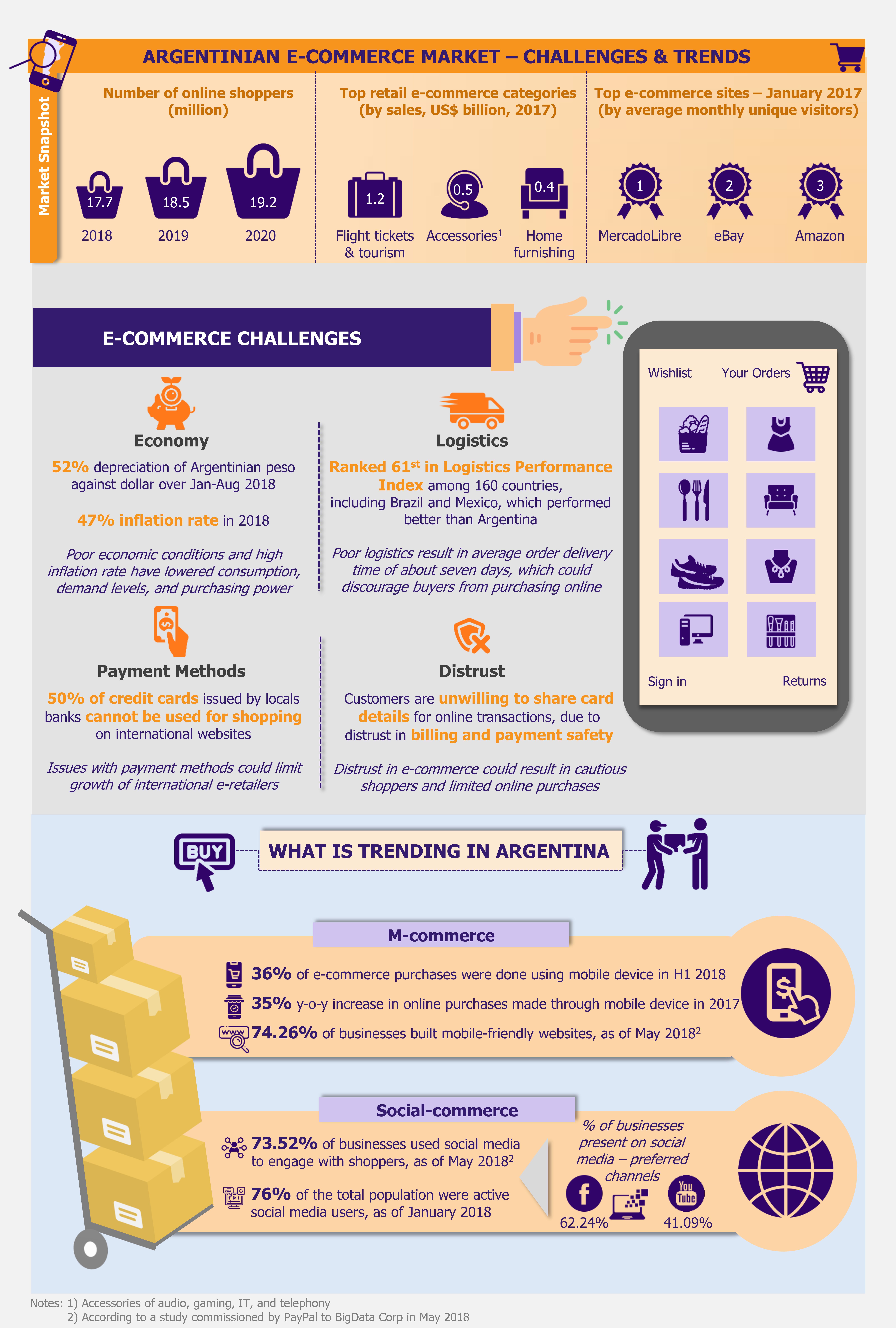
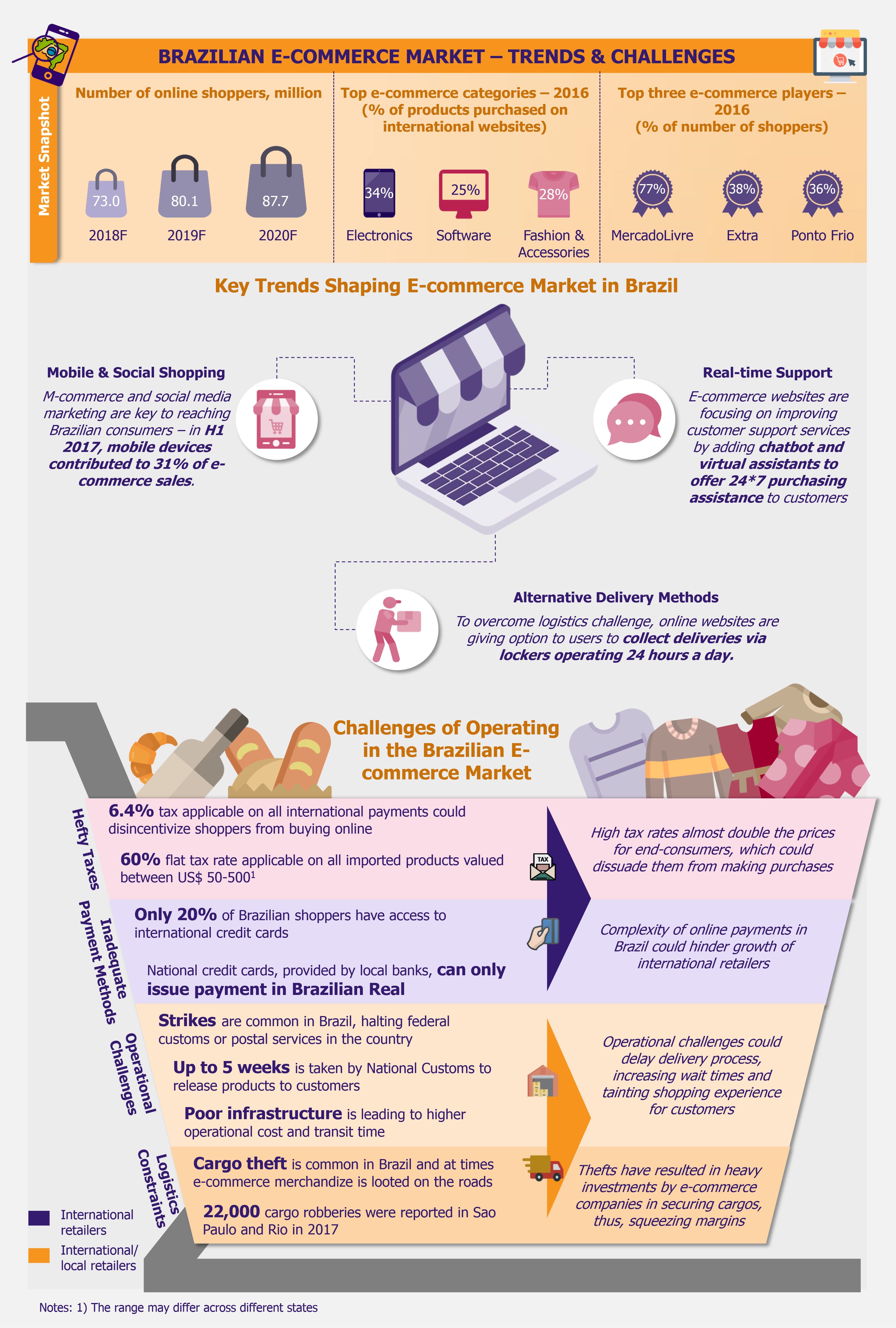
Blockchain technology, which initially became popular with cryptocurrency (especially bitcoin), is now making its way into many other industries, including retail. Though still in its infancy, blockchain holds tremendous potential for retailers and has applications across supply chain data management, customer retention through loyalty programs, digital advertising, among many others. While several industry experts have proclaimed blockchain to be the next revolutionary technology in the retail sector, it is yet to be seen if these applications gain commercial acceptability (or remain niche solutions for niche products).
While the financial services industry has been one of the early adopters of blockchain technology, other sectors are also increasingly realizing the potential that blockchain can unlock for their businesses.
One such sector is retail, which is increasingly going digital – shedding its paper-based and centralized way of doing business. With an increasingly demanding customer and growing need for transparency, blockchain technology is expected to play a big role in the retail sector.
In addition to its inherent application as a payment-medium supporter (i.e. increasing acceptance of cryptocurrencies as a payment mode by retailers), blockchain has several other applications in the retail space – encompassing supply chain management, customer loyalty programs, and digital advertising.
Blockchain in supply chain
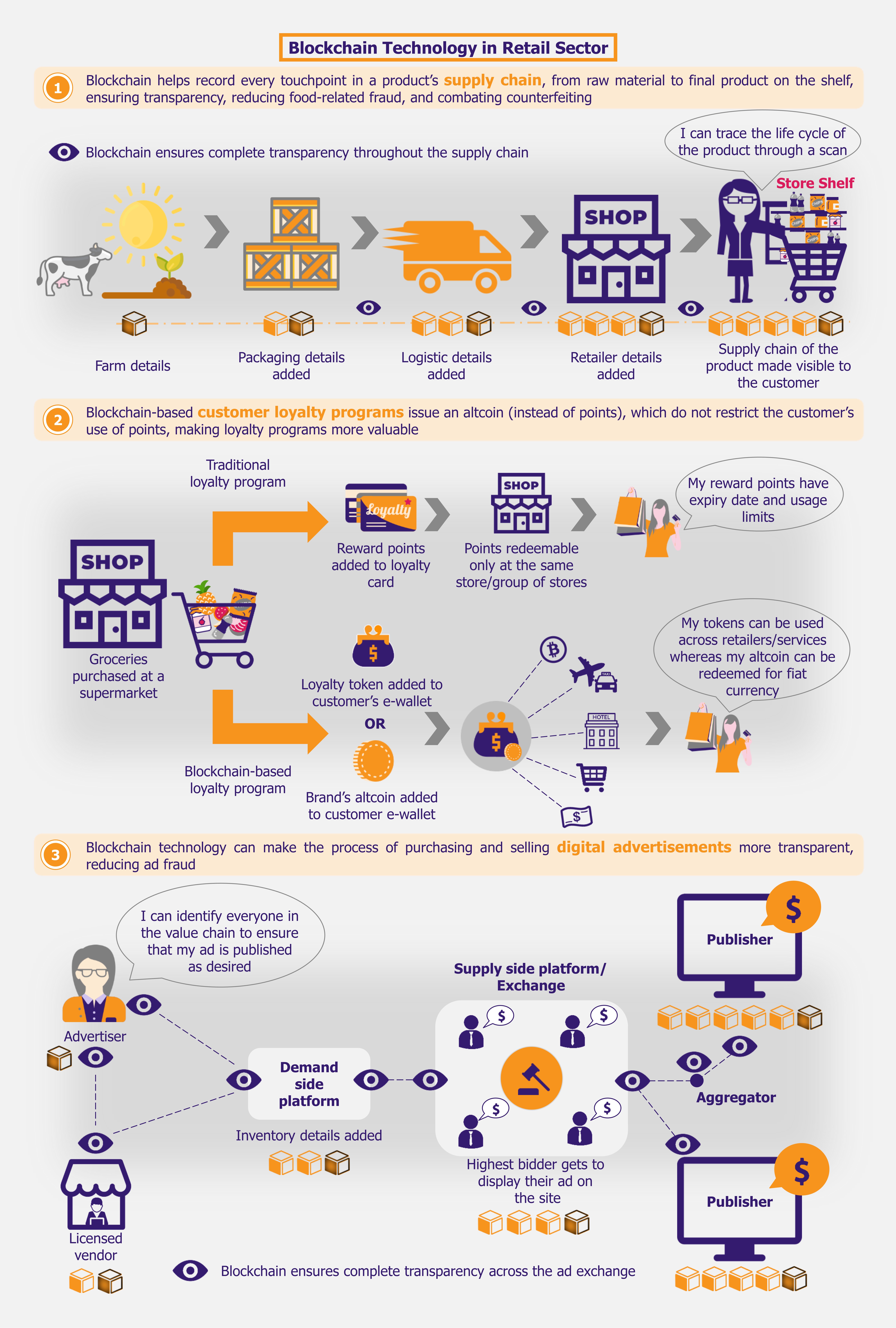
Blockchain helps improve transparency
Blockchain technology makes it possible to record every touchpoint of the product’s life as it moves through the supply chain – from manufacturer to shipper to supplier to seller – adding blocks of verifiable record to the product’s heritage.
For instance, if a supermarket is selling a box of cookies, blockchain data would record exactly when, where, and by whom the cookies were made, as well as what ingredients were used during manufacturing. By placing the cookies supply chain on the blockchain, the process becomes more transparent through inerasable tracking of how cookies have been handled at each node all the way up to the store shelves. This makes any affected ingredient traceable faster. For instance, if milk or eggs used in the cookies were affected due to poor storage, the affected ingredient (or its batch) could be traced back to the storage location and could be withdrawn from the warehouse without the tedious and error-prone process of checking each supply chain node. This ensures greater food safety and helps hold suppliers accountable throughout the chain. This is also useful in case of tracing of organic products where it is particularly important to trace whether each ingredient used to make a product is organic and matches the claims made by the producer.
There are several players in the industry who are already taking advantage of the benefits brought to their operations by blockchain. One of the largest retail giants, Walmart, has partnered with IBM and has been working together since October 2016 to develop a food safety blockchain technology called, IBMs Food Trust, to facilitate the digitization of the food supply chain process. The technology, which was previously in its testing phase, was launched for commercial use in October 2018. With the help of this technology, the source of the product can be tracked in 2.2 seconds, which previously could take up to seven days (with the use of paper-based ledgers).
In September 2018, Walmart announced a Food Trust Initiative, under which it has requested all its greens suppliers to upload data about their produce on the blockchain and ensure end-to-end traceability by September 2019. It is likely that the company extends the use of this technology to other fresh foods and vegetable suppliers in future.
Post the commercial launch of the IBM Food Trust platform in October 2018, France-based retail giant, Carrefour, also announced that it will be using IBM’s blockchain technology to track animal and vegetable product lines. Furthermore, it expects to expand this technology to other fresh products by 2022.
Blockchain effectively combats food-related fraud
Another issue that blockchain helps combat in the retail space is food-related fraud, i.e. the misrepresentation of product contents by substituting the ingredients with cheaper alternatives. It is estimated that the global food industry suffers losses of about US$40 billion annually due to food fraud. An example of such a fraud was the Tesco horsemeat scandal in 2013, where some of Tesco’s packaged beef meals were found to include 60% horsemeat (undeclared on the label).
To fight such frauds, one of the world’s largest e-commerce players, Alibaba, has partnered with four Australian and New-Zealand-based companies, among whom are Blackmores (an Australian health supplement company) and Fonterra (a multinational dairy co-operative) to create a food tracing system built on blockchain technology. The project entered into its pilot phase in 2018. Through this system, Tmall Global’s (Alibaba’s international online marketplace) customers in China will be able to trace the goods that they order online (from partnering companies) across each node of the supply chain before the goods are finally delivered. The partnership is not only expected to help customers track the supply chain of food ordered online but also to prevent food fraud thanks to greater visibility and traceability of such fraudulent actions potentially attempted by producers.
Blockchain helps bring down the counterfeit luxury goods market
As a digital ledger where multiple stakeholders share and authenticate the same information, blockchain also makes counterfeiting more difficult. Counterfeiting is a big issue in the luxury and premium goods market owing to high prices and limited availability. The scale of counterfeiting in the luxury retail segment is overwhelming and it is sometimes nearly impossible to distinguish legitimate goods from the counterfeit ones. Forbes estimated the counterfeit luxury goods market in 2018 to be worth approximately US$1.2 trillion.
However, the use of blockchain technology can help luxury brands fight against the menace of counterfeiting. By using blockchain, companies can track every link in their supply chain and customers can access information to ensure the origins of the product and its authenticity.
Greats, a US-based premium sneaker brand, has been using blockchain and embedding smart tags in its footwear since 2016. Customers can use their smartphones to scan the tags to verify the authenticity of the sneakers.
The use of blockchain technology can help luxury brands (and other retail companies) fight against the menace of counterfeiting. By using blockchain, companies can track every link in their supply chain and customers can access this information through smartphones to ensure the origins of the product and its authenticity.
In 2018, a Paris-based blockchain company, Arianee, announced that it will be building a registry to combat counterfeiting of luxury brands, where every product will be classified with a unique token that differentiates it from the rest of the products.
Another example of this is De Beers, one of the world’s largest diamond producers, which along with five other diamond players (Diacore, Diarough, KGK Group, Rosy Blue NV, and Venus Jewel) has developed a blockchain platform, called Tracr in 2017. Through this platform, a diamond can be tracked from miner to end customer, i.e. throughout its complete value chain, using ethereum blockchain technology. In 2018, De Beers announced that it has successfully tracked 100 high-value diamonds along the value chain during the pilot run of its blockchain platform. The platform is expected to bring transparency in the diamond trade through physical identification of diamonds. A diamond could be tracked through its unique number from mining to cutting to polishing and to retail, which will ensure its purity.
Owing to its ability to empower companies to track, trace, and authenticate their products from the point of origin to the retail shelf, blockchain is likely to become the standard in supply chain tracking for the retail sector. However, this application is currently in its nascent stage of development and is being experimented on by only few large and niche players before it reaches industry-wide adoption.
Blockchain in customer loyalty programs
Customer loyalty points is another area where blockchain could be considered very useful. Loyalty programs generally work by awarding points to customer account for each purchase, which later can be redeemed for discounts on future purchases. While it follows the principle that retaining existing customers is less expensive than attracting new customers, loyalty programs are not always successful.
Most loyalty programs are centralized, where the customer could only redeem its value with the same retailer (or in some cases a small group of retailers), thereby limiting their use and appeal. Moreover, in many cases, loyalty programs also have stipulations that further restrict the use of the points and reduce the program’s perceived value, which in turn results in lower loyalty of the customer. According to Colloquy Loyalty Census 2017, there were approximately 3,000 loyalty programs in North America, where 6.7 trillion points were issued every year and about 21 trillion points were dormant or not used. This suggests that more often than not, customers find loyalty programs more exhausting than benefitting, defeating the entire purpose of having loyalty programs.
Blockchain technology allows customers the flexibility to use their loyalty points when and how they please. Blockchain-based loyalty programs award customers with tokens or cryptocurrencies instead of points, which could be redeemed by customers during future retail purchases and could even be redeemed for fiat currency (as the value of tokens grow overtime and do not expire).
This can be seen in the case of Rakutan’s loyalty program. In 2018, Rakutan, one of Japan’s largest retailers, announced an alt-coin, called Rakutan Coin, with which customers could redeem reward points for gifts at all Rakutan Group companies and also for other cryptocurrencies. The company has moved US$9 billion worth of existing Super Points (customer loyalty program points) into the blockchain to provide a boost to the Rakutan Coin.
Blockchain-based loyalty programs award customers with tokens or cryptocurrencies instead of points, which could be redeemed by customers during future retail purchases and could even be redeemed for fiat currency.
In another example, in 2017, University of New South Wales in Australia partnered with LoyaltyX, an experimental loyalty agency for a blockchain loyalty research project, wherein students and staff earned US$5 of ether (cryptocurrency ethereum) for every ten transactions made at any of the eleven campus retailers including Boost Juice (Australian fruit juice and smoothie retail outlet) and IGA (Australian chain of supermarkets). It was found that 86% of the participants were more attracted to earn cryptocurrencies where they had the option to redeem them for fiat currency.
Thus, blockchain-powered programs seem to encourage customers to engage in the loyalty programs as they not only curb the problem of set expiration of traditional loyalty points but also give the power to the customer to use the tokens as and when they require with any retailer. This is likely to help retailers renew customer interest in their loyalty programs, which in turn is likely to improve brand loyalty.
In addition to adoption in the retail space, players from other related industries are also experimenting with blockchain-based loyalty programs. In 2018, American Express (an American financial services company) partnered with Boxed (an American online wholesale retailer) to make its membership rewards program more versatile by integrating blockchain. With blockchain, merchants will be able to create custom membership rewards program for American Express card holders. The power to structure the offers will be with the merchants, whereas American Express will have the right to regulate the products or brands being promoted.
Also in the same year, Singapore Airlines partnered with KPMG and Microsoft and created a blockchain-based digital wallet KrisPay, where customers can turn travel miles into units of payment that can be used with partner merchants such as eateries, beauty parlors, gas stations, and some retailers, including LEGO store outlets within Singapore. This shows that some large brands are experimenting with this technology for their loyalty programs.
While integration of blockchain seems to be the ideal solution to invigorate the fading customer loyalty programs, it is still in its embryonic stage. Such applications need mass adaption to be successful and this will require significant time and investments.
Moreover, the adoption and success of blockchain-based loyalty programs to an extent also depend on the overall sentiment towards cryptocurrencies – their value and ease of transactions.
Lastly, scalability is also an extremely critical point for the smooth running of such loyalty programs. With numerous retail transactions happening every second, it is yet to be seen if blockchain can cater to these huge numbers without a slag time.
Blockchain in digital advertising
Another space where blockchain technology is likely to have significant potential is digital advertising, which is used by numerous retailers as a medium to reach their prospective customers. However, the process of buying online advertising is susceptible to fraud, especially with the increasing use of automated real-time bidding through ad-exchanges (programmatic advertising).
Under real-time programmatic advertising, publishers (themselves or through ad vendors) showcase their inventory along with details about the kind of visitors that their site targets. The advertisers then bid for these ad impressions and the highest bidder gets to display their ad on the site.
The entire process and ad marketplace lacks a sufficient level of transparency. Sometimes vendors misrepresent remnant inventory for a publisher as premium inventory, thereby charging higher fees from advertisers. In other cases, fraudulent sellers enter the exchange, claiming to represent publishers and having access to their inventory, in turn selling fake inventory to advertisers.
Blockchain has the potential to make the online ad marketplace more robust and legitimate by providing transparency, which is currently missing. Since blockchain is a peer-to-peer online ledger where all transactions between the participating parties are recorded (and cannot be deleted or changed), the advertisers can see for themselves where the inventory that they are bidding for has originated and who has access/authority to sell it.
Some examples of implementations are already found in the market. In June 2017, MetaX, a blockchain technology company, along with DMA (The Data and Marketing Association) launched adChain, an open protocol built on the public ethereum. adChain is an open access ledger that tracks and reports the origin, sale, resale, and publishing of an online ad.
Explore our other Perspectives on blockchain
In December 2017, MetaX also launched a blockchain-based solution ‘Ads.txt Plus’ to improve transparency in the digital advertising space. Ads.txt Plus is based on a technology by IAB Tech Lab, called Ads.txt, which helps prevent fraud in the industry by allowing publishers to broadcast a list of authorized sellers of their ad inventory. By bringing this technology to ethereum blockchain, MetaX aims to further improve efficiency and transparency for its users.
If blockchain is adopted successfully in the digital advertising space, the advertisers can see exactly where their ad dollars are being spent, which players made commission, and how much of the total amount paid by them for the ad reached the site publisher.
Further, with the help of blockchain, buyers and sellers (advertisers and publishers) can enter into smart contracts for the sale and purchase of digital ads without the need for intermediaries, eliminating them from the ad bidding process.
Alternatively, buyers and sellers can choose to add other verifying parties/service providers to the smart contracts, such as measurement provider, ratings provider, payment provider, and arbitrator. In 2017, Kochava Labs (the R&D subsidiary of Kochava Inc.) launched XCHNG, an open and unified blockchain-based framework for the digital advertising ecosystem. Through the use of smart contacts, XCHNG aims at reducing the number of middlemen in the digital advertising ecosystem by facilitating transactions between the buyer and the seller and measurement providers.
While blockchain-based solutions fit perfectly in the digital advertising space on paper, the practicality and adaptability are yet to be seen.
One of the key issues challenging the adoption of blockchain in the digital ad space is scalability. The process of chaining and verifying on a blockchain takes much longer, especially, when compared with the current speed of real-time bidding transactions. It is yet to be seen if blockchain technology can evolve to offer faster processing speed, which is critical for industry-wide adoption.
While blockchain-based solutions fit perfectly in the digital advertising space on paper, the practicality and adaptability are yet to be seen. One of the key issues challenging the adoption of blockchain in the digital ad space is scalability.
While few blockchain solutions, such as XCHNG (which claims it can handle 180,000 transactions per second per smart contract composed of multiple insertion orders), refute this challenge, the other challenge in this area is that of intent. Since blockchain is expected to make transactions more transparent and also reduce the number of intermediaries, industry players may not fully embrace the technology and despite its inherent benefits, blockchain may take time to gain ground in the digital advertising industry.
EOS Perspective
In an era where businesses are becoming more customer centric, blockchain helps bring the customer and retailer together on the same platform and promises a future with more transparency. It is clear that blockchain technology has the ability to transform the retail sector just as it is likely to transform several other industries (such as healthcare, car rental and leasing, or aviation).
However, despite holding immense potential and promise, most applications in this space are still to move beyond just being proof-of-concepts. Several issues, such as high investment requirements, scalability, and to an extent, willingness to change, remain to be addressed before there is an industry-wide acceptance for these solutions.
That being said, executives are definitely keeping an eye open for the latest developments in this space and several of them are open to testing and investing in blockchain-based solutions, hoping for them to be the key differentiator/value-proposition that attract the customers towards them. While most investments currently are being seen in the supply chain space (since its benefits seem most achievable and tangible), solutions in the space of loyalty programs and digital advertising may take a little more time to gain traction.
It is safe to say that retailers cannot afford to ignore the benefits of blockchain technology anymore. Many retailers lack specific understanding of this concept and its potential across different areas of their operations. This could cost them dearly in terms of customers. Technological innovations are happening at light-speed in today’s day and age and while blockchain technology currently may lack commercial acceptability and scalability, it is expected to seep into the operations of the real sector in a significant way in the coming future.