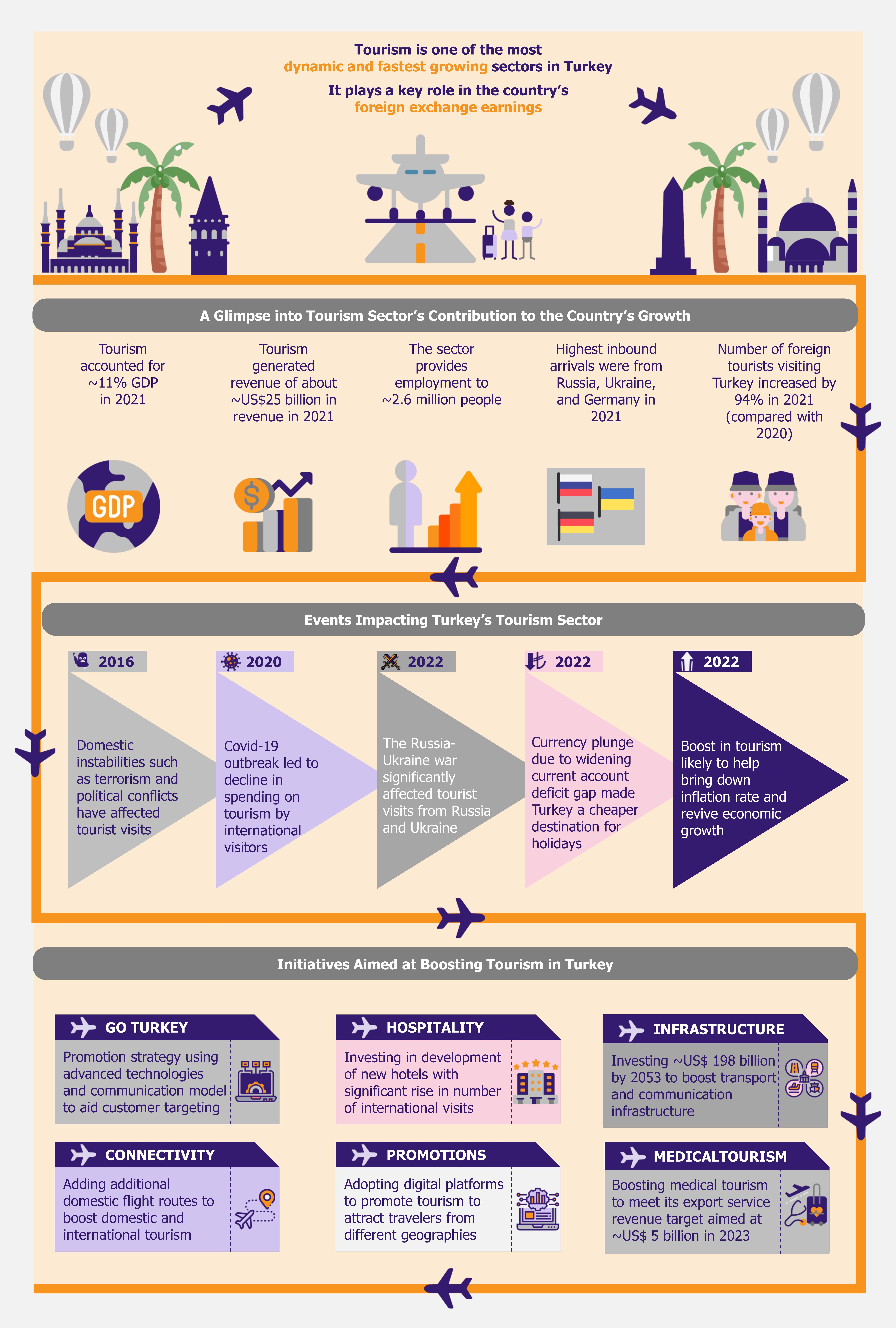
Tourism is one of the most dynamic and fastest-growing sectors in Turkey. The country is highly reliant on tourism for foreign exchange earnings. However, the COVID-19 outbreak and the Russia-Ukraine war have affected the country’s tourism industry and resulted in a decline in tourist visits. While the spike in energy and commodity costs due to war has widened the current account deficit gap, it has also made tourism cheaper in the country due to a significant decline in currency value. This has resulted in an unprecedented influx of tourists once the pandemic subsided. Furthermore, various initiatives have been taken by the government to boost tourism in hopes of reducing the current account deficit, bringing down inflation rates, and supporting economic growth.
Turkey is known for its vast historical sites in the major cities of Istanbul and Antalya, as well as the Aegean and Mediterranean Sea coasts. The tourism sector employs about 2.6 million people in the country. The sector also contributes significantly to new tourism-related business sources and foreign exchange earnings and, thus, plays a crucial role in the economic development of the country, especially in the post-COVID era. In 2021, it is estimated that Turkey generated about US$25 billion in revenue from the tourism sector.
The country’s dependence on tourism has increased significantly over the past few years. Turkey’s travel and tourism sector contribution to GDP increased to 11% in 2019 as compared with 4.7% in 2014. As per the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), Turkey was the sixth-most visited country in the world in 2019. While the country’s rank came down to 15th in 2020 due to the COVID-19 outbreak, it jumped to fourth in 2021 in the post-COVID-19 recovery phase.
In addition to this, as per the 2022 Economic Impact Report (EIR) by the World Travel and Tourism Council, Turkey’s Travel and Tourism GDP is expected to increase by about 5.5% on an annual basis over the next decade (2022-2032) and create over 716,000 new jobs in the country. The projected growth rate in the country’s travel and tourism sector is more than double the projected growth rate of the overall economy, which is expected to be 2.5% during the same time period.
Challenges faced by the tourism sector over the years
While the tourism sector remains one of the best-performing sectors in Turkey, it has faced its own set of challenges over the past several years. Inflation has been rapidly rising in the country since 2016 due to factors such as low-interest rates, the energy crisis, an increase in commodity prices, and declining currency value. This has significantly affected domestic travelers and business owners in the tourism sector. Several terrorist attacks, particularly in the southeast part of the country and Istanbul and Ankara by the Kurdistan Workers’ Party (PKK) and ISIS, also severely affected tourist visits and economic growth in 2016.
Owing to the 2020 COVID-19 outbreak, spending on tourism by international visitors in Turkey declined by about US$20 billion, a 70% decline in comparison with 2019. This led to a decline in demand and unemployment in related sub-sectors, including airlines, travel agencies, hotels, and car rental companies, among others.
Stringent measures and trade restrictions resulted in a significant decline in air traffic and affected the aviation industry. For instance, the National carrier, Turkish Airlines, reported a net loss of about US$761 million in 2020.
The hospitality industry was also hit due to a fall in tourism in the country. Most hotels faced significant revenue loss during lockdown months. According to the Turkish Hotel Association (TUROB), the hotel occupancy rate in the first nine months of 2020 was just 35.4%, a decline of 47.8% from the same time period in the previous year. Moreover, revenue per available room declined by 52.5% to US$24.7 during the same period.
The 2022 war between Ukraine and Russia further affected the tourism sector growth in Turkey. Tourist visits from Russia and Ukraine used to account for a significant share of the total number of tourists visiting the country for holidays from Europe. Over 4.7 million Russians and 2 million Ukrainians visited Turkey for vacation in 2021. While 2.2 million Russians visited Turkey during January-July 2022, it is expected that the total number of tourists from Russia in 2022 will fall short of the 2021 figures due to prolonged war and the imposition of western sanctions and flight suspension. The number of tourists from Ukraine declined to 374,000 in the first seven months of 2022, in comparison with 1.1 million during the same period in 2021. The war also spiked Turkey’s inflation rate, which touched about 80% in August 2022.
While the Turkish government is trying to attract tourists from Russia by collaborating with Turkish aircraft to transport foreign guests amid war, it is not likely to recover tourist visits to pre-war levels.
Depreciating currency value boosts tourism in the country
The increase in the current account deficit due to rising energy and commodity costs in the backdrop of war in Ukraine has led to a massive currency value plunge for the Turkish Lira in 2022. Turkey is a net importer of oil and gas, and a spike in energy costs amid the Ukraine-Russia war has widened the current account deficit gap. As per the Turkish Central Bank data, the current account deficit increased to about US$32.4 billion in the first half of 2022. As of September 2022, the Turkish Lira declined to about TRY18.3 per US$1 compared with an average of TRY 8.9 per US$1 in September 2021 and is likely to decline further in 2023 with rising inflation rates due to interest rate cut.
A significant plunge in the currency value has made Turkey a more affordable destination for holidays in comparison with other European tourist destinations. The cost of stay, food, and travel has become significantly lower for foreigners. Adding to this, there has been a decline in COVID-19 cases across the globe, which has also provided the tourism sector a strong boost.
The number of foreign tourists visiting Turkey increased by 94% in 2021 (compared with 2020), reaching 24.7 million. It further witnessed a y-o-y increase of about 128% for the period of January-July 2022 to reach 23.3 million tourists during the period. The country’s revenue from tourism also witnessed a y-o-y increase of 190% in Q2 2022 to reach US$8.72 billion. In 2022, Germany accounted for the largest share of visitors, reaching 2.9 million from January to August. The number of tourists from Middle Eastern and European countries has also increased significantly in 2022. This has also resulted in an increase in share prices of Turkish Airlines. For instance, the share value of Turk Hava Yollari AO, also known as Turkish Airways, increased by about 147% between January and May 2022.
Since Turkey is highly reliant on tourism for its foreign exchange earnings, the significant boost in tourism is likely to help lower the widening current account deficit in the country. A low current account deficit is likely to increase the value of the Lira and, thus, bring down the inflation rate and support economic growth. However, further decline in interest rates by the Central Bank is resulting in an increase in the inflation rate, which reached 80.2% in September 2022. Therefore, while tourism can help soften the blow on the economy by reeling in foreign currency and earnings, it is unlikely that it will single-handedly help the economy recover from the ongoing crisis. That being said, the government is undertaking several efforts to capitalize on the growth in the tourism sector and provide a much-needed cushion to the economy as a whole.
Initiatives aimed at boosting tourism in the country
The Turkish government realizes the role tourism can play in uplifting the economy and has been undertaking several initiatives to boost the sector. For instance, in 2021, the government adopted a new promotion strategy, ‘Go Turkey’, to boost tourism. The ‘Go Turkey’ website encompasses the use of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and communication models. It follows over 100 media and social media outlets which cover news about the country. Additionally, it also analyses positive or negative content on Turkey and determines promotion priority based on this analysis. The aim is to focus on advanced public relations by integrating all 81 provinces under the system and promoting tourism together as a single voice.
A few other initiatives taken up to boost tourism in the country include additional domestic flight routes, medical tourism support, transportation infrastructure development, and several hotel investments. In August 2022, Turkish Airlines signed a deal with the Services Exporters’ Association (HİB) to help increase medical tourism in Turkey to meet the medical tourism industry’s export service revenue target aimed at US$5 billion in 2023.
About US$172 billion has also been invested in communication and transportation infrastructure during 2003-2021, and the government is planning to invest an additional US$198 billion by the end of 2053. Some of the key ongoing projects include The MBB – Gari – Mezitli Metro, The IBB – Kazlicesme – Sogutlucesme Metro Line, and the IMM – Ucyol-Buca Koop Light Rail, among others, aimed at boosting the transportation network in the country. Additionally, according to the Hotel Association of Turkey (TÜROB), new investments were planned in about 30 provinces in the first half of 2022. The new investment incentive includes applications for 11 five-star hotels, 18 four-star hotels, and 26 three-star hotels.
As of March 2022, TUI Group, a leading German travel and tourism company, together with its partners in Turkey, planned on expanding its holiday program and developing a winter program across destinations to attract more tourists as compared with pre-pandemic levels.
Additionally, in July 2022, Cengiz Construction, a leading construction company, started the construction of villas and hotels in Bodrum’s Cennet Bay together with Bulgari, a luxury hospitality company, with a significant increase in international visitors in the country.
Furthermore, travel companies and agencies are focusing on the adoption of digital platforms to promote tourism in the country as people are becoming more technology savvy and prefer online booking. It also helps attract travelers from different countries across the globe. Hotel booking through digital platforms increased to 81% in 2019, up from 73% in 2014, and is expected to increase further with rising penetration of smartphones and easy internet access. Turkey’s Tourism Development Agency (TGA) is likely to spend about US$100 million to promote tourism in over 120 countries through internet platforms and media in 2022.
EOS Perspective
Tourism contributes a significant amount to the Turkish GDP and is likely to help limit the consequences of increasing commodity and energy prices by reducing the widening current account deficit gap and easing the pressure on the economy. That being said, it is unlikely to help the country recover completely from its economic woes. Although the depreciating Lira has made Turkey a very affordable destination for holidays, people operating in tourism businesses are significantly affected by the high inflation levels as well. Hotels and resorts are facing high costs of employee wages, food supplies, and car rents, among others, which hurt their profits. Interest rates cut by the Central Bank are further increasing the inflation rate. In addition to this, the key tourist season, which is the summer season for Turkey, lasts for just a few months, and the sector’s revenue and profitability fall in the winter season. This makes it evident that the Turkish economy must base its recovery on a balanced mix of support across several sectors.