector to ensure that travelers will have an easy and reassuring path back to the sector’s services.
In the current scenario, regions where governments have been able to contain the spread of the virus, even if to a small extent, leisure traveling is slowly resuming. However, reduction in disposable income (due to unemployment), safety concerns, and overall economic slump are causing people to plan affordable regional trips rather than international vacations.
Globally, the impact of the pandemic on leisure tourism has been detrimental to the latter’s growth, to say the least. In some regions, people are slowly keener on booking vacation trips again but the volumes are low. They are likely to remain so, at least in the near future, especially with the returning spikes in number of infections and increased travel restrictions that follow.
Safety is not the only factor holding people back from traveling. Equally important is the financial crunch, fueled by job losses and uncertainty about the future. Travel and tourism industry stakeholders are observing this trend and trying to alter their strategies and business models in collaboration with government agencies to survive in these changing, challenging, and uncertain times.
Safety is not the only factor holding people back from traveling. Equally important is the financial crunch, fueled by the job losses and uncertainty about the future.
More so, partnerships among tourism industry stakeholders, regional communities, government authorities, and private sector enterprises would also contribute to the sector’s recovery. For instance, in October 2020, Nigeria Tourism Development Corporation (NTDC) partnered with Google to launch Google’s Arts & Culture collection called ‘Tour Nigeria’, which is an online exhibition that includes videos, photographs, and commentaries highlighting the country’s scenic beauty and cultural festivals. This collaboration aims to provide online training programs to small businesses and impart digital skills training to individuals in order to support the local tourism sector. As part of the initiative, a video series named ‘Explore Nigeria’ was also launched wherein social media influencers are roped in to publicize ‘best of Nigeria’ in order to reach a large number of viewers via influencers’ social media followers.
Post the lockdown, stakeholders in the travel and tourism landscape restarted their operations by evolving their product offerings (hotel stay packages with increased flexibility or airlines not flying to full capacity, thus practicing social distancing), experience services (such as tours and excursions or offering upgrades at no or minimal fee), and overall business approach. However, in some regions, this re-opening was short-lived and was paused by the second wave of the pandemic (with the third one on the horizon for spring 2021).
In the foreseeable future, it would not come as a surprise if customers can book a service provider for a leisure trip based on the hygiene and sanitation rating associated with it. Businesses are therefore being promoted on the basis of adopting upgraded cleaning procedures. It is highly likely that the pandemic may push tourism councils and governing bodies to come up with a hygiene assurance standard, either on a global or national level, that all players in the travel industry might need to abide by – this could be a bit of a stretch but such an initiative, if taken, is very likely to be embraced by many travelers.
Automation, though already at the forefront of travel and tourism, is likely to pick up pace. Travelers can expect to witness increased contactless interactions such as contactless check-in or check-out and usage of mobile apps such as hotel room keys, virtual reality for sightseeing, and chatbots and robots for concierge services. The usage of contact tracking apps to monitor traveler’s health and automatic disinfectors will also increase.
The adoption of digital identity and biometric tools will drive the travel industry in the future. Consolidated technology solutions offering a transparent and seamless flow of information ensuring travelers’ safety are essential. One such digital identity tool is the Known Traveler Digital Identity (KTDI), which holds the potential to offer a secure and seamless travel experience. An initiative by the World Economic Forum, KTDI not only aims at optimizing passenger processing experience but also manages risks in real time by monitoring a traveler’s health records.
Nevertheless, while it is optimistic to think that once the vaccine is widely available, the virus will be eradicated and travel will resume as before, one thing that the pandemic has brought to the forefront is that adaptability and adjustment are the key for travel and tourism sector players to keep their businesses running.