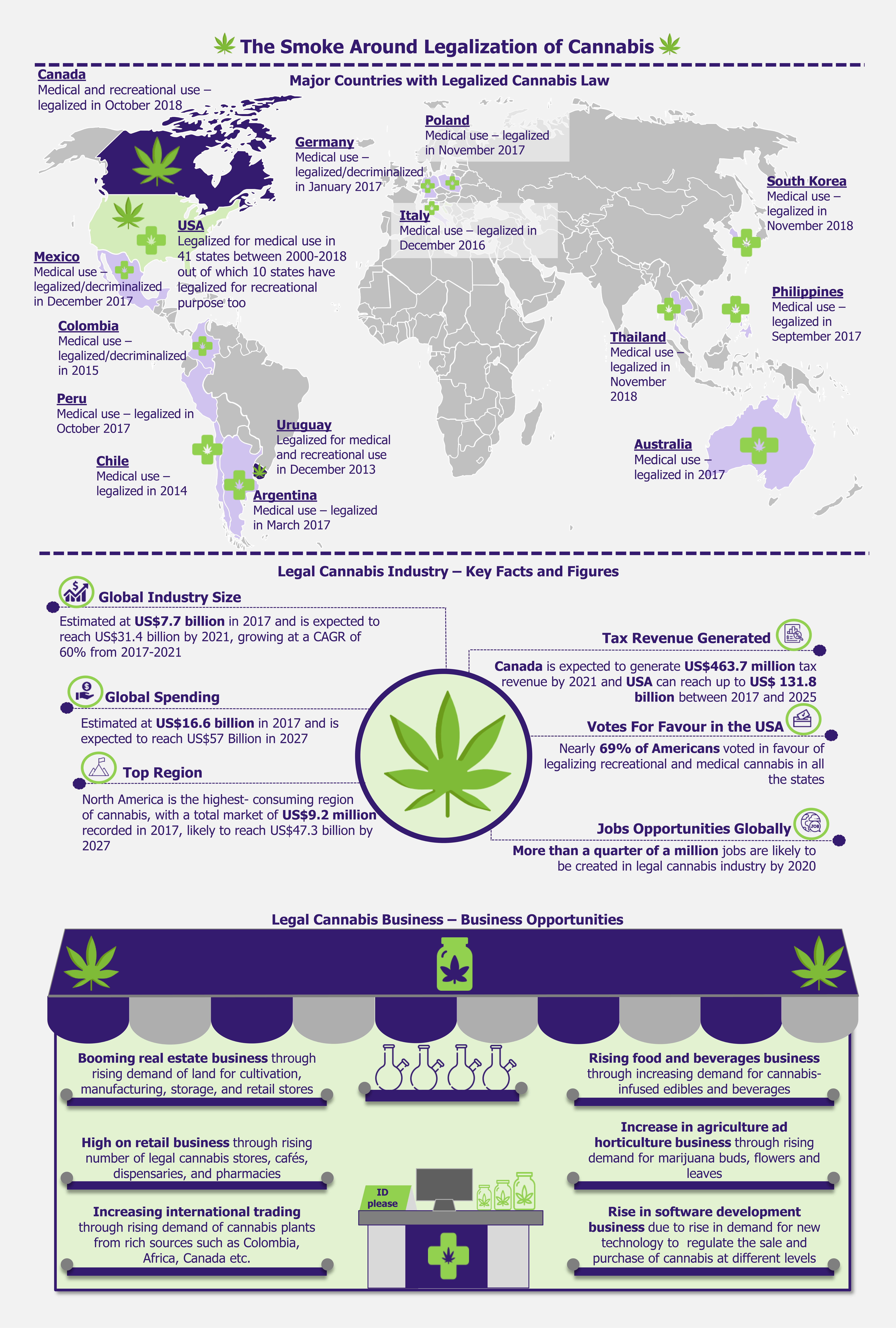
Till date, 31 countries and 41 states in the USA either legalized cannabis in various forms, including making it legal for medical or recreational use, or decriminalized it while still maintaining its illegal status. Few countries are preparing to legalize or decriminalize the use of marijuana for all purposes while many countries are still debating over the legalization of this plant only for medical and not for recreational use. With the rise in education about cannabis and its benefits for humans, economies, and culture, chances of positive changes in laws around cannabis are growing across the world. As legalizing cannabis is still a topic of debate with variety of business, political, and cultural views involved, we are looking at how the legalization of cannabis might impact the economy and businesses in the countries taking the step towards less restrictive approach to handling the issue.
Cannabis – a controversial medicinal plant
Cannabis or marijuana plant and its alleged benefits and risks for human body have been a difficult topic of debate amongst law makers, medical professionals, researchers, economists, politicians, and (of course) cannabis users. In many parts of the world, it still has negative connotations with a narcotic drug, due to presence of psychoactive substance tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) which brings an intoxicating effect to human mind.
In many countries, cannabis has been treated similarly to other chemical drugs, such as cocaine, heroin, etc., in terms of its legal status, by banning from legal cultivation, purchase, or selling for any purpose. However, there has been a continuous development in spreading awareness by the medical professionals, researchers, and scientists on the benefits of using cannabis for medical purposes. This has been followed by voices being raised on people’s right to legalized cannabis also for recreational purposes, comparing it with alcohol and tobacco, which are claimed to have far worse impact on human health, yet are enjoying legal status in many countries.
In addition to this, many economists too are coming forward in favor of legalizing cannabis to bring a boost to economies. As a result of such strong petitions, more and more countries are considering legalization of cannabis and the future might see countries such as USA (including all 50 states), Mexico, New Zealand, The Netherlands, Columbia, France, Spain, Italy, Czech Republic, Jamaica, and Portugal legalizing the plant for all purposes, along with legalization of personal cultivation of cannabis with an aim of bringing cure or relief to several diseases, helping to control healthcare costs, curbing illegal drug businesses, and stimulating country’s economy through adding another taxable business activity.
Countries signal green light for marijuana
The league of countries with full legalization of cannabis for all purposes is still a small, two-member club, which was most recently entered by Canada (in October 2018) with more than 100 legal cannabis retail stores running across the country. After Uruguay that started this league in December 2013, Canada is the second country in the world to completely legalize cannabis, and it does not seem that the club will expand any time soon.
The USA are considering to gradually legalize cannabis for recreational use along with medical use. As of November 2018, The District of Columbia and 10 states including Alaska, California, Colorado, Maine, Massachusetts, Michigan, Nevada, Oregon, Vermont, and Washington have legalized the recreational use of cannabis. An addition of 30 states along with US territories of Puerto Rico and Guam allow the use of cannabis only for medical purposes.
Amongst the European countries, none of them has legalized smoking cannabis or using it for recreational purposes yet, but there are several countries which have legalized the medical use of cannabis under a treatment process, while also decriminalizing the use of cannabis for recreational purposes. Malta, Greece, Luxemburg, and Denmark are amongst the European countries that legalized medical cannabis in 2018 adding to the group of other European countries such as Italy, Norway, Poland, The Netherlands, France, Spain, Slovenia, to name a few.
Some Asian countries are also moving towards legalizing cannabis but exclusively for medical purposes and that too with strict policies. Recently, in November 2018, Thailand legalized medical marijuana, but with very stringent rules to get access to marijuana plants. Also, in November 2018, South Korea became the second Asian country to legalize medical cannabis, while Malaysia is expected to be the third nation to fall into this group. Interestingly though, India, known to be the origin of cannabis sativa plant, has not legalized the use of cannabis for any purpose yet, although the country runs a huge illegal trade of marijuana as well as hashish (a drug made of cannabis resin). There are many petitions already submitted by various Indian economists and politicians in favor of legalizing cannabis for use in cancer patients and even hemp cultivation for horticulture use, but due to changing political environment in India, the petitions are still pending to be considered by the relevant law-making bodies.
Cannabis business – boom in economies
According to a report published in 2018 by Brightfield Group, with the on-going trend of countries moving towards legalizing cannabis, the global legal cannabis market is expected to reach US$ 31.4 billion by the end of 2021, owing to the growing adoption of medical cannabis in treatment or relief in a range of diseases and ailments, such as cancer, mental disorders, chronic pains, and others.
Apart from medical applications, the recreational use of cannabis too has led to a continuous rise in sales of cannabis for direct and indirect use, thus giving a push to retail businesses as well as tourism sector in countries that moved towards legalization. As a result of the rise in sales, governments of these countries and states have registered increased tax revenues and a boost to local economies. For instance, California that legalized cannabis for recreational use in January 2018, generated US$74.2 million of tax revenue during second quarter, with a rise of 22% over the first quarter. In another, more hypothetical example, according to a report by Canada’s Parliamentary Budget Officer, Canada could generate US$463.74 million in tax revenue by 2021 if the projections of nearly 734 metric tons of legal cannabis to be consumed by that year are correct.
Similarly, according to a study by New Frontier Data, if cannabis was legalized in all American states, it would generate a combined US$131.8 billion in federal tax revenue between 2017 and 2025, considering 15% retail sales tax, payroll deductions, and business tax revenue. In fact, according to a research study by Ameri Research Inc. in 2017, in the USA, tax revenues from legal cannabis are now comparable with revenues from other products, such as draft beer and e-cigarettes, a fact highlighting the recent growth of sales in legal cannabis market in the USA.
Apart from tax revenue generation, creating new business opportunities is also one of the reasons for countries to seriously consider legalization of cannabis. States such as Colorado, for example, have registered some 431,997 new business entities between 2014 and 2017. In 2017, it also experienced a 17.7% rise in employment over 2016 with 17,281 full-time equivalent jobs. Also, in 2017, across the USA, there were 9,397 active licenses with slightly more than 3,000 licenses active in Colorado. These licenses were made active for cannabis businesses dealing with cultivation, manufacturing, retailing, distributing, delivering, and even lab testing that generated 121,000 jobs in 2017 across the District of Columbia plus 10 US states. This number is expected to reach 1.1 million jobs by 2025, if cannabis is legalized in all 50 states, across all ends of cannabis industry supply chain, from farmers to transporters to sellers.
It is expected that through legalization of cannabis, several countries, especially Mexico, USA, and Canada, are also expected to witness significant drop in illicit activities related to drugs industry. According to a study by Deloitte in 2018, cannabis users in Canada are willing and in fact looking forward to pay more for legal purchase of cannabis grown and processed under federal laws and sold through legal channels rather than going for illegal drug purchase options. This goes hand in hand with Canadian government’s hopes to crack down on illegal drug trade while also finding new sources of stimulation to the country’s economy.
Impact of legal cannabis market on other business sectors
The emergence of legal cannabis market has raised many business opportunities in various sectors such as retail, food and beverages, real estate, and even tobacco and alcohol industry.
Amongst these sectors, real estate has been developing strongly in many countries allowing for legal cannabis for medical as well as recreational use. Properties and facilities that are well-suited for cannabis-related operations are experiencing rise in industrial rents and sales price premiums owing to the rise in demand for warehouses, industrial and storage facilities, agricultural, and other properties.
In Canada, legalization of growing and sales of recreational cannabis has fueled a six-fold surge in plant-growing facilities to 8.7 million square feet in 2018 according to data from Altus Group, Canadian real estate company. Aurora Cannabis, one of Canada’s leading cannabis companies, has already started its project for cultivation of cannabis in a new 8 million square feet facility in 2018. Canopy Growth, market leader in cannabis industry of Canada, has announced plans in October 2018 to develop 3 million square feet of greenhouse space in British Columbia through October 2019, which will be more than double its production surface as of 2018. With the legalization of cannabis, the demand is also rising for commercial real estate thus giving an opportunity for struggling retailers to make a move into a new market. Alberta, where cannabis industry is fully private, has experienced a sharp surge in demand for 1,200 to 3,000 square feet retail real estate to set up cannabis shops and dispensaries in malls and street-front locations.
Similarly, within the USA, Colorado, experienced a rise in real estate sector through increase in housing values by about 6% owing to increasing development in retail sector through legal cannabis pharmacies, dispensaries, cafés, and retail shops. Going beyond real estate, the retail industry is also likely to receive a push thanks to opportunities in auxiliary businesses such as accessory shops, cannabis cafés, weed gardening products stores, bakeries, and candy shops, contributing to rising demand for retail locations.
The impact of cannabis legalization is visible also in food and beverage industry thanks to new products such as cannabis-infused edibles such as cakes, candies, and drinks. In 2017, California reported sales of US$180 million of edibles, whereas Colorado has seen about a 60% rise in edibles sales volume (with 11.1 million edibles unites been sold in the same year). The future of food and beverage industry with cannabis-infused edibles is projected to be promising due to the benefits of cannabis plant for using it in food products. According to a food and beverage industry expert, Sylvian Charlebois, cannabis offers good nutrients (proteins, vitamin E and C, to name a few), hence for food products manufacturers looking for new avenues of growth, cannabis could be deemed the next ‘superfood’.
On the other hand, the legalization of cannabis has affected alcohol industry due to the emerging inclination of people towards choosing the “green high” over alcoholic drinks.
According to a study by Deloitte in 2018, in Canada, cannabis is likely to be increasingly perceived as a substitute to beer, spirits, and wine which could negatively impact the alcoholic beverages-related revenues for governments, liquor companies, and retailers. This is already observed in the USA, where a joint recent research study of 10 years conducted by two US-based universities, namely University of Connecticut, Storrs and Georgia University, Atlanta in cooperation with Universidad del Pacifico in Peru, has suggested that the counties located in medical marijuana states showed almost a 15% decline in monthly alcohol sales between 2006 and 2015.
At the same time, some industry experts believe that since it is part of American and European food culture to drink alcoholic drinks such as beer and wine with food, the legalization of cannabis is not going to affect the demand for such food-complementing alcoholic drinks. In fact, cannabis legalization is also coming out to be a stepping stone for large alcohol brands to enter the cannabis industry with cannabis-infused alcoholic beverages, mostly through mergers and acquisitions with leading cannabis growing companies. In August 2018, New-York based Constellation Brands acquired more that 50% stake of Ontario-based Canopy Growth for US$4.0 billion, the largest investment registered in cannabis industry so far. The received investment is believed to help Canopy Growth strengthen and expand its leadership position in Canada and other countries with legalized cannabis. It is expected that in the future, other alcohol industry leaders will also consider getting involved in cannabis industry in order to expand through cannabis-infused drinks, creating a new segment of products with combination of alcohol and cannabis.
EOS Perspective
The benefits of cannabis on human body in diseases such as cancer, acute and chronic pains, or neurological and mental illness, have resulted in a growing count of countries legalizing use of cannabis. On the other hand, the legalizing of cannabis for recreational purpose is still receiving mixed views by industry experts and public opinions in several countries. The only way to make this experiment work, is to follow the steps of those countries that have legalized recreational cannabis and are simultaneously focusing on implementing a completely regulated system to scrutinize the whole supply chain in order to curb illegal drug activities and over-dose of cannabis by the users.
For this purpose, the leaders – Uruguay and Canada – have created systems of registration cards with a specific limit to purchase a quantity of cannabis for recreational use per month. As a result of this, the situation is expected to be under control and authorities believe that this will help in curbing illegal trade activities while keeping check on personal consumption of cannabis.
It is also recommended to consider the fact that legalization of cannabis for recreational and medical purposes is likely to reduce the use of other, more harmful and addictive drugs, as well as curb (at least to some extent) the over-consumption of alcohol that is associated with serious health hazards and many deaths, generating huge social burden and healthcare costs in many countries.
Considering all these factors, the success of legalizing cannabis for all purposes in any country depends on how the processes across cultivation, distribution, retail, all the way to the end buyer is regulated and scrutinized by the law makers and law enforcers of the country. There surely are both pros and cons of legalizing cannabis but with solid work towards improved awareness, and, more importantly, a regulated system with proper (enforced) laws, it can give the countries a boost to their economies along with rise in employment, better medical treatments, and decline in illegal drug activities.













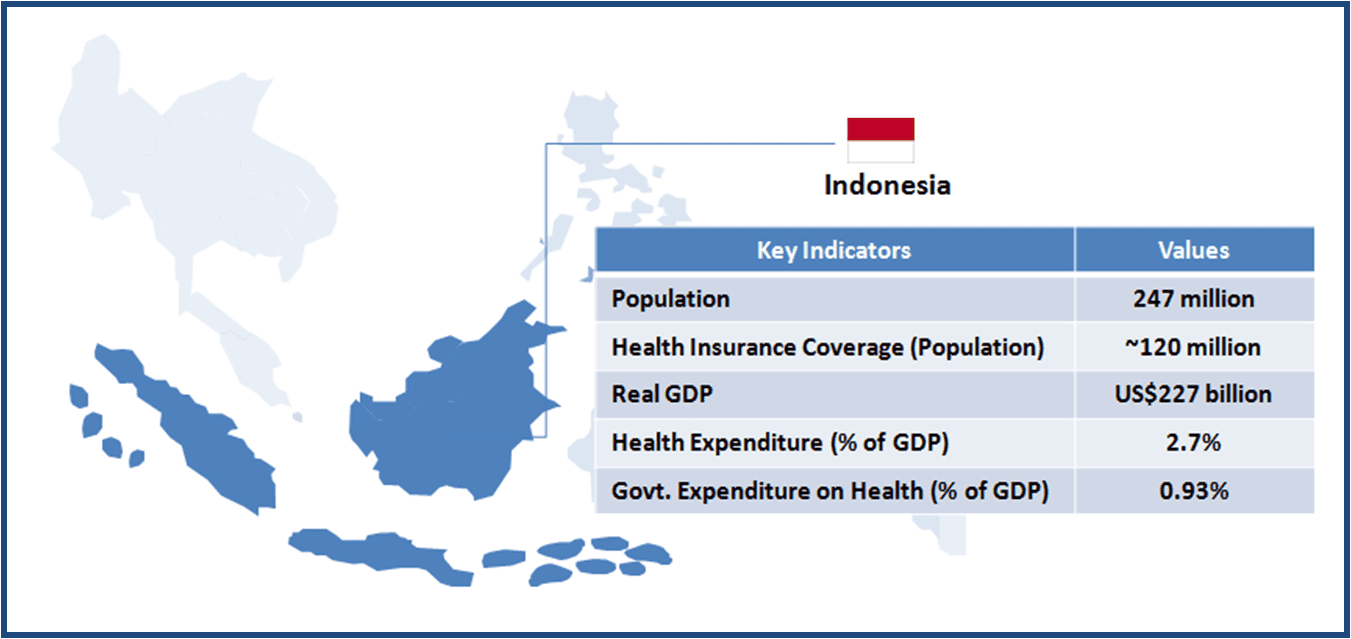
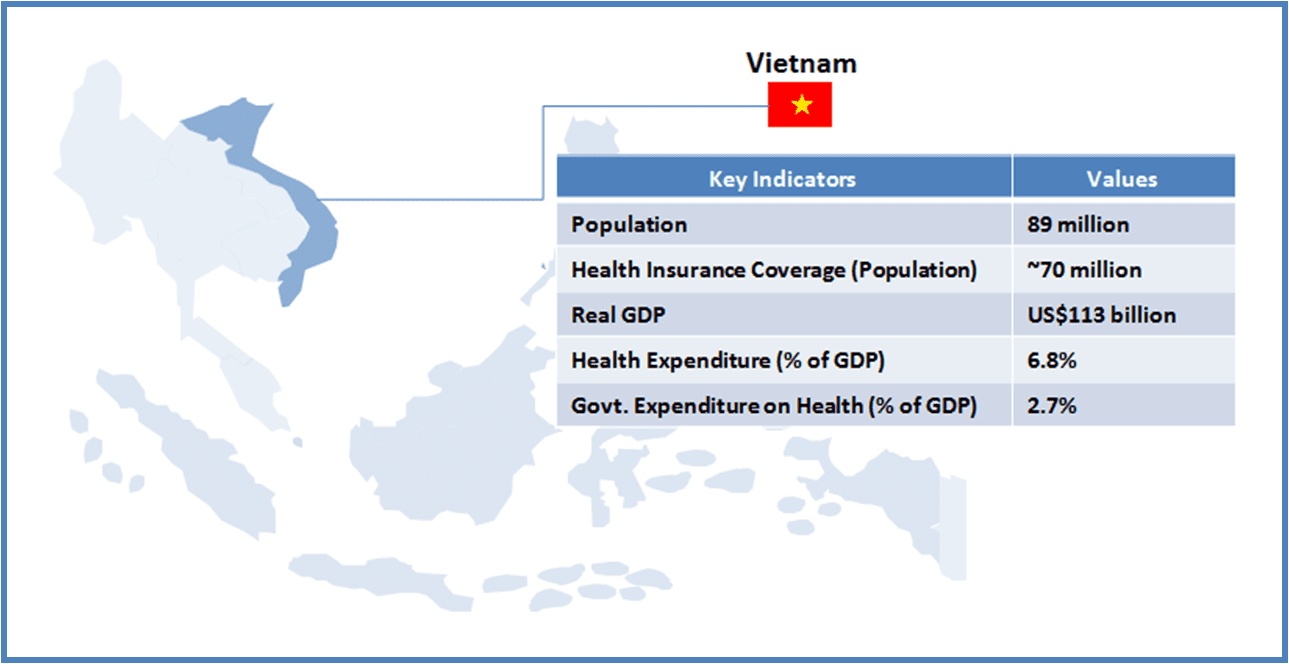
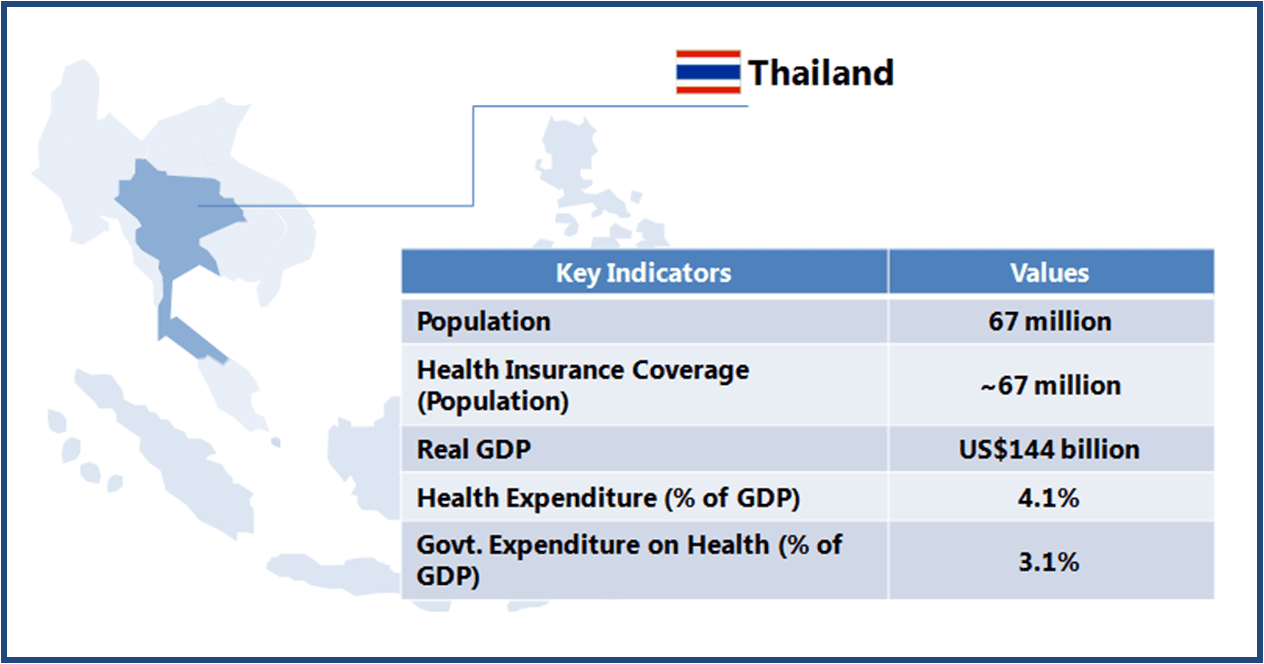 Thailand boasts of world class medical facilities (especially in the private healthcare sector), and is among the world’s largest medical tourism markets. The government is looking to further develop Thailand into an “International Health Center for Excellence” under its second strategic five-year plan (2012-2016).
Thailand boasts of world class medical facilities (especially in the private healthcare sector), and is among the world’s largest medical tourism markets. The government is looking to further develop Thailand into an “International Health Center for Excellence” under its second strategic five-year plan (2012-2016).